ARCHIVE NEWS
02.09.2024Prof. Jan Plefka appointed to the Board of Trustees of the Volkswagen Foundation
Jan Plefka, Professor of Theoretical Physics (Quantum Field and String Theory) at the Department of Physics and member of IRIS Adlershof at HU Berlin, has been appointed to the Board of Trustees of the Volkswagen Foundation by the German Federal Government. The Board of Trustees is the highest decision-making body of the Volkswagen Foundation. It consists of 14 personalities from science and society, half of whom are appointed by the Federal Government and half by the State Government of Lower Saxony. The tasks of the Board of Trustees include defining the funding guidelines, selecting the projects to be funded, monitoring the funded projects and advising the Board of Directors. more... 18.07.2024Prof. Nicola Pinna pioneered a novel technique for coating nano-particles and creates yolk-shell nanostructures.Prof. Pinna, member of IRIS Adlershof, and colleagues have revolutionized the Stöber method, originally for amorphous SiO2 colloids, by extending it to metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and coordination polymers (CPs). Their innovative approach harnesses the slow, continuous diffusion of triethylamine (TEA) vapor to precisely control the deprotonation of organic ligands, paving the way for creating finely crafted amorphous CP spheres. 03.07.2024DFG bewilligt neue Forschungsgruppe MFOSA im Bereich der Quantenfeldtheorie
Eine Gruppe führender theoretischer Physiker*innen hat sich zusammengeschlossen, um die Grundlagen von Streuamplituden - fundamentalen Größen in der Quantenfeldtheorie - zu erforschen. Die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) fördert diese neue Forschungsgruppe unter der Leitung von Prof. Dr. Claude Duhr von der Universität Bonn für vier Jahre mit einer Summe von etwa 4 Millionen Euro. Maßgeblich beteiligt sind auch Forschende des IRIS Adlershof (HU): Prof. Dr. Valentina Forini und Prof. Dr. Jan Plefka, die ihre Expertise in den Bereichen Quantenfeldtheorie, Stringtheorie und Gravitationsphysik einbringen. Streuamplituden beschreiben die Wechselwirkungen zwischen Elementarteilchen und sind von zentraler Bedeutung für unser Verständnis der fundamentalen Naturkräfte – der elektromagnetischen, der starken und schwachen Kernkraft, sowie der Gravitation. Die Forschungsgruppe wird innovative Methoden entwickeln, um diese komplexen mathematischen Objekte zu berechnen und ihre zugrundeliegende Struktur zu entschlüsseln. Zu den Hauptzielen gehören:
Prof. Plefka wird insbesondere seine Arbeit zu Weltlinien-Quantenfeldtheorien einbringen, die innovative Ansätze für die Gravitationswellenphysik liefert. Prof. Forini wird ihre Expertise in der Anwendung von Unitaritätstechniken auf gekrümmte Raumzeiten, insbesondere Anti-de-Sitter-Räume, beisteuern. Die Forschungsgruppe vereint Expertinnen und Experten aus verschiedenen Bereichen der theoretischen und mathematischen Physik von sechs führenden deutschen Forschungseinrichtungen sowie der University of Hertfordshire (UK). Durch die enge Zusammenarbeit und den Austausch von Ideen sollen bahnbrechende Fortschritte in diesem wichtigen Forschungsgebiet erzielt werden. Die gewonnenen Erkenntnisse werden nicht nur das fundamentale Verständnis der Naturgesetze erweitern, sondern auch direkte Anwendungen in der Teilchen- und Gravitationsphysik ermöglichen. Dies betrifft zum einen hochpräzise Vorhersagen für den Ausgang von Streuprozessen am Large Hadron Collider am CERN in Genf, sowie die Berechnung der Gravitationswellenformen aus Begegnungen von schwarzen Löchern und Neutronensternen in unserem Universum, die in modernen Gravitationswellendetektoren gemessen werden. Kontakt:
20.06.2024Dr. Gustav Mogull Receives the Karl Scheel Prize from the Physical Society of Berlin 2024
Dr. Gustav Mogull, a young researcher at the Department of Physics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and associated with the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics (Albert Einstein Institute), is receiving the prestigious Karl Scheel Prize for his groundbreaking work in the field of general relativity and gravitational wave physics. Since the first observation of gravitational waves in 2015, a new field of research has emerged to study black holes, neutron stars, and test general relativity in extreme gravitational fields. Dr. Mogull has created a novel theoretical framework called the Worldline Quantum Field Theory (WQFT), developed in the research group of IRIS Adlershof-member Prof. Dr. Jan Plefka, to compute high-precision analytical predictions for the classical two-body problem in general relativity. Using WQFT, Dr. Mogull has derived important physical observables for the dynamics of black holes and neutron stars in a series of papers published in prestigious journals such as Physical Review Letters. His results are already being applied in modeling gravitational wave signals for data analysis of current and planned future gravitational wave detectors. The prize honors Dr. Mogull's outstanding theoretical work on the two-body problem, which is of great importance for future high-precision tests of general relativity and our understanding of gravitational waves. The crucial advance of WQFT lies in the transfer of methods from quantum field theory, which usually describes elementary particle physics, to the interaction of black holes. In this sense, one replaces the theoretical description of the scattering of protons in particle accelerators with the scattering of black holes in our universe. The Karl Scheel Prize, endowed with 5,000 euros, is awarded annually by the German Physical Society of Berlin for outstanding achievements in physics. Gustav Mogull studied at the University of Cambridge and received his PhD in Edinburgh with work on scattering amplitudes in quantum field theory. After a postdoc in Uppsala (Sweden), he has been a long-term postdoc at the DFG Research Training Group "Rethinking Quantum Field Theory" (Speaker: Prof. Dr. J. Plefka) since 2020, which was recently extended for a second funding phase. The award-winning work was carried out within the framework of this research project, and Mr. Mogull is also actively involved in co-supervising doctoral and master’s thesis students in the program. He has recently received a fellowship from the Royal Society, which will lead him to a lectureship at Queen Mary University London starting in the fall of 2024. Contact: Dr. Mogull and Prof. Dr. Plefka, Department of Physics, GRK 2575. 19.06.2024Breakthrough in Gravitational Wave Physics:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
| Jan Plefka, member of IRIS Adlershof |
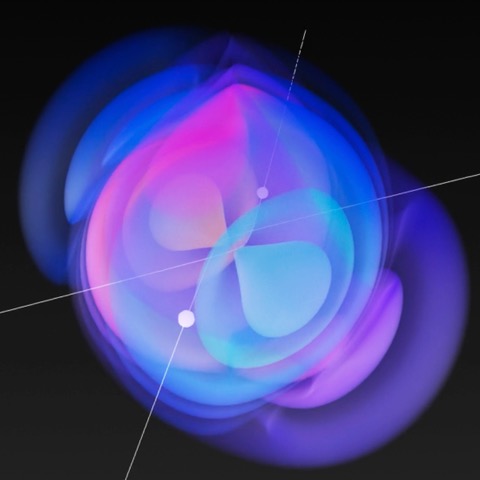 |
| Visualization of the scattering of two black holes including a wave profile |
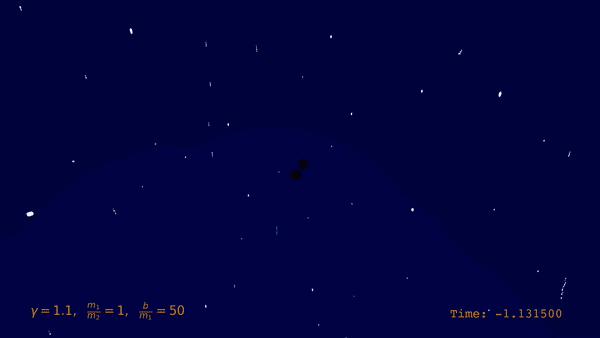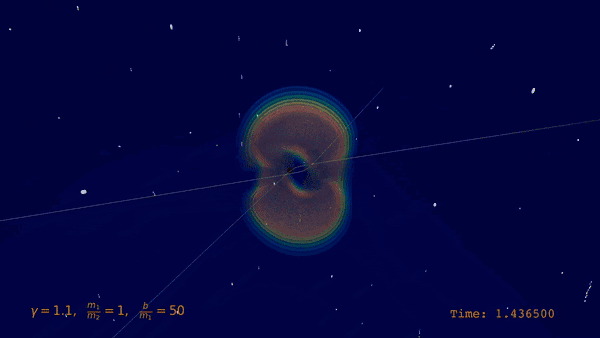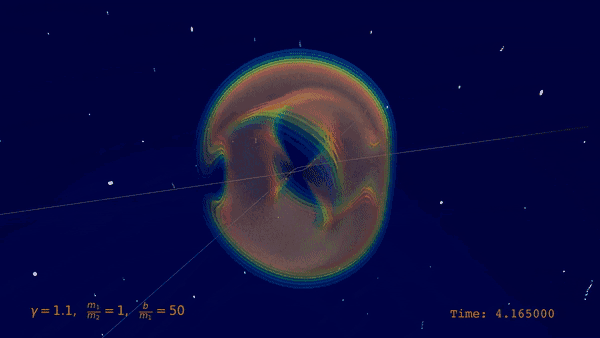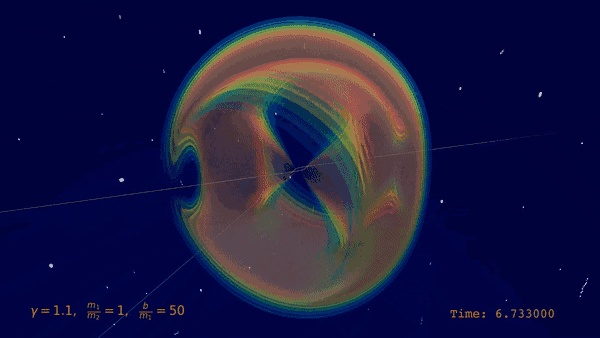 |
| Visualization of the gravitational Bremsstrahlung from the scattering of two black holes (BSc thesis O. Babayemi) |
In a groundbreaking achievement, an international team led by IRIS Adlershof member Jan Plefka has computed the dynamics of two black holes scattering off each other at the highest level of precision ever attained. Their work, published as an Editor's Choice in the prestigious journal Physical Review Letters, provides new insights into the powerful gravitational interactions between these extreme objects.
Black hole scattering is a fundamental problem in Einstein's theory of general relativity, with wide-ranging implications for astrophysics and gravitational wave astronomy. Understanding the gravitational interactions and radiation emitted when two black holes encounter each other is crucial for interpreting observations from gravitational wave detectors like LIGO and future third generation wave detectors scheduled to go nonline in the 2030s.
The new calculations, performed by researchers from Humboldt University Berlin, the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics, and CERN, push the theoretical description of black hole scattering to unprecedented accuracy - the fifth post-Minkowskian order and next-to leading self-force order. This enormously challenging four-loop computation required state-of-the-art integration techniques and high-performance computing resources.
"Resolving this problem represents a new frontier in multi-loop calculations and effective field theory techniques," said group leader Jan Plefka. Co-author Benjamin Sauer commented "We had to optimize every aspect, from the integrand generation to developing new integration-by-parts methods." In total millions of 16 dimensional integrals had to be reduced to a basis of 470 master integrals, which were then computed.
Remarkably, the researchers found that at this new level of precision, the resulting scattering angle exhibits striking simplicity, without the appearance of new transcendental functions beyond polylogarithms of weight three. All theoretical checks, both internal and by matching to previous results, were passed successfully.
With this breakthrough, the researchers have laid the groundwork for incorporating their calculations into advanced gravitational waveform models for the next generation of gravitational wave detectors. The higher precision will enable exquisitely accurate tests of Einstein's theory and new insights into nuclear and fundamental physics from binary inspirals.
"Our results bring the prediction of gravitational waves from black hole encounters to unprecedented accuracy," said co-author Gustav Uhre Jakobsen. "This opens brilliant new avenues for extracting fundamental physics from gravitational wave observations in the future."
The research was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft in the context of the Research Training Group 2575 “Rethinking Quantum Field Theory” and the European Research Council Advanced Grant “GraWFTy” of Jan Plefka.
Article:
Conservative Black Hole Scattering at Fifth Post-Minkowskian and First Self-Force Order
Mathias Driesse, Gustav Uhre Jakobsen, Gustav Mogull, Jan Plefka, Benjamin Sauer, and Johann Usovitsch
Phys. Rev. Lett. 132, 241402 – Published 13 June 2024
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.132.241402
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Jan Plefka
Sprecher Graduiertenkolleg 2575 „Rethinking Quantum Field Theory“
ERC Advanced Grant „GraWFTy"
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, IRIS Adlershof &
Institut für Physik, Arbeitsgruppe Quantenfeld- und Stringtheorie
Zum Großen Windkanal 2, D-12489 Berlin
Postal adress: Unter den Linden 6, 10099 Berlin, Germany
Email: jan.plefkahu-berlin.de
Tel: +49 (0)30 2093 66409
Sekr.: +49 (0)30 2093 66413
qft.physik.hu-berlin.de
www2.hu-berlin.de/rtg2575/
X: @JanPlefka
19.06.2024Enhanced surface-to-bulk Raman signal ratio using a transferable porous gold membrane
Enhanced surface-to-bulk Raman signal ratio using a transferable porous gold membrane
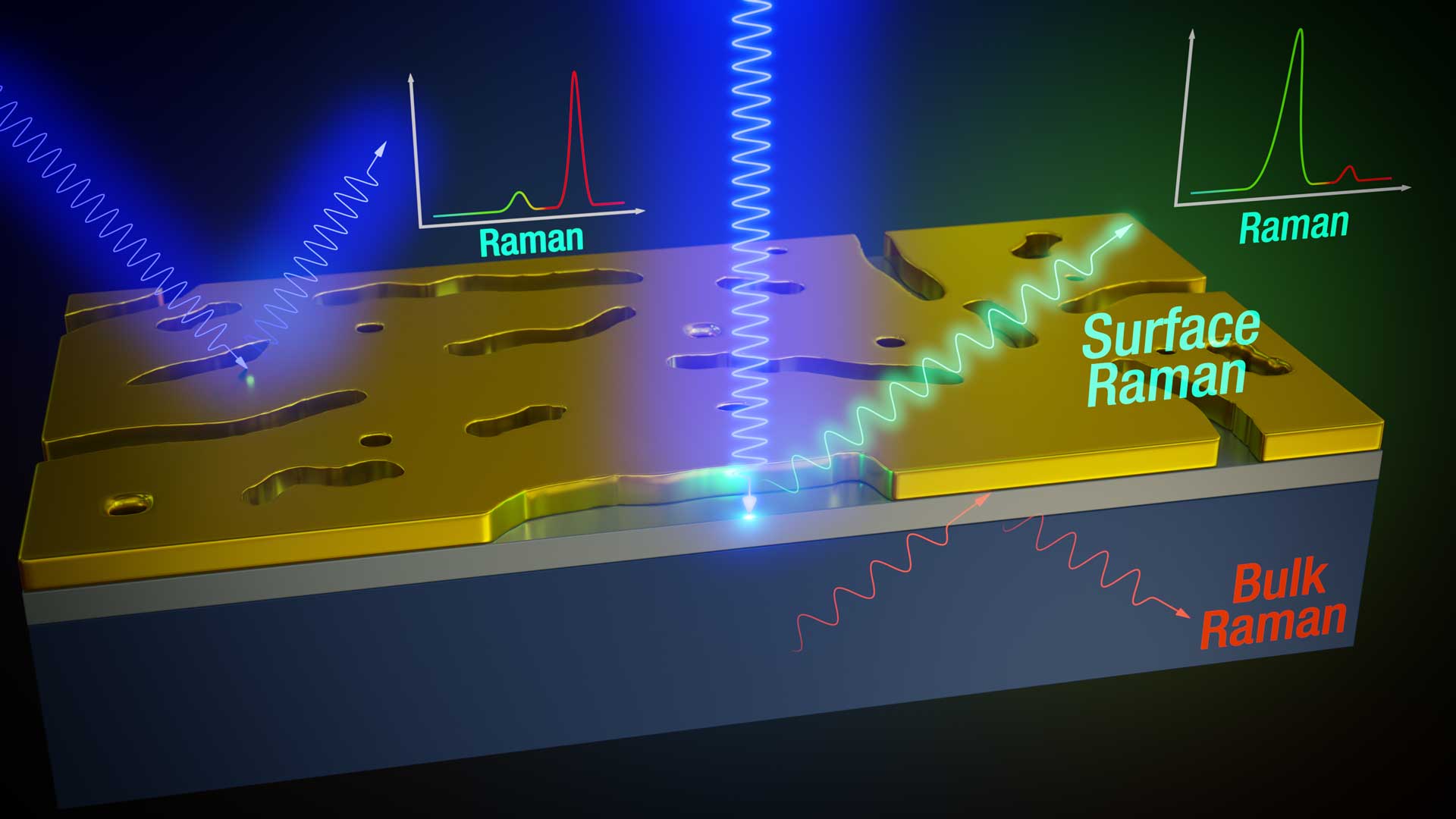
In a recent collaboration of the Emmy Noether Research Group "Physics of low-dimensional systems" around IRIS Adlershof member Dr. Sebastian Heeg at HU Berlin, researchers from the Leibniz-Institut für Kristallzüchtung (IKZ), the Université Le Mans, and the ETH Zurich, realized a novel modality in Raman spectroscopy through the development of surface-sensitive Raman scattering. This new approach addresses a major limitation of conventional Raman spectroscopy, where signals from surfaces or thin films are often weak and obscured by dominant bulk signals.
Surfaces play a pivotal role in science and industry as they are where most environmental interactions occur, including chemical reactions, adhesion, friction, and light interactions. Surface properties may differ significantly from bulk properties in terms of chemical composition, atomic arrangement, and electronic structure, influencing technological advancements such as catalysts and solar cells. Raman spectroscopy, a powerful, non-destructive technique for analysing molecular vibrations, provides insights into a material's chemical composition, crystallinity, defects, and strain. It is particularly valuable for characterising nanomaterials, thin films, and biological samples where precise surface information is essential.
The application of conventional Raman spectroscopy to surfaces and thin films has been constrained by dominant bulk signals. However, using transferable porous gold membranes (PAuMs) allows for the study of surface-specific Raman signals with unprecedented clarity. PAuMs contain irregular, slot-shaped nanopores that act as plasmonic antennas. When placing PAuM on a surface or thin film of interest, the nanopores amplify the Raman signal of the surface directly below while the membrane itself suppresses bulk signals. Combining these effects improves the surface-to-bulk Raman signal ratio by three orders of magnitude and enables truly surface-sensitive Raman scattering.
The researchers used graphene as a model surface, observing that the nanopores in the membranes enhance the graphene Raman signal a hundredfold. Placing a spacer between graphene and the PAuM reveals that the Raman enhancement is confined to the first 2 – 3 nm of the material below the membrane, which demonstrates true surface sensitivity. A first prototypal application regards quantifying the strain in a 12.5 nm thin Si quantum well layer using PAuMs. The layer is part of a Silicon-Germanium heterostructure designed to use spin qubits as a promising and fast-developing technology for quantum computing.
In a second use-case, PAuMs are used to study the surface of thin LaNiO3 film, a metallic perovskite used as an electrode material. The electrical conductivity of LaNiO3 films is strongly coupled to its crystallographic structure and can be tuned by the film thickness. With PAuM placed on top of LaNiO3, the authors observed a Raman mode splitting arising from the film’s surface and indicating a difference in the surface structure compared to the bulk. This finding is consistent with theoretical predictions and observations from scanning tunnelling microscopy studies.
“Our work connects two separate fields” says Heeg, “Conceptually, we extend the field of plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, which is almost exclusively used to study and sense molecular compounds and nanostructures, to the field of solid states materials like Silicon quantum wells, thin complex oxides films, and related surfaces.” The team is now exploring the potential of the method with partners in Berlin and international collaborators. Dr. Pietro Marabotti, Einstein International Postdoctoral Fellow in Heeg’s group and co-author of the study, remarks that “our approach is not limited to crystalline surfaces, which we use as a showcase, but may also be used to study, for example, biological surfaces or surface-bound chemical reactions.” Researchers interested in the method are invited to get in touch with the team.
Bulk-suppressed and surface-sensitive Raman scattering by transferable plasmonic membranes with irregular slot-shaped nanopores
Roman M. Wyss, Günther Kewes, Pietro Marabotti, Stefan M. Koepfli, Karl-Philipp Schlichting, Markus Parzefall, Eric Bonvin, Martin F. Sarott, Morgan Trassin, Maximilian Oezkent, Chen-Hsun Lu, Kevin-P. Gradwohl, Thomas Perrault, Lala Habibova, Giorgia Marcelli, Marcela Giraldo, Jan Vermant, Lukas Novotny, Martin Frimmer, Mads C. Weber, and Sebastian Heeg
Nat. Commun. 15, 5236 (2024).
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-49130-2 OPEN ACCESS
ACCESS
➔ Article on the paper in ETH News
➔ Article on the paper from Humboldt Innovation
Kontakt:
Dr. Sebastian Heeg
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
IRIS Adlershof & Institut für Physik
Tel.: 030 2093-82295
E-Mail: sebastian.heegphysik.hu-berlin.de
Website: https://www.physik.hu-berlin.de/en/pld
05.06.2024DFG extends the Collaborative Research Centre FONDA
 The CRC ‘FONDA - Foundations of Workflows for Large-Scale Scientific Data Analysis’ has been extended by the German Research Foundation (DFG) for a funding period of four years. IRIS Adlershof member Prof Dr Ulf Leser from the Department of Computer Science at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is the CRC's spokesperson.
The CRC ‘FONDA - Foundations of Workflows for Large-Scale Scientific Data Analysis’ has been extended by the German Research Foundation (DFG) for a funding period of four years. IRIS Adlershof member Prof Dr Ulf Leser from the Department of Computer Science at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is the CRC's spokesperson.
The SFB FONDA is dedicated to researching methods for increasing productivity in the development, execution and maintenance of data analysis workflows (DAWs) for large scientific data sets. In today's research, ever larger amounts of data are being generated in all scientific disciplines. These need to be analysed using complex DAWs running on distributed and parallel computing infrastructures. Traditionally, these workflows are optimised for speed, which leads to individual solutions that are difficult to reproduce and use for other researchers.
The aim of FONDA is to develop methods and tools that significantly reduce the development time and costs of DAWs. This is to be achieved through new abstractions, models and algorithms that can form the basis for a new generation of workflow infrastructures. The CRC is investigating the following questions, among others: How can DAWs be developed that run equally efficiently on different software and hardware infrastructures? How must these workflows be designed so that they can adapt to changing input data or requirements? And how can reliable data analysis systems be built that recognise and control their own requirements in order to increase the reliability of their execution?
22.05.2024Joachim Sauer receives the 2024 Blaise Pascal Medal in Chemistry
 The renowned chemist and founding member of IRIS Adlershof, Prof. Joachim Sauer, has been awarded the 2024 Blaise Pascal Medal in Chemistry by the European Academy of Sciences (EURASC) for his pioneering research in the field of catalytic reactions based on quantum chemistry. The EURASC honours his innovative research methods, such as hybrid quantum mechanical calculations and Grand Canonical Monte Carlo simulations, which have raised the understanding of heterogeneous catalysis to a new level. With the award of the medal, named after the French mathematician, physicist and philosopher Blaise Pascal, Prof Sauer joins a list of people who have made outstanding contributions to science, technology and research education. The award ceremony will take place on 29 and 30 October 2024 at the Academia das Ciências de Lisboa in Lisbon.
The renowned chemist and founding member of IRIS Adlershof, Prof. Joachim Sauer, has been awarded the 2024 Blaise Pascal Medal in Chemistry by the European Academy of Sciences (EURASC) for his pioneering research in the field of catalytic reactions based on quantum chemistry. The EURASC honours his innovative research methods, such as hybrid quantum mechanical calculations and Grand Canonical Monte Carlo simulations, which have raised the understanding of heterogeneous catalysis to a new level. With the award of the medal, named after the French mathematician, physicist and philosopher Blaise Pascal, Prof Sauer joins a list of people who have made outstanding contributions to science, technology and research education. The award ceremony will take place on 29 and 30 October 2024 at the Academia das Ciências de Lisboa in Lisbon.
We congratulate our founding member on this honour.
13.05.2024DFG extends Research Training Group 2575 “Rethinking Quantum Field Theory”
Quantum field theory (QFT) as a union of quantum mechanics and special relativity represents one of the most important intellectual achievements of the last century, in which a large part of modern theoretical physics culminates. In recent years, innovations have given rise to seriously rethinking the core concepts of QFT. These include the methodology of perturbation theory, the theory of Feynman integrals, dualities and hidden symmetries, the prominent role of effective field theories, and the gradient flow methodology in lattice field theory.
In the first funding period, the RTG 2575 (Spokesperson: IRIS Memeber Prof. Jan PLefka) made important contributions to this innovative research area. It aims to transform the theoretical foundations of the field, coupled with the development of new technologies for the phenomenology of particle physics and gravitational wave research. The proven qualification program is to be continued in the second funding period.
18.04.2024Exciting breakthrough in battery technology through innovative sulphur-based cathodes
 |
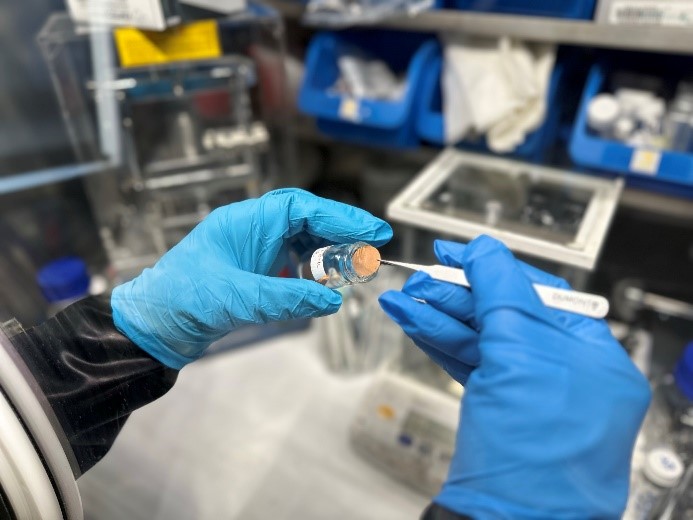 |
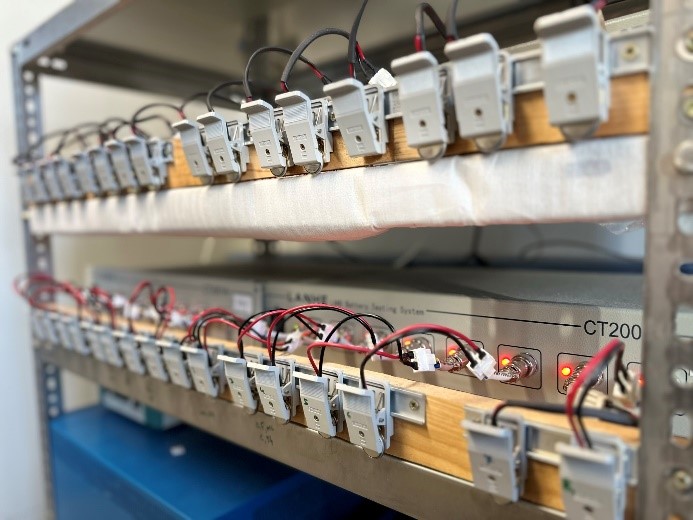
| Battery test circuit at bojdysLAB | Battery cell manufacture at bojdysLAB |
Prof. Dr Michael J. Bojdys is an expert in the field of sustainable energy materials and, as part of the BMBF's "GreenCHEM" initiative, is helping to transform the chemical industry in the Berlin capital region by combining science and industry to create a circular economy based on sustainable resources.
For further information and details on the study, please contact Prof Dr Michael J. Bojdys and his team, Barbora Balcarova and Guiping Li, as scientific contacts. They can be contacted at michael.janus.bojdyshu-berlin.de or via bojdyslab.org.
28.03.2024Automated calculation of surface properties in crystals
The surface properties of complex crystalline materials can be calculated reliably and automatically using only the fundamental laws of physics, thanks to a new computer-based method. Writing in the journal npj computational materials, researchers from the University of Oldenburg in Germany outline how their method could speed up the search for new materials for important technologies such as photovoltaics, batteries or data transmission.
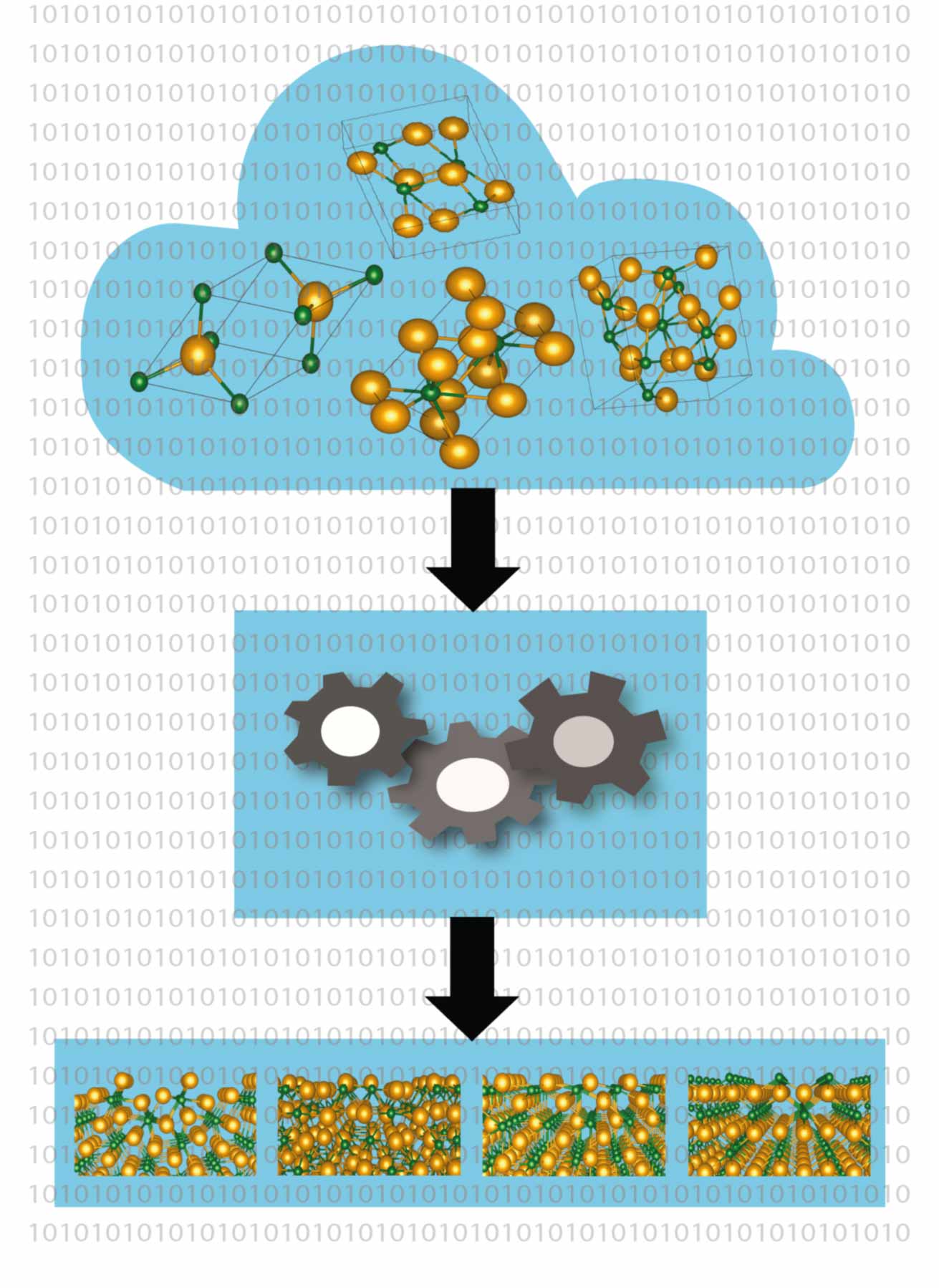
Computer-aided methods are becoming an increasingly powerful tooI in the search for new materials for key technologies such as photovoltaics, batteries and data transmission. Member of IRIS Adlershof Prof. Dr. Caterina Cocchi and Holger-Dietrich Saßnick from the University of Oldenburg’s Institute of Physics have now developed a high-throughput automatised method to calculate the surface properties of crystalline materials starting directly at the level of established laws of physics (first principles). In an article published in the journal npj computational materials, they report that this can speed up the search for relevant materials for applications in key areas such as the energy sector. They also plan to combine the method with artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to further accelerate the process.
So far similar methods have focused on bulk materials rather than surfaces, the two physicists explain. “All the relevant processes for energy conversion, production, and storage occur on surfaces,” says Cocchi, who heads the Theoretical Solid State Physics research group at the University of Oldenburg. However, calculating the material properties of surfaces is far more challenging than for complete crystals because the surface facets often have a complex structure due to factors such as defects in the crystal structure or the uneven growth of a crystal, she explains.
This complexity poses problems for researchers in the field of materials science: “It is often not possible to clearly determine the properties of samples in experiments," says Cocchi. This motivated Cocchi and her colleague Saßnick to develop an automated procedure for high-quality screening of the characteristics of new compounds.
The result of their work was incorporated into the aim2dat computer programme, which only requires the chemical composition of a compound as input. The information about the crystal’s structure is extracted from existing databases. The software then calculates the conditions under which the surface of the material is chemically stable. In a second step it determines key properties, in particular the energy required to excite electrons into conduction states or detach themselves from a surface. This parameter plays an important role in materials that convert solar energy into electricity, for example. "We don't make any assumptions in our calculations; we use only the fundamental equations of quantum mechanics, which is why our results are very reliable," Cocchi explains.
The two scientists demonstrated the applicability of the method using the semiconductor cesium telluride. The crystals of this material, which is used as an electron source in particle accelerators, can occur in four different forms. “The composition and quality of the material samples are difficult to control in experiments,” notes Saßnick. Nevertheless, the Oldenburg researchers were able to perform a detailed analysis of the physical properties for the different configurations of the caesium telluride crystals.
Cocchi and Saßnick have embedded the software in a publicly accessible programme library so that other researchers can also use and improve the procedure. “Our method has great potential as a tool for discovering new materials – and in particular physically and structurally complex solids – for all kinds of applications in the energy sector," says Cocchi.
Originalpublikation:
Saßnick, HD., Cocchi, C. “Automated analysis of surface facets: the example of cesium telluride.” npj Computational Materials 10, 38 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-024-01224-7
Weitere Informationen:
https://uol.de/en/est
19.03.2024Markus Krutzik zu Quantentechnologie bei "Weiß der Adler"
 It's magic! Wissenschaft und Magie, das schließt sich eigentlich aus. Nur, wenn Quantenforscher:innen über ihren Fachbereich sprechen, dann fallen schon mal diese Worte…
It's magic! Wissenschaft und Magie, das schließt sich eigentlich aus. Nur, wenn Quantenforscher:innen über ihren Fachbereich sprechen, dann fallen schon mal diese Worte…Für viele Staaten ist die Forschung an der Quantentechnologie der Schlüssel zur Zukunft. Wohl auch deshalb will der Standort Berlin-Adlershof hier ganz vorn mitspielen.
Wie das funktionieren und was Quantenforschung alles können soll, darüber spricht in dieser Ausgabe FluxFM-Podcaster Danilo Höpfner mit IRIS Adlershof Mitglied Markus Krutzik vom Ferdinand-Braun-Institut / HU Berlin sowie Gabrielle Thomas von Menlo Systems.
➔ Podcast-Folge auf FluxFM
07.02.2024New high-tech instrument for the nanospectroscopy research of Sebastian Heeg
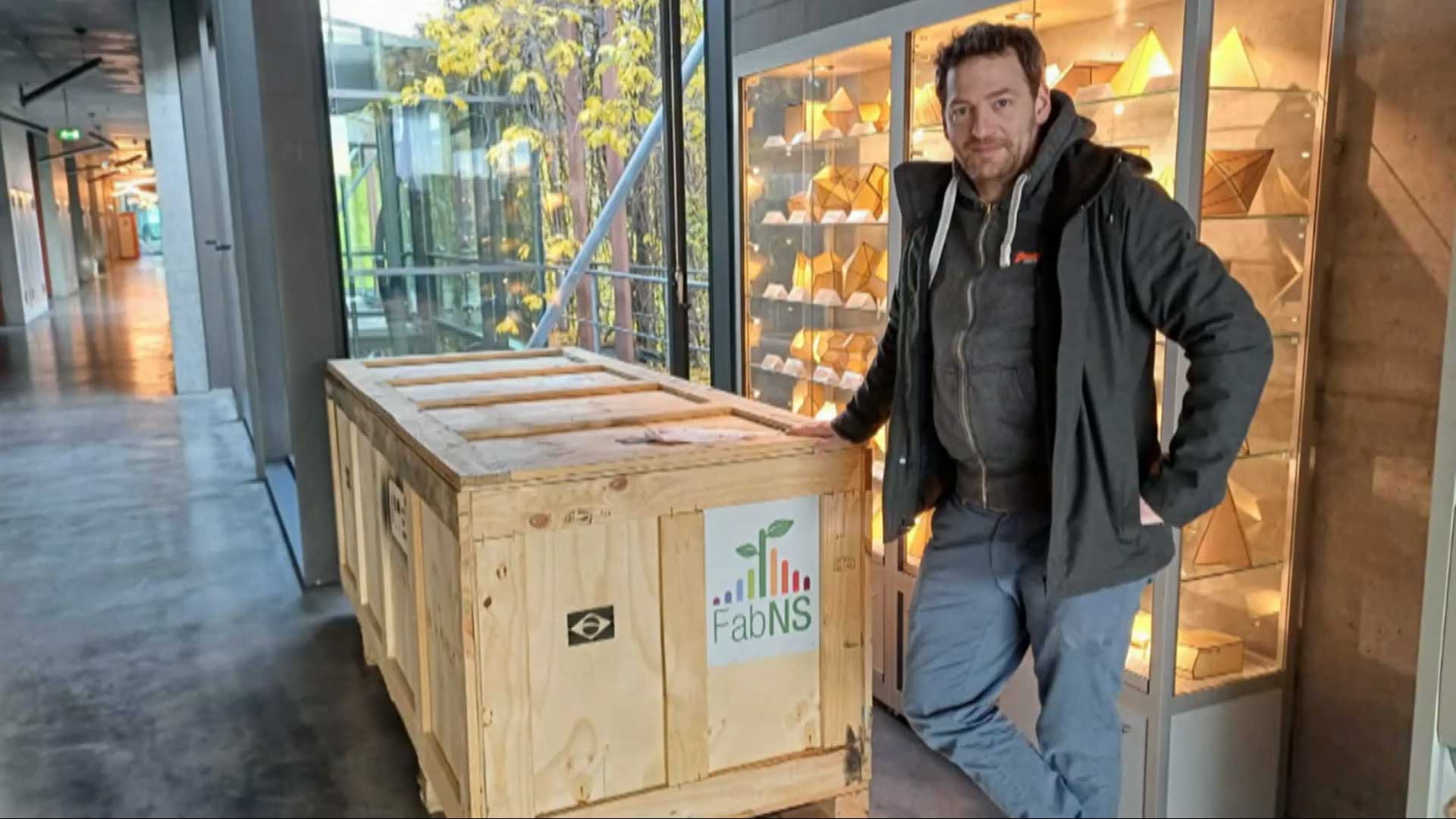 Sebastian Heeg, junior research group leader at the Department of Physics and member of IRIS Adlershof, has now officially opened two laboratories. The centrepiece is the Porto Nanoscope from the Brazilian tech start-up FabNS, which was delivered in November 2023 after a two-year wait.
Sebastian Heeg, junior research group leader at the Department of Physics and member of IRIS Adlershof, has now officially opened two laboratories. The centrepiece is the Porto Nanoscope from the Brazilian tech start-up FabNS, which was delivered in November 2023 after a two-year wait.
FabNS has thus set a milestone, as Brazil, which has historically been dependent on foreign technology, is now taking a different direction and starting to export cutting-edge scientific instruments itself. This freedom between import and export puts Brazil in a protagonist position in global technology. Sebastian Heeg's working group will be able to provide the start-up with valuable feedback as its first customer within the framework of a development partnership.
The Porto Nanoscope images the structure of nanomaterials using tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. This enables a 1,000-fold magnification compared to conventional microscopes and thus a resolution of structures in the sub-nanometre range. This allows the surfaces of 2D materials such as graphene, a layer of hexagonally arranged carbon atoms, to be analysed. Understanding and modifying the properties of 2D materials on these smallest length scales will be used in future for nanoscale photodetectors, flexible displays and transistors.
Sebastian Heeg is enthusiastic about the new measuring device. The Brazilians have created a device with high stability, efficiency and performance. It can do everything he needs for his research: "This system is the best system." The new system will also be available to other scientists, such as the Center for the Science of Materials Berlin (CSMB), for their research.
➔ TV report from the Brazilian News
Contact:
Dr. Sebastian Heeg
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
IRIS Adlershof & Department of Physics
Tel.: 030 2093-82295
sebastian.heegphysik.hu-berlin.de
30.01.2024Dr. Niklas Grabicki nominated for the Dissertationspreis Adlershof

On Tuesday, February 13, 2024, starting from 3:00 PM, three young researchers will present the topics of their dissertations at the Erwin Schrödinger Center. Among the three nominees presenting their work at the event is Dr. Niklas Grabicki. He completed his doctoral studies under IRIS member Prof. Dr. Oliver Dumele, who now teaches at Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg. Dr. Niklas Grabicki, as part of his dissertation, synthesized functional molecules that can be classified as new molecular sensors or light-responsive magnets. Potential applications of these new functional molecules range from targeted membrane transport to data storage.
Additionally, Dr. Andrei Bud (Farkas Group) and Dr. Lisa Kröll (Rolfs Group) were nominated. The award ceremony will also be broadcasted via livestream.
We wish Niklas the best of luck!
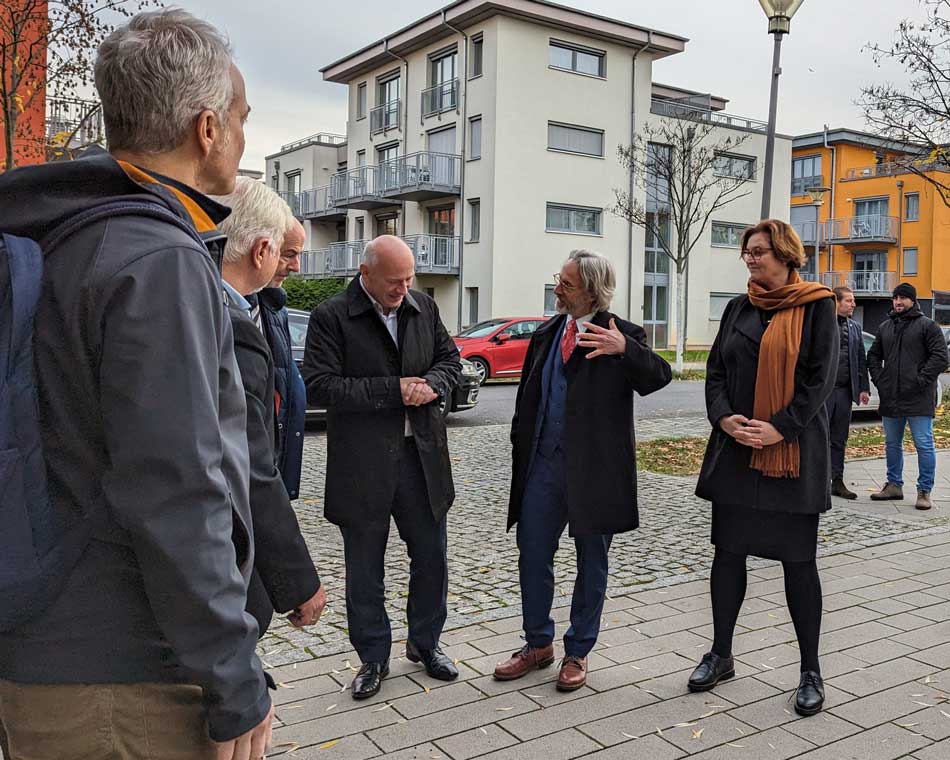
22.11.2023Kai Wegner and Dr. Ina Czyborra visited IRIS Adlershof
IRIS Adlershof welcomed a visit from the Governing Mayor, Kai Wegner, and the Senator for Science, Health, and Care, Dr. Ina Czyborra. IRIS-member Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil provided them with insights into our cleanroom laboratory, where our colleagues are actively researching new materials, and he explained ongoing projects with the distinguished guests.
Following the visit, our guests celebrated the 20th anniversary of Campus Adlershof, which they opened together with Prof. Julia von Blumenthal, President of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, and Roland Sillmann, WISTA. The lively exchange and discussions during the festivites were complemented by engaging presentations from Prof. Elmar Kulke, IRIS-member Prof. Eva Unger, and Prof. Thomas Kosch.
IRIS Adlershof, as a part of this success story, congratulates the entire campus on the milestones achieved together.
 |
 |
 |
| (fltr:) Prof. Ulf Leser, Dr. Nikolai Puhlmann, Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil, Kai Wegner, Prof. Christoph Schneider and Dr. Ina Czyborra in front of IRIS Adlershof | Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil explains ongoing research in new materials with Kai Wegner, governing mayor of Berlin | Prof. Eva Unger looks forward to the next 20 years of energy materials research at the Festakt: 20 Jahre Campus Adlershof |
01.11.2023Oliver Dumele is going to Freiburg
 Dr. Oliver Dumele, member of IRIS Adlershof, received a call to the Albert-Ludwigs University of Freiburg and started his role as a Professor (W3) for Functional Organic Materials on November 1st.
Dr. Oliver Dumele, member of IRIS Adlershof, received a call to the Albert-Ludwigs University of Freiburg and started his role as a Professor (W3) for Functional Organic Materials on November 1st.
Oliver Dumele studied chemistry at the University of Mainz and UC Berkeley in the USA. After his thesis at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research in Mainz and an industrial internship at BASF in Ludwigshafen, he obtained his doctorate at ETH Zurich in Switzerland. In a subsequent postdoctoral phase, he conducted research at Northwestern University in the USA. Since 2019, he has been a junior group leader at the Institute of Chemistry at Humboldt University in Berlin, where he has been leading the BMBF group on "Organic Battery Electrodes from Framework Compounds" since 2022. His work has been honored with various awards, such as the Lecturer's Prize from the Foundation of the Chemical Industry, the Young Investigator Award from the European Chemical Society, and recently, the Ernst Haage Prize from the Max Planck Society.
He remains a member of IRIS Adlershof.
Congratulations!
19.10.2023Materialzing the future: CSMB's Opening Event
Sustainable batteries, novel catalysts, efficient solar cells, and 3D printing technology - all of this is set to emerge in the future at the new Center for the Science of Materials Berlin (CSMB) at Humboldt University in Berlin. The grand opening took place on Thursday, October 19th in the IRIS Research Building in Berlin-Adlershof. Not only the HU news page, but also the newspaper B.Z. (with a quarter-million readers) featured a noteworthy article on 'Berlin's new gem of research'.
"Many global challenges related to sustainable resource utilization can only be addressed through innovation in materials science," explains CSMB founding director Prof. Stefan Hecht. With the new materials research center, Humboldt University is consolidating the expertise available in Adlershof's science and technology hub for innovation processes and materials science. At CSMB, researchers are working on future materials aimed at achieving global sustainability goals. Scientists from various disciplines, both academic and non-academic institutions, as well as entrepreneurs, are working together. The development of innovative materials at CSMB will be accelerated using modern methods such as high-throughput synthesis and screening, in-situ synchrotron analytics, data science, and artificial intelligence.
Collaborative Research on Future Materials
In the labs at CSMB, 150 scientists are already working in jointly operated labs, known as Joint Labs. Here, researchers from chemistry, physics, and computer science collaborate with colleagues from the life and cultural sciences, each bringing their unique perspective on materials. Startup entrepreneurs also have access to the new labs. Together, they are researching highly efficient solar cells, sustainable sodium-ion batteries, novel catalysts for efficient green hydrogen production, and printable organ models for animal-free drug testing.
State-of-the-Art Research Building in Berlin-Adlershof
The state-of-the-art research building at CSMB provides researchers with excellent infrastructure, including electron microscopes for atomic-level material imaging, ultrafast spectroscopy for tracking chemical processes in femtoseconds, and innovative printing techniques.
CSMB is the logical extension of Humboldt University's first integrated research institute, IRIS Adlershof, which laid the foundation for interdisciplinary collaboration and a new, state-of-the-art research building.
Here are some impressions, gathered by our colleague Collin
19.10.2023Jan Plefka and Stefan Hecht among the 100 most prominent scientists in Berlin

The editorial team of the Berlin Science section of Tagesspiegel has identified the top 100 personalities in the Berlin research scene for the year 2023. These experts have significantly influenced the research region of Berlin throughout the year with their remarkable achievements and innovations. Some have enriched their respective fields with groundbreaking studies and innovative research methods, secured substantial research funding, and excelled in education. Others have actively participated in public discourse, shaped the urban community, and established international networks connecting regional research institutions with the world. These researchers all contribute to shaping the profile of the scientific community and laying the foundations for future discoveries and innovations. Among the selected scientists are two members of IRIS Adlershof.
Jan Plefka: Researching at the Heart of the Universe
One of the selected top scientists is Jan Plefka, a researcher at the Institute of Physics and the Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences (IRIS) at Humboldt-University in Adlershof, Berlin. His work focuses on fascinating questions related to the formation of black holes, the validity of Einstein's theories in strong gravitational fields, and the quest for signs of physics beyond known natural forces and particles. In his research, he employs quantum field theory, a mathematical description of the fundamental building blocks of our universe, to, for example, investigate gravitational waves.
Stefan Hecht: Innovations in Materials Science
Another outstanding scientist who made it into the top 100 is Stefan Hecht, a professor of chemistry and the founding director of the Center for the Science of Materials Berlin. Stefan Hecht is dedicated to materials science and conducts intensive research on light-controlled polymers. Particularly notable is his development of "Xolography," a method for highly precise 3D printing, which he has brought to market readiness. His commitment to promoting university-based startups was recognized this year with the prestigious Unipreneurs Award.
The inclusion of these two exceptional researchers from IRIS Adlershof among Berlin's top 100 scientists recognizes their significant contributions to research and their impressive achievements in their respective fields. Jan Plefka and Stefan Hecht utilize their expertise and dedication to answer critical questions and advance innovations that will shape our world of tomorrow.
13.10.2023IOP–HU early career researcher conference on condensed matter physics
The Institute of Physics (IOP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and Humboldt-Universtät zu Berlin recently concluded their IOP-HU Early Career Researcher Conference on Condensed Matter Physics in Liyang, and it was hailed as a resounding success. The event, held from October 13th to 14th, offered a platform for early career researchers to present their groundbreaking research and engage with domestic and international experts in the field, including the director of IRIS Adlershof, Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe, and the IRIS professors Christoph T. Koch, Claudia Draxl and Mathias Scheffler.
Event Highlights:
Day 1 - Early Career Researcher Conference: On the first day, junior postdoctoral candidates, senior PhD candidates, and students took the stage to present talks and posters, sharing their innovative research findings. The participants also had the invaluable opportunity to learn about postdoctoral fellowship opportunities at IOP CAS and partner institutes, followed by stimulating discussions with principal investigators from both organisations.Day 2 - PI Program and Discussions with Early Career Researchers: The second day of the conference featured stimulating talks from distinguished researchers on a range of topics, including theory and simulation, scanning probe and electron microscopy, and magnetism and quantum information. These sessions fostered intellectual exchange and collaboration between seasoned researchers and the next generation of scientists.
Day 3 - Participants had the exclusive opportunity to embark on an optional visit to Beijing, a modern city with profound history and marvelous culture, further immersing themselves in the world of scientific excellence.

13.10.2023The IOP–Humboldt Postdoctoral Fellowship in Physics
Nominations are open for postdoctoral fellowships between two cities, Berlin and Beijing, as part of a joint physics program between the Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences (IRIS Adlershof) of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU Berlin) and the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, (IOP) Beijing.
FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM
Established in 2020, the prestigious two-year research fellowships are intended for exceptional early-career scientists, in preparation for an independent career in research at the frontier of condensed matter physics, quantum materials or device physics. Successful candidates will spend one year in Berlin and one in Beijing at the research groups of their choice, supported by up to 4,500 EUR/month. The selected fellows are expected to be appointed in 2023 and 2024. A first networking event is scheduled in Berlin. Fellows will work at the Campus Adlershof of HU Berlin and the IOP Zhongguancun Beijing Campus. The fellows have the possibility to visit and interact with associated Partners at the Max Born Institute, the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin and its Electron Storage Ring BESSY II, the Leibniz-Institut für Kristallzüchtung or the Fritz-Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society.The prestigious two-year research fellowships are intended for exceptional early-career scientists, in preparation for an independent career in research at the frontier of condensed matter physics, quantum materials or device physics. Successful candidates will spend one year in Berlin and one in Beijing at the research groups of their choice, supported by up to 4,500 EUR/month.
The selected fellows will be appointed from August 2022 onwards. A first networking event is programmed in Berlin. Fellows will work at the Campus Adlershof of HU Berlin and the IOP Zhongcuancun Beijing Campus. The fellows have the possibility to visit and interact with associated Partners at the Max Born Institute, the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin and its Electron Storage Ring BESSY II, the Freie Universität Berlin, at the Leibniz-Institut für Kristallzüchtung or the Fritz-Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society.
A full list of participating groups can be found at HU Physics and the IOP website. Exemplary fields and participating groups includeCondensed Matter Theory
Prof. Claudia Draxl, Prof. Sheng Meng, Prof. Hongming Weng, Prof. Chen Fang, Prof. Xinguo Ren, Prof. Jiangping Hu, Prof. Zhong Fang, Prof. Tao Xiang, Prof. Matthias Scheffler
Ultrafast Laser Spectroscopy
Prof. Zhiyi Wei, Prof. Jianing Chen
Photoemission Spectroscopy and Surface Science
Prof. Norbert Koch, Prof. Tian Qian, Prof. Xingjiang Zhou, Prof. Jiandong Guo
Optoelectronic Devices and Quantum Transport
Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil, Prof. Thomas Schröder, Prof. Guangyu Zhang, Prof. Yongqing Li
Scanning Probe Microscopy
Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe, Prof. Carlos-Andres Palma, Prof. Kui Jin, Prof. Shuheng Pan, Prof. Hong-Jun Gao
Quantum Information
Prof. Tim Schröder, Prof. Oliver Benson, Prof. Li Lu
Electron Microscopy
Prof. Christoph Koch, Prof. Xuedong Bai
ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA
Commitment to a one-year research stay at IOP followed by a further year at HU Berlin. Special travel preferences will be considered. A PhD degree in physics, chemistry, mathematics, or materials, obtained no more than five years prior to the application deadline. Previous international experience, such as conference talks and research abroad.
HOW TO APPLY
Applicants should send their CV and one publication (in PDF format), along with a cover letter and two reference letters to: fellowshipsphysik.hu-berlin.de. Only candidates specifying two or more preferred host research groups in Berlin and Beijing will be considered.- Program closing date: November 15th, 2023.
DECISION
The decision announcements for the 2023 program are sent no later than 2 months after the closing date. Decisions will be made by a joint committee from IOP and HU Berlin. The HU Berlin and IOP specifically encourage qualified female scholars to apply.25.09.2023Eva Unger on her research on perovskites in the Adlershof Journal
 "Perovskite is a collective term for materials with a specific crystal structure," explains Eva Unger, chemistry professor at HU Berlin and member of IRIS Adlershof. As semiconductors, perovskites are ideally suited for use in solar cells. In the laboratory, small-area perovskite solar cells already achieve efficiencies similar to those of classic silicon solar cells. The potential is great, because perovskites can be produced cheaply and even combined with other solar cell materials. The new issue of the Adlershof Journal deals with the questions Eva Unger and her team still have to clarify on the way to the large-scale use of perovskite solar cells.
"Perovskite is a collective term for materials with a specific crystal structure," explains Eva Unger, chemistry professor at HU Berlin and member of IRIS Adlershof. As semiconductors, perovskites are ideally suited for use in solar cells. In the laboratory, small-area perovskite solar cells already achieve efficiencies similar to those of classic silicon solar cells. The potential is great, because perovskites can be produced cheaply and even combined with other solar cell materials. The new issue of the Adlershof Journal deals with the questions Eva Unger and her team still have to clarify on the way to the large-scale use of perovskite solar cells.
to the online article...
06.09.2023Prof. Stefan Hecht was honored by Minister of Education Bettina Stark-Watzinger for Entrepreneurial Commitment
 The member of IRIS Adlershof, Professor Stefan Hecht, Founding Director of the Center for the Science of Materials Berlin (CSMB) at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, was honored on September 6, along with 19 other university professors, with the #UNIPRENEURS Award for his dedication to university spin-offs.
The member of IRIS Adlershof, Professor Stefan Hecht, Founding Director of the Center for the Science of Materials Berlin (CSMB) at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, was honored on September 6, along with 19 other university professors, with the #UNIPRENEURS Award for his dedication to university spin-offs.
The prestigious award ceremony was hosted by Federal Minister for Education and Research, Bettina Stark-Watzinger, and Dr. Anna Christmann, Commissioner for Digital Economy and Startups at the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action.
Stefan Hecht, a Berlin native, pursued his chemistry studies at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Following several academic stints he returned to his alma mater as an Einstein Professor and the Founding Director of the newly established Center for the Science of Materials Berlin (CSMB).
"When research addresses genuinely relevant issues, commercial applications naturally follow," says the patent holder. As a specialist in photoswitchable molecules, he found a way to cure liquid specialty plastics with two intersecting beams of light. He co-founded Xolo GmbH with two colleagues and is currently developing 3D printers of which the first ones are being used by researchers. He generously shares his expertise with other startups and collaborates closely with them in his labs.
As the founding director of the CSMB on Humboldt-Universität’s science campus in Berlin-Adlershof, he aims to realize his vision: "We want to be not only a place for enquiring minds but also for innovative minds. The center should attract researchers who not only answer questions but also translate their answers into practical applications." The ideal place to develop sustainable energy materials that are well thought out from beginning to end: from design and sustainability considerations to validation and implementation.
Minister Stark-Watzinger expressed enthusiasm:"We want to strengthen entrepreneurship at our universities. Professors play a pivotal role in this. They significantly contribute to the entrepreneurial culture at universities and are crucial drivers of Germany's innovation and future viability." (Original: "Wir wollen das Gründungsgeschehen an unseren Hochschulen stärken. Professorinnen und Professoren spielen dabei eine zentrale Rolle. Sie tragen maßgeblich zur Gründungskultur an Hochschulen bei und sind wichtige Impulsgeber für die Innovationskraft und Zukunftsfähigkeit Deutschlands.")
Commissioner Christmann also praised the professors' achievements: "The distinguished professors from UNIPRENEURS embody the outstanding combination of academic excellence and entrepreneurial spirit. Their contributions to transferring innovations to the business world are invaluable to Germany's innovation landscape and deserve the highest recognition."
(Original: "Die ausgezeichneten Professorinnen und Professoren von UNIPRENEURS verkörpern die herausragende Verbindung von akademischer Exzellenz und unternehmerischem Geist. Ihre Verdienste für den Transfer der Innovationen in die Wirtschaft sind von unschätzbarem Wert für den Innovationsstandort Deutschland und verdienen höchste Anerkennung.")
UNIPRENEURS is an initiative aimed at bolstering university spin-offs in German universities and awards the highest recognition in Germany for outstanding commitment to entrepreneurship at universities. The "Award for the Best University Professors for Entrepreneurs" by UNIPRENEURS seeks to honor entrepreneurial engagement at universities and raise the prominence of entrepreneurship within higher education. Out of nearly 700 nominations, 20 exceptional professors were selected by a prestigious board.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates its founding member Stefan Hecht very warmly on this wonderful award.
Contact:
Prof. Stefan Hecht
Humboldt University in Berlin
CSMB, IRIS Adlershof, & Department of Chemistry
Tel.: 030 2093-7365
shhu-berlin.de
20.08.2023Prof. Dr. Valentina Forini back at HU
 Dr. Valentina Forini has accepted the call to join Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin as a W2 professor for "Theoretical particle physics: Gauge fields and string theory" at the Department of Physics. The professorship is initially funded by the DFG within the framework of the Heisenberg Program.
Dr. Valentina Forini has accepted the call to join Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin as a W2 professor for "Theoretical particle physics: Gauge fields and string theory" at the Department of Physics. The professorship is initially funded by the DFG within the framework of the Heisenberg Program.
With a background in theoretical physics, Valentina bridges the gap between mathematical and high-energy physics, particularly focusing on string and quantum field theory. She is known for developing advanced methods to quantitatively analyze their quantum behaviors and their relationship through the AdS/CFT correspondence, exploring the interplay between space-time and matter.
Currently serving as a Lecturer in Mathematics at City, University of London since 2018, Dr. Forini is also affiliated with Humboldt-Universität as a Principal Investigator and Guest Professor, supported by the Kolleg Mathematik Physik Berlin.
Her career includes roles as Project Leader in the European Network EuroPLEx, Principal Investigator in the RTG 2575 "Rethinking Quantum Field Theory”, as well as prestigious research grants like the Simons Emmy Noether Fellowship 2018/19 at Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics in Waterloo (CA), the Einstein Junior Fellowship from 2018 to 2021 at Humboldt-Universität. Here she also has served as Emmy-Noether Group Leader from 2012 to 2017. She became a IRIS Junior Member in 2018 and is a full member of IRIS Adlershof since 2021.
Her academic journey has encompassed diverse institutions, including the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics in Golm and the University of Barcelona. Dr. Forini earned her PhD in Physics from the University of Trento in 2006 and habilitated in Theoretical Physics in 2017. Her qualifications also include a Laurea in Physics from the University of Perugia and a Diploma in Piano from the Perugia Conservatory of Music.
The announcement of Dr. Forini's appointment is met with the warmest congratulations, and she will begin in the upcoming winter semester.
Even if you were never really away:
Welcome back, Valentina!
04.08.2023Einstein International PostDoctoral Fellow at the Department of Physics and IRIS Adlershof
 |
| Dr. Pietro Marabotti |
Pietro Marabotti obtained his PhD in Energy and Nuclear Science and Technology at the Politecnico di Milano in Italy. With the Einstein International Postdoctoral Fellowship, He will join the Emmy-Noether group "Physics of low-dimensional systems" of Dr. Sebastian Heeg at IRIS Adlershof and the Department of Physics at HU Berlin and conduct research on confined carbyne, which are linear chains of carbon atoms inside carbon nanotubes.
Pietro Marabotti will set up a near-field scanning optical microscope that performs infrared spectroscopy using entangled photon pairs at nanoscale resolution. He will study how structural non-linearities like defects, kinks or bends affect the optical and electronic properties of confined carbyne, and explore its potential for nanoscale light transduction. The Einstein Foundation funds Pietro Marabotti for 3.5 years with a total funding of 375,000 euros.
We look forward to working with Pietro and welcome him to IRIS Adlershof .
13.07.2023IRIS Summer Party 2023
 |
 |
 |
Yesterday, 12 July, IRIS Adlershof and CSMB celebrated a summer party to which all researchers and staff were cordially invited.
The party was introduced with an inspiring and pathetic speech by Prof. Stefan Hecht. The festivities took place in front of the IRIS research building, allowing attendees to relish the beautiful weather while seeking refuge in the cool shade. Additional refreshment was provided by a wide range of drinks. Culinary delights in the form of grilled specialities and a variety of salads provided further enjoyment.
Many participants expressed their appreciation for the opportunity to connect with scientists from different groups and start-ups.
A sly but unregistered creature sneaked into the BBQ event, carefully assessing the surroundings for any remains of roasted chicken.
The festivities continued until 10:30 pm, with the last guests lending a hand to clean up, adding a final touch of camaraderie to the event.
10.07.2023Scientific insights into the record-breaking tandem solar cell
 The world's best tandem solar cells, consisting of a silicon bottom cell and a perovskite top cell, can today convert about one third of the incident solar radiation into electrical energy. These are record values, especially for a potentially very low-cost technology. A team at HZB, including IRIS Adlershof member Prof. Eva Unger, now provides the scientific data for the first time and describes in the renowned journal Science how this development was achieved (DOI: 10.1126/science.adf5872).
The world's best tandem solar cells, consisting of a silicon bottom cell and a perovskite top cell, can today convert about one third of the incident solar radiation into electrical energy. These are record values, especially for a potentially very low-cost technology. A team at HZB, including IRIS Adlershof member Prof. Eva Unger, now provides the scientific data for the first time and describes in the renowned journal Science how this development was achieved (DOI: 10.1126/science.adf5872).
The tandem solar cell, described in detail for the first time in the article, had achieved a world record in efficiency and generated headlines with it in December 2022: it converts 32.5% of the incident sunlight into electrical energy. The research field is very competitive, which is why many working groups are conducting research in this area. In recent years, there has been a continuous increase in efficiency values by various research institutions and photovoltaic companies worldwide. The KAUST research centre (Saudi Arabia) has therefore already surpassed the HZB record in the meantime. But, the HZB team has now presented a solid and scientifically rigorously peer-reviewed technical publication with exact data sets from the measurements as well as detailed information on the structure of the tandem cell.
A significantly improved perovskite compound and a novel molecule of piperazinium iodide were used to produce this cell, thus reducing losses. Using special measurement methods, the researchers were able to analyse the fundamental processes at the interfaces and in the individual layers of the tandem cell in detail and optimise them further. The production and development of the tandem cell was possible thanks to cooperation with groups from Potsdam, San Sebastian (Spain) and Kunas (Lithuania). Only the combination of all modifications made it possible to achieve maximum values for the photovoltage (open-circuit voltage), as well as the photocurrent and consequently in terms of efficiency.
With continued progress in the field, there is hope that this technology can make a major contribution to a sustainable energy supply in the fight against climate change in the coming years, because the upscaling and industrial production of perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells is also feasible.
In the upcoming CSMB–IRIS colloquium on 25 July on "Chemical transformation processes in halide perovskite semiconductors", Prof. Eva Unger will further expand this topic.
01.07.2023Conclusion of the Highly Successful CRC 951 - Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS) after 12 Years
 After an 12-year run, the Collaborative Research Centre CRC 951 - Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS) reached the end of its maximum funding period. Throughout these years, IRIS Adlershof has worked closely with the CRC 951, fostering a productive and symbiotic relationship. The connection between us went beyond just thematic alignment, as many members of IRIS, including aspiring scientists, actively participated in the CRC 951.
After an 12-year run, the Collaborative Research Centre CRC 951 - Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS) reached the end of its maximum funding period. Throughout these years, IRIS Adlershof has worked closely with the CRC 951, fostering a productive and symbiotic relationship. The connection between us went beyond just thematic alignment, as many members of IRIS, including aspiring scientists, actively participated in the CRC 951.
The CRC 951's headquarter was located within the IRIS Research Building, reflecting the deep integration and collaboration between the two entities. Together, we embarked on joint projects, including colloquia, workshops, conferences, celebrations, and publications. These endeavors were instrumental in advancing research and fostering innovation in the field of hybrid systems.
We extend our heartfelt gratitude to all those involved for their close and highly successful collaboration. The fruitful partnership between IRIS Adlershof and the CRC 951 has significantly contributed to the progress and achievements made in this interdisciplinary domain.
22.06.2023Prof. Yan Lu appointed to HIPOLE and the University of Jena
 IRIS member Prof. Dr. Yan Lu will take up a professorship at the University of Jena in the winter semester. She will also become co-spokesperson of the "Helmholtz Institute for Polymers in Energy Applications" (HIPOLE), which will most likely be officially founded on 1 July 2023.
IRIS member Prof. Dr. Yan Lu will take up a professorship at the University of Jena in the winter semester. She will also become co-spokesperson of the "Helmholtz Institute for Polymers in Energy Applications" (HIPOLE), which will most likely be officially founded on 1 July 2023.
The aim of HIPOLE is to develop sustainable polymer materials for energy technologies that can be rapidly brought into use, in particular polymer-based batteries and perovskite solar cells with polymer additives. The founding director is Prof. Dr. Ulrich S. Schubert from the University of Jena, with whom Yan Lu has already conducted research in previous years.
more...We offer our warmest congratulations!
19.06.2023Open Access textbook "Scattering Amplitudes in Quantum Field Theory" by Jan Plefka et al.

 We are very happy to announce the new open access textbook "Scattering Amplitudes in Quantum Field Theory". Jan Plefka reviews the modern theory of scattering amplitudes together with Badger, Henn, and Zoia.
We are very happy to announce the new open access textbook "Scattering Amplitudes in Quantum Field Theory". Jan Plefka reviews the modern theory of scattering amplitudes together with Badger, Henn, and Zoia.
These lecture notes bridge a gap between introductory quantum field theory (QFT) courses and state-of-the-art research in scattering amplitudes. They cover the path from basic definitions of QFT to amplitudes relevant for processes in the Standard Model of particle physics. The book begins with a concise yet self-contained introduction into QFT, including perturbative quantum gravity. It then presents modern methods for calculating scattering amplitudes, focusing on tree-level amplitudes, loop-level integrands and loop integration techniques. These methods help reveal intriguing relations between gauge and gravity amplitudes, and are of increasing importance for obtaining high-precision predictions for collider experiments, such as those at CERN's Large Hadron Collider, as well as for foundational mathematical physics studies in QFT, including recent applications to gravitational wave physics.
These course-tested lecture notes include numerous exercises with detailed solutions. Requiring only minimal knowledge of QFT, they are well-suited for MSc and PhD students as a preparation for research projects in theoretical particle physics. They can be used as a one-semester graduate level course, or as a self-study guide for researchers interested in fundamental aspects of QFT.
more...16.06.2023The IOP-HU workshop on condensed matter physics

The Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Humboldt-Universität Berlin (IOP–HU) Condensed Matter Physics Workshop 2023 is a two–day workshop which will take place on October 13th–14th in Liyang (near Shanghai & near Suzhou) with an optional visit to IOP Beijing campus on October 15th.
The workshop is directed at early career researchers looking to present their research and interact with domestic and international condensed matters physicists. Every year a few topics are chosen based on the speakers. Ten travel awards will cover travel and accommodation expenses for international early career researchers.
This year, the program will cover:
- Density functional theory and simulation
- Scanning probe and electron microscopy
- Magnetism and quantum information
The workshop will consist of sessions of invited talks and contributed poster sessions. Young researchers are encouraged to participate in the workshop and present their work in the form of posters. The workshop is expected to be a highly exciting and stimulating event. We look forward to meeting you in Beijing in October, 2023.
more...16.06.2023FCI-Lecturer Award for Oliver Dumele
 The Lecturer Award (Dozentenpreis) of the Fund of the Chemical Industry (FCI) is one of the most prestigious and highly endowed awards in the field of promoting young researchers and is awarded to outstanding young scientists in the field of chemistry. The award winners are proposed by members of the Fund's Board of Trustees, former Lecturer Award winners or spokespersons of the review boards of the German Research Foundation and selected in a two-stage nomination process.
The Lecturer Award (Dozentenpreis) of the Fund of the Chemical Industry (FCI) is one of the most prestigious and highly endowed awards in the field of promoting young researchers and is awarded to outstanding young scientists in the field of chemistry. The award winners are proposed by members of the Fund's Board of Trustees, former Lecturer Award winners or spokespersons of the review boards of the German Research Foundation and selected in a two-stage nomination process.
On 16 June 2023, it was awarded to Dr Oliver Dumele (HU Berlin, Inst. Chemie & IRIS Adlershof), Prof. Dr A. J. Barbara Lechner (TUM) and Dr Sabine Richert (U Freiburg). The prize money will also support further steps in their careers.
In his current research, Mr. Dumele is working on organic functional materials at the molecular as well as supramolecular level and in covalent-organic frameworks (COFs). Novel aromatic building blocks are incorporated into framework compounds and are thus intended to answer fundamental questions or contribute to new energy storage systems as battery electrodes. Furthermore, purely organic photomagnetic switches that can change their electronic spin state by light pulse are currently being developed in his research group for future applications in quantum information technology. more...
Congratulations on another great award!
23.05.2023The IOP–Humboldt Postdoctoral Fellowship in Physics
Nominations are open for postdoctoral fellowships between two cities, Berlin and Beijing, as part of a joint physics program between the Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences (IRIS Adlershof) of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU Berlin) and the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, (IOP) Beijing.
FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM
Established in 2020, the prestigious two-year research fellowships are intended for exceptional early-career scientists, in preparation for an independent career in research at the frontier of condensed matter physics, quantum materials or device physics. Successful candidates will spend one year in Berlin and one in Beijing at the research groups of their choice, supported by up to 4,500 EUR/month. The selected fellows are expected to be appointed in 2023 and 2024. A first networking event is scheduled in Berlin. Fellows will work at the Campus Adlershof of HU Berlin and the IOP Zhongguancun Beijing Campus. The fellows have the possibility to visit and interact with associated Partners at the Max Born Institute, the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin and its Electron Storage Ring BESSY II, the Leibniz-Institut für Kristallzüchtung or the Fritz-Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society.The prestigious two-year research fellowships are intended for exceptional early-career scientists, in preparation for an independent career in research at the frontier of condensed matter physics, quantum materials or device physics. Successful candidates will spend one year in Berlin and one in Beijing at the research groups of their choice, supported by up to 4,500 EUR/month.
The selected fellows will be appointed from August 2022 onwards. A first networking event is programmed in Berlin. Fellows will work at the Campus Adlershof of HU Berlin and the IOP Zhongcuancun Beijing Campus. The fellows have the possibility to visit and interact with associated Partners at the Max Born Institute, the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin and its Electron Storage Ring BESSY II, the Freie Universität Berlin, at the Leibniz-Institut für Kristallzüchtung or the Fritz-Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society.
A full list of participating groups can be found at HU Physics and the IOP website. Exemplary fields and participating groups includeCondensed Matter Theory
Prof. Claudia Draxl, Prof. Sheng Meng, Prof. Hongming Weng, Prof. Chen Fang, Prof. Xinguo Ren, Prof. Jiangping Hu, Prof. Zhong Fang, Prof. Tao Xiang, Prof. Matthias Scheffler
Ultrafast Laser Spectroscopy
Prof. Zhiyi Wei, Prof. Jianing Chen
Photoemission Spectroscopy and Surface Science
Prof. Norbert Koch, Prof. Tian Qian, Prof. Xingjiang Zhou, Prof. Jiandong Guo
Optoelectronic Devices and Quantum Transport
Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil, Prof. Thomas Schröder, Prof. Guangyu Zhang, Prof. Yongqing Li
Scanning Probe Microscopy
Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe, Prof. Carlos-Andres Palma, Prof. Kui Jin, Prof. Shuheng Pan, Prof. Hong-Jun Gao
Quantum Information
Prof. Tim Schröder, Prof. Oliver Benson, Prof. Li Lu
Electron Microscopy
Prof. Christoph Koch, Prof. Xuedong Bai
ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA
Commitment to a one-year research stay at IOP followed by a further year at HU Berlin. Special travel preferences will be considered. A PhD degree in physics, chemistry, mathematics, or materials, obtained no more than five years prior to the application deadline. Previous international experience, such as conference talks and research abroad.
HOW TO APPLY
Applicants should send their CV and one publication (in PDF format), along with a cover letter and two reference letters to: fellowshipsphysik.hu-berlin.de. Only candidates specifying two or more preferred host research groups in Berlin and Beijing will be considered.- First 2023 Program closing date: June 15th, 2023.
- Second 2023 Program closing date: November 15th, 2022.
DECISION
The decision announcements for the 2023 program are sent no later than 2 months after the closing date. Decisions will be made by a joint committee from IOP and HU Berlin. The HU Berlin and IOP specifically encourage qualified female scholars to apply.11.05.2023Joachim Sauer appointed member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
 Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Dr. h.c. Joachim Sauer, who is a Senior Researcher at the Department of Chemistry at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, has been appointed a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences based on his research activities at the department, in two Collaborative Research Centres at Humboldt-Universität and in the Cluster of Excellence UNICAT. Admission to the Academy will take place in a formal ceremony on 30 September 2023 in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Prof. Dr. rer. nat. Dr. h.c. Joachim Sauer, who is a Senior Researcher at the Department of Chemistry at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, has been appointed a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences based on his research activities at the department, in two Collaborative Research Centres at Humboldt-Universität and in the Cluster of Excellence UNICAT. Admission to the Academy will take place in a formal ceremony on 30 September 2023 in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences is one of the oldest and most prestigious honorary societies in the US, founded in 1780. It honours excellence and gathers leaders from all fields to explore new ideas and address and collaborate on issues of importance to the nation and the world.
Congratulations to our founding member!
12.04.2023Prof. Eva Unger interviewed: "Only5mins! - Self-healing properties of perovskite solar key to industrial development."
IRIS-Mitgleid Eva Unger gave pv magazine a short interview and explained the viperlab projekt and the selfhealing of perovskite solar cells.
11.04.2023An important step towards the quantum internet
A cornerstone for 1000-fold improved communication rates to bridge long distances
 |
| Illustration: Defect centres in diamond nanostructures can be used as quantum bits. The quantum information can be stored in individual photons via quantumoperation and than be transmitted in optical fibres in the future quantum internet. |
Diamond material is of great importance for future technologies such as the quantum internet. Special defect centers can be used as quantum bits (qubits) and emit single light particles that are referred to as single photons. To enable data transmission with feasible communication rates over long distances in a quantum network, all photons must be collected in optical fibers and transmitted without being lost. It must also be ensured that these photons all have the same color, i.e., the same frequency. Fulfilling these requirements has been impossible until now.
Researchers in the "Integrated Quantum Photonics" group led by Prof. Dr. Tim Schröder, member of IRIS Adlershof, have succeeded for the first time worldwide in generating and detecting photons with stable photon frequencies emitted from quantum light sources, or, more precisely, from nitrogen-vacancy defect centers in diamond nanostructures. This was enabled by carefully choosing the diamond material, sophisticated nanofabrication methods carried out at the Joint Lab Diamond Nanophotonics of the Ferdinand-Braun-Institut, Leibniz-Institut für Höchstfrequenztechnik, and specific experimental control protocols. By combining these methods, the noise of the electrons, which previously disturbed data transmission, can be significantly reduced, and the photons are emitted at a stable (communication) frequency.
In addition, the Berlin researchers show that the current communication rates between spatially separated quantum systems can prospectively be increased more than 1000-fold with the help of the developed methods—an important step closer to a future quantum internet.
The scientists have integrated individual qubits into optimized diamond nanostructures. These structures are 1000 times thinner than a human hair and make it possible to transfer emitted photons in a directed manner into glass fibers. However, during the fabrication of the nanostructures, the material surface is damaged at the atomic level, and free electrons create uncontrollable noise for the generated light particles. Noise, comparable to an unstable radio frequency, causes fluctuations in the photon frequency, preventing successful quantum operations such as entanglement.
A special feature of the diamond material used is its relatively high density of nitrogen impurity atoms in the crystal lattice. These possibly shield the quantum light source from electron noise at the surface of the nanostructure. "However, the exact physical processes need to be studied in more detail in the future," explains Laura Orphal-Kobin, representative of the junior scientist at IRIS Adlershof, who investigates quantum systems together with Prof. Dr. Tim Schröder. The conclusions drawn from the experimental observations are supported by statistical models and simulations, which Dr. Gregor Pieplow from the same research group is developing and implementing together with the experimental physicists.
L. Orphal-Kobin, K. Unterguggenberger, T. Pregnolato, N. Kemf, M. Matalla, R.-S. Unger, I. Ostermay, G. Pieplow, and T. Schröder
Physical Review X (2023)
Contact:
Laura Orphal-Kobin, phone: +49 30 2093 82146, mail: orphalphysik.hu-berlin.de
Prof. Dr. Tim Schröder, phone: +49 30 2093 82140, mail: tim.schroederphysik-hu-berlin.de
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Department of Physics and IRIS Adlershof, Integrated Quantum Photonics Group & Joint Lab Diamond Nanophotonics, Ferdinand-Braun-Institut
30.03.2023Prof. Jan Plefka receives ERC Advanced Grant
 |
| Prof. Jan Plefka |
Jan Plefka receives a prestigious Advanced Grant from the European Research Council (ERC). He and his team at the Department of Physics and IRIS Adlershof of HU Berlin will receive 2.2 million euros over the next five years for the GraWFTy project (High-Precision Gravitational Wave Physics from a Worldline Quantum Field Theory) to describe gravitational waves using quantum field theory. The predictions made possible in this way are needed for the wave detectors of the next generation to go online in the 2030s.
The ERC Advanced Grant
ERC Advanced Grants are endowed with up to 2.5 million euros and support excellent and self-initiated research projects of leading top researchers. It is the most highly endowed European research grant. The awardees are exceptional leaders who distinguish themselves through the originality and significance of their approaches.
About the awardee
Professor Jan Plefka is a renowned theoretical physicist and professor at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. After studying physics and receiving his PhD from the University of Hannover in 1995, he was a postdoctoral researcher in New York, Amsterdam, and at the MPI Potsdam. He was a visiting professor at ETH Zurich and at CERN. His research is concerned with quantum field theory and its relation to gravity. Here, he made important contributions to questions of quantum gravity and string theory, in particular in the area of AdS/CFT correspondence and hidden symmetries in supersymmetric quantum field theories. More recently, he has developed together with his group an innovative quantum field theoretical formalism to answer questions in classical gravitational wave physics. The ERC Advanced Grant was awarded to him to fully unfold the potential of this quantum approach to classical physics. He is the spokesperson of the DFG Research Training Group 2575, "Rethinking Quantum Field Theory." Jan Plefka has received several awards, including a Feodor Lynen Fellowship from the Humboldt Foundation and the Lichtenberg Professorship from the Volkswagen Foundation.
The GraWFTy Projekt: High-Precision Gravitational Wave Physics from a Worldline Quantum Field Theory
Gravitational waves are tiny ripples of the space-time fabric that travel through our universe at the speed of light. They arise as soon as masses are accelerated. They are a direct prediction of Einstein's theory of relativity, which he established during his fruitful Berlin years as early as 1916. They were first directly detected only 100 years later in 2015 with the LIGO detector, emerging from a merger of two black holes and after a journey of billions of light years through our universe to us. There are currently three gravitational wave observatories in operation: LIGO, Virgo, and Kagra. They routinely detect gravitational waves emanating from such mergers of black holes and neutron stars. To date, about 90 such events have been detected. In the 2030s, a new generation of ground- and space-based gravitational wave detectors will come on-line that will significantly increase the sensitivities of these measurements. To match these sensitivities, theoretical physics must predict highly accurate waveforms from Einstein's theory that greatly exceed the current state of the art. The GraWFTy project will provide these predictions for the high-precision form of gravitational waves. With their help, fundamental questions in physics will be studied:
- Is Einstein's theory correct in the strong gravitational field regime?
- How are black holes formed, what is their population in the universe?
- Can we see signals for physics beyond the known natural forces and particles?
 |
| Visualization of gravitational bremsstrahlung from the scattering of two black holes (BSc thesis O. Babayemi) |
Jan Plefka explains his approach: "Together with my research group, we have been able to develop an innovative method since 2020 that addresses this problem of classical physics using methods from quantum field theory. Quantum field theory is the mathematical description of elementary particle physics, that is the smallest building blocks of our universe and their interactions. It is exceedingly fascinating that this language can also be applied to classical gravitational physics with high efficiency. In short, we replace the scattering of protons, as it happens in accelerators like the LHC at CERN, in our formalism by the scattering of black holes or neutron stars. There is, of course, the initial simplification that we can now neglect the quantum effects in the extensive calculations - which in the case of gravity are also still ill understood. Yet, this simplification is compensated by the complexity of Einstein's theory compared to the standard model of elementary particle physics relevant to proton scatterings.
The great advantage of our so-called "world-line" approach is that we can directly target the observable quantities in the detector, using the modern mathematical technology of quantum field theory, namely Feynman integrals. Another peculiar aspect of our approach is that the spin of black holes is described by a supersymmetry. Its existence has been speculated so far in elementary particle physics. We could show that it appears in the effective description of rotating black holes. The idea for this approach comes from string theory. For me, this project represents a crucial step in my career. So far, I have focused my research primarily on the question of quantum gravity and its relation to gauge field theories. This was primarily mathematical physics and far away from direct measurements. With GraWFTy, I am now applying these ideas priorly developed in an abstract setting to pressing, to pressing questions in gravitational wave physics. We have already been able to prove the efficiency of this approach. The ERC Advanced Grant will allow me to fully unfold the potential of our approach."
Contact
Prof. Dr. Jan Christoph Plefka
jan.plefkaphysik.hu-berlin.de
Department of Physik and IRIS Adlershof
Zum Großen Windkanal 2, 12489 Berlin
20.03.2023Multi-million-Euro funding for two collaborative quantum technology projects: The Institute of Physics and IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität are involved in both projects
Quantum technologies promise a variety of completely new applications. In addition to quantum computers, quantum sensing and quantum communication are among the areas of quantum technology in which the first, also commercially successful product developments are expected. The Federal Ministry of Education and Research is now funding Humboldt University Berlin (HU) in two new collaborative projects in the field of quantum technologies.
 |
| Researchers are working on the novel QEED microscopy for quantum-based early cancer diagnostics. Image: LaVision BioTec GmbH |
The first funded project, QEED, deals with quantum sensing with entangled photons - for applications in medical research and cancer diagnostics. Funded as a BMBF "Lighthouse Project" for 5 years (project volume 11.9 million euros, HUB 1.7 million euros), the collaboration will jointly develop a very powerful microscope that can work in the mid-infrared (MIR). In order to transfer measurement information from the clinically relevant MIR to the near infrared (NIR), which can be detected particularly fast and with low noise, a novel, spectrally resolving imaging method based on entangled photon pairs will be used.
In the "Nonlinear Quantum Optics" group at HU and IRIS Adlershof, led by Dr. Sven Ramelow, who also serves as scientific director of the overall collaboration, high-performance quantum interferometer modules are being developed and the quantum sensing measurement techniques underlying the collaborative project are being optimized. The core innovation here is the significant increase in the rate of generated entangled photon pairs, as well as the significant extension of the MIR measurement range compared to the state-of-the-art.
Among the total of ten project partners are five research institutions - including three from Berlin: FBH-Berlin, Charité-Berlin, and HU-Berlin. Also five corporate partners are part of the team and will, in addition to their work in the project, after project completion promote a commercialization of the microscope and its components. The project officially started on 01.01.23.
The second funded collaborative project named "High Performance Light Sources for Quantum Communication" - MIHQU (project volume 5.3 million Euro, HUB 1.4 million Euro) is about quantum communication - an important building block for the future security of digital infrastructures in our society. In quantum communication, the exchange of cryptographic keys is based on the laws of physics, which means that security, in contrast to currently used encryption, remains fundamentally guaranteed - even in the event of attacks by novel, previously unknown algorithms or by powerful quantum computers.
 |
| Image: AIXEMTEC GmbH, Herzogenrath |
The goal of the project is to miniaturize sources for photon pairs in such a way that their reproducible industrial production can be established in small series. At Humboldt-Universität, the group "Nonlinear Quantum Optics" is mainly working on the development of functional models of the sources as a basis for the subsequent integration.
In addition to the HU-Berlin (Dr. Sven Ramelow with his group "Nonlinear Quantum Optics"), the total of 5 project partners includes the Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., Berlin in the person of Prof. Janik Wolters, who will coordinate the project, as well as the Technische Universität Berlin, and two company partners – son-x GmbH, Aachen and AIXEMTEC GmbH, Herzogenrath. The project started on 01.03.2023.
Project profile QEEDProject profile MIHQ
Infobox: Nonlinear interferometers with entangled photons
Spontaneous parametric down-conversion (SPDC) in nonlinear optical crystals is a standard process for generating correlated or entangled photon pairs for quantum communication, quantum-assisted imaging or quantum sensing. If one now uses two identical SPDC processes that are coherently pumped and superimposes the emissions, one can observe simultaneous, identical interference for both photons of a pair - the so-called signal and idler photons. Such a setup as shown in the figure below represents such a so-called "nonlinear interferometer". (Chekhova, Ou, “Nonlinear interferometers in quantum optics“, AOP 8, 1, 104 (2016)).
Schematic of a nonlinear interferometer, here in Mach-Zehnder configuration
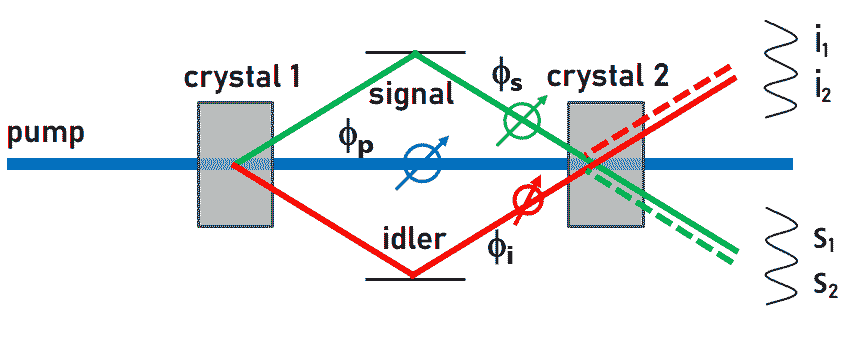
The essential point is that the entangled photon pairs interfere as a single quantum object! This means that a phase (or absorption) of the idler photons also affects the signal photons as an interference signal (and vice versa). The interference pattern - i.e. its phase position and contrast - thus depends on the transmission coefficients of pump radiation, idler and signal photons as well as on the total phase difference (ϕs+ ϕi - ϕp) that all three waves have accumulated in the interferometer. In particular, the phase and absorptions of the idler can thus be determined solely by measuring the signal photons. This effect is called "measurement with non-detected photons", since the actual "measuring" Idler photons never have to be measured themselves. If photon pairs are now generated with a large wavelength spread (e.g. signal in the visible, idler in the mid-infrared), the spectral information (absorption, dispersion) recorded by the idler photons in the MIR can be registered by measuring the wavelength-dependent interference in the signal with a silicon detector. These are particularly powerful and low-noise and thus enable a variety of very practical applications of this measurement principle.
Dr. Sven Ramelow
Head of "Nonlinear Quantum Optics" at the Department of Physics and IRIS Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
Phone: +49 30 2093-7799
sven.ramelowphysik.hu-berlin.de
02.03.2023Lively interest at the second IRIS Junior breakfast

Dr. Edgar Nandayapa introduces the HyD group and explains solar cell printing.
We would like to thank Pablo and Laura, who organized the whole thing again!
24.02.2023xolo GmbH selected as the first investment of the 'Deep Tech & Climate Fonds'
 |
| V.l.n.r.: Dirk Radzinski (CEO, xolo), Prof. Stefan Hecht (CSO, xolo), Frank Cartsen Herzog (HZG Group), Dr. Elisabeth Schrey (DeepTech & Climate Fonds), Tobias Faupel (DeepTech & Climate Fonds), Dr. Anna Christmann (Bundesministerium Wirtschaft und Klimaschutz) |
The Berlin-based company xolo was founded in Berlin in 2019 by IRIS Adlershof- member Stefan Hecht, Martin Regehly and Dirk Radzinski. With Xolography, they have developed a novel volumetric 3D printing technology that prints quickly and produces very smooth surfaces. Xolography uses two beams of light with different wavelengths that collide in the resin and harden it into the desired material. This enables a resolution of a few micrometers. The process is many times faster than previous methods and enables centimetre-sized objects to be printed in a few seconds instead of several hours as was previously the case. This makes printing cheaper and potentially more rewarding for mass production. It also does not rely on formative support structures and allows the use of materials previously unsuitable for 3D printing.
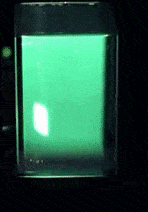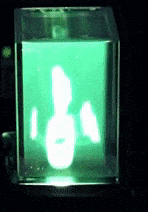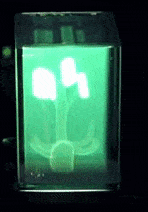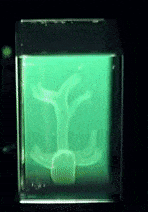 |
| xolo Aneurisma Print Source: xolo, youtube |
Xolo has now received eight million euros from Deep Tech & Climate Fonds (DTCF), HZG Group, Onsight Ventures and Square One to enable the transition to industrial scale use. The first 10 devices were delivered specifically to research institutes to test different fields of application, e.g. in medical technology for the reproduction of organs or in optics for the production of high-precision lenses.
The investment is intended to help xolography achieve a breakthrough and strengthen Germany as a location for industry and research.
16.02.2023Canadian delegation visits IRIS Adlershof
 |
|
f.l.t.r.: Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe, Dr. Nikolai Puhlmann, Prof. Fred Wrona, Dr. Helge Neumann, Ms. Natalka Cmoc, Dr. Johannes Müller
|
A delegation from Canada visited us today to find out how the IRIS Adlershof is successfully networking with other institutes and companies at the science location Berlin-Adlershof. IRIS director Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe gave a brief insight into the institute. Helge Neumann from WISTA reported on Adlershof as a science location. A tour of the research building followed. Dr. Felix Hermerschmidt showed the network laboratory with the impressive glovebox cluster, followed by an explanation of the NION-TEM with its atomic resolution by Johannes Müller and a tour of the campus.
Ms. Natalka Cmoc, the Director General for Science & Policy at Public Services & Procurement Canada, was visibly impressed, and Prof. Dr. Fred Wrona (University of Calgary, Canada) was also highly interested and praised the many opportunities offered to top scientific research.
14.02.2023Dr. Jannes Münchmeyer receives 2023 Adlershof Dissertation Award
 |
| f.l.t.r.: Dr. Dominique Lungwitz, Dr. Jannes Münchmeyer, Dr. Julia Baum |
On February 14, 2023, the Adlershof Dissertation Prize was awarded for the 21st time in a row. Dr. Jannes Münchmeyer received the EUR 3,000 prize, which is awarded annually by the research network IGAFA e. V., the Humboldt University of Berlin and WISTA Management GmbH.
Earthquake early warning is an essential step in avoiding major damage: There are often valuable seconds between the start of an earthquake and the occurrence of strong vibrations in which to take protective measures. But how early are warnings possible and where do the physics and the natural stochasticity of earthquakes set us limits? dr In his doctoral thesis, Jannes Münchmeyer showed how artificial intelligence can help to answer these questions and what effects his results can have on dealing with earthquake risks. He was mentored by IRIS member Ulf Leser.
Two other outstanding researchers made it into the final selection: Dr. Dominique Lungwitz (Humboldt University of Berlin) did her doctoral thesis in the group of Prof. Norbert Koch's, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, on "Polymer semiconductors for the future: on the way to efficient and cost-effective OLEDs and solar cells" and Dr. In her dissertation, Julia Baum (Humboldt University of Berlin) examined “Defamation sticks: How “fake news” influence our judgments”. Both received prize money of 1,000 euros for their nomination.
IRIS Adlershof warmly congratulates on this wonderful success!
18.01.2023Stefan Hecht's visions of the CSMB in the Adlershof Journal
 Chemistry professor and CSMB founding director Stefan Hecht is certain: Many global challenges related to sustainable resource use can only be mastered through innovation in the field of materials science. While achieving this, he hopes for successful interdisciplinary cooperation with other university and non-university institutions. The member of IRIS Adlershof explains the methods he targets to advance materials research in the new issue of the Adlershof Journal.
Chemistry professor and CSMB founding director Stefan Hecht is certain: Many global challenges related to sustainable resource use can only be mastered through innovation in the field of materials science. While achieving this, he hopes for successful interdisciplinary cooperation with other university and non-university institutions. The member of IRIS Adlershof explains the methods he targets to advance materials research in the new issue of the Adlershof Journal.
to the online article...
12.01.2023Straining of a suspended 2D semiconductor drives different energy states into hybridization, enabling single photon emission
 By applying strain on WSe2 membranes with a high degree of control, Dr. Sebastian Heeg and colleagues characterized the different excitonic species present in the material according to their energetic dependence with strain. At certain strain levels, strain-independent defect states and strain dependent dark excitons became energy degenerated and their photoluminescence intensity increased an order of magnitude. “The high tunability of the hybridized state enabled by our device architecture will be likely key for the operation of single quantum emitters in WSe2” highlights Pablo Hernández López, a PhD candidate at Dr. Heeg’s group and co-author of the paper, “On the other hand, the characterization and tuning of the energy hierarchy of the excitons present on suspended materials using our electrostatic straining approach opens the door for more exciting discoveries in the future”.
By applying strain on WSe2 membranes with a high degree of control, Dr. Sebastian Heeg and colleagues characterized the different excitonic species present in the material according to their energetic dependence with strain. At certain strain levels, strain-independent defect states and strain dependent dark excitons became energy degenerated and their photoluminescence intensity increased an order of magnitude. “The high tunability of the hybridized state enabled by our device architecture will be likely key for the operation of single quantum emitters in WSe2” highlights Pablo Hernández López, a PhD candidate at Dr. Heeg’s group and co-author of the paper, “On the other hand, the characterization and tuning of the energy hierarchy of the excitons present on suspended materials using our electrostatic straining approach opens the door for more exciting discoveries in the future”.
more...
Strain control of hybridization between dark and localized excitons in a 2D semiconductor
P. Hernández López, S. Heeg, C. Schattauer, S. Kovalchuk, A. Kumar, D.J. Bock, J.N. Kirchhof, B. Hoefer, K. Greben, D. Yagodkin, L. Linhart, F. Libisch, K.I. Bolotin
Nature Communications, 13, 7691 (2022) OPEN ACCESS
ACCESS
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-35352-9
16.12.2022Prof. Michael Hintermüller elected speaker of the Math+ Cluster of Excellence
 The annual MATH+ Day 2022 took place on November 18 with over 100 participants. The General Assembly elected Prof. Michael Hintermüller, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, as chair for the next two years. The previous co-chair Hintermüller castles with Prof. Christof Schütte. The other newly elected board members also include Prof. Holger Reich as the new BMS chairman, replacing IRIS member Prof. Jürg Kramer.
The annual MATH+ Day 2022 took place on November 18 with over 100 participants. The General Assembly elected Prof. Michael Hintermüller, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, as chair for the next two years. The previous co-chair Hintermüller castles with Prof. Christof Schütte. The other newly elected board members also include Prof. Holger Reich as the new BMS chairman, replacing IRIS member Prof. Jürg Kramer.
more...
13.12.2022X-mas party for Junior scientists
 On 13.12. the young researchers celebrated a Christmas party at a common room in the IRIS research building. In keeping with the occasion, they were also asked science quiz questions related to Christmas, resulting in many interesting conversations. Of course, Christmas music was also not to be missed. Fortified by stollen and mulled wine, they thus celebrated the holiday season and share their love of science with their colleagues and friends.
On 13.12. the young researchers celebrated a Christmas party at a common room in the IRIS research building. In keeping with the occasion, they were also asked science quiz questions related to Christmas, resulting in many interesting conversations. Of course, Christmas music was also not to be missed. Fortified by stollen and mulled wine, they thus celebrated the holiday season and share their love of science with their colleagues and friends.
24.11.2022First IRIS juniors breakfast and lab tours session
On Nov 21 2022 the IRIS junior scientists met for a breakfast and a lab tours session focused on quantum optics.

Pablo Hernández López, the juniors representative and organizer, explains: "Our colleagues Elisa & Martin (AG Markus Krutzik) and Julian & Jonas (AG Tim Schröder) showed their labs and introduced their fields of research. This event was the first one of a series of lab tours that will continue next year. Thanks to the presenters and to everyone who came. It was great to meet so many new colleagues and to discover some of the very interesting work done at IRIS Adlershof."
22.11.2022Humboldt-ProMINT-Kolleg erfolgreich in der Ausschreibung Interdisziplinäre Zentren der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
 Das Humboldt-ProMINT-Kolleg wird ab 2023 ein Interdisziplinäres Zentrum der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
Das Humboldt-ProMINT-Kolleg wird ab 2023 ein Interdisziplinäres Zentrum der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
Ziel des Interdisziplinären Zentrums Humboldt-ProMINT-Kolleg ist die exzellente Erforschung von Prozessen der wissenschaftlichen Erkenntnisgewinnung in der MINT-Lehrkräftebildung an der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Dabei stellen die Mitglieder des Kollegs die Themen „Technologiegestütztes Lehren und Lernen“, „Messprozesse und Umgang mit Daten“, „Problemlösen“ sowie „Modelle und Modellierungsprozesse“ in das Zentrum ihrer Arbeit.
Zukünftig widmet sich das IZ ProMINT-Kolleg der Stärkung der fachdidaktischen Forschung durch die Intensivierung der internationalen Forschungskooperationen, der Vernetzung von Fachdidaktik und Fachwissenschaft durch Innovation und Transfer sowie der Verbreitung von wissenschaftlichen Forschungsergebnissen durch Third Mission und Wissenschaftskommunikation.
Es schließt damit an seine über die Jahre gewachsene Struktur als ProMINT-Kolleg und sein Renommee innerhalb und außerhalb der Universität an und überführt dies in die sichtbareren, effizienteren und nachhaltigeren Strukturen eines interdisziplinären Zentrums.
Das Humboldt-ProMINT-Kolleg wurde 2010 auf Initiative der MINT-Fachdidaktiker*innen der HU und mit Unterstützung der Deutsche Telekom Stiftung gegründet. Ein zentrales Anliegen des Kollegs ist es seitdem, die wissenschaftliche Fundierung der MINT-Lehrkräftebildung inhaltlich und strukturell als eines der zentralen Tätigkeitsfelder an der HU auf- und auszubauen. Zwölf Jahre nach seiner Gründung gehört das Humboldt-ProMINT-Kolleg zu den wichtigsten und mit einem Drittmittelvolumen von ca. 2,7 Millionen Euro auch zu den erfolgreichsten Projekten der Lehrerbildung an der HU.
Weitere Informationen: https://www.promint.hu-berlin.de
27.10.2022Einstein-Professur für Chemiker Stefan Hecht stärkt Berliner Materialwissenschaften
Das Gründungsmitglied von IRIS Adlershof, Stefan Hecht, widmet sich zukünftig als Einstein-Professor der Herausforderung, neue Materialien mit verbesserten Eigenschaften zu entwickeln. Seit Oktober beschäftigen sich der Chemiker und sein Team mit der Entwicklung lichtgesteuerter molekularer Materialien und volumetrischer 3D-Druckverfahren (Xolographie) am Campus Adlershof. Insbesondere möchte er Materialentwicklungsprozesse beschleunigen: „Neben einem umfassenden Verständnis aller relevanten Parameter, bei dem uns künstliche Intelligenz sicherlich helfen kann, müssen wir vor allem anfangen zu lernen, evolutionäre Prinzipien zu nutzen. Dann wird sich das beste Material quasi von selbst durchsetzen.“
von IRIS Adlershof, Stefan Hecht, widmet sich zukünftig als Einstein-Professor der Herausforderung, neue Materialien mit verbesserten Eigenschaften zu entwickeln. Seit Oktober beschäftigen sich der Chemiker und sein Team mit der Entwicklung lichtgesteuerter molekularer Materialien und volumetrischer 3D-Druckverfahren (Xolographie) am Campus Adlershof. Insbesondere möchte er Materialentwicklungsprozesse beschleunigen: „Neben einem umfassenden Verständnis aller relevanten Parameter, bei dem uns künstliche Intelligenz sicherlich helfen kann, müssen wir vor allem anfangen zu lernen, evolutionäre Prinzipien zu nutzen. Dann wird sich das beste Material quasi von selbst durchsetzen.“
Neben diesem neuen wissenschaftlichen Schwerpunkt möchte Hecht vor allem die Berliner Forschung im Bereich der Materialwissenschaften weiter stärken und die insbesondere am Campus Adlershof vorhandenen Expertisen in einem neuen interdisziplinären Materialforschungszentrum bündeln. „Durch intensive disziplinen- und institutionenübergreifende Zusammenarbeit können noch viele Synergien im Berliner Forschungsraum gehoben werden“, so Hecht.
mehr...
27.10.2022Tandemsolarzellen mit Perowskit: Nanostrukturen helfen mehrfach

Tandemsolarzellen aus Perowskit und Silizium ermöglichen deutlich höhere Wirkungsgrade als Siliziumsolarzellen allein. Mehrere Arbeitsgruppen am HZB forschen daran, solche Tandemsolarzellen gezielt zu entwickeln und zu optimieren. Mit großem Erfolg, Tandemzellen aus dem HZB haben bereits mehrere Weltrekorde erreicht. Zuletzt erzielten HZB-Forschungsteams im November 2021 mit einer Tandemzelle aus Perowskit- und Silizium einen zertifizierten Wirkungsgrad von 29,8%. Dies war ein absoluter Weltrekord, der acht Monate ungeschlagen an der Spitze stand. Erst im Sommer 2022 ist es einem Schweizer Team an der EPFL gelungen, diesen Wert zu übertreffen.
An der Entwicklung der Rekord-Tandemzelle war unter anderem IRIS Adlershof-Mitglied Prof. Eva Unger beteiligt. Nun stellen die Wissenschaftler in Nature Nanotechnologie die Details vor. Die Zeitschrift lud sie darüber hinaus ein, ein so genanntes „Research Briefing“ zu verfassen, in dem sie ihre Arbeit kurz zusammenfassen und einen Ausblick auf künftige Entwicklungen geben.
„Unsere jeweiligen Kompetenzen ergänzen sich sehr gut“, erklärt Prof. Dr. Christiane Becker. Ihr Team hat eine nanooptische Texturierung in die Tandemzelle eingebracht: Eine sanft gewellte Nanotextur auf der Silizium-Oberfläche. „Überraschend war, dass diese Textur gleich mehrere Vorteile bringt“, betont Becker: „Die Nanotextur reduziert nicht nur wie erwartet die Reflexionsverluste, sondern führt auch noch dazu, dass sich der extrem dünne Film aus Perowskit deutlich regelmäßiger bildet.“ Außerdem reduziert eine dielektrische Pufferschicht auf der Rückseite des Siliziums die parasitäre Absorption bei Wellenlängen im nahen Infrarotbereich.
Als Fazit halten die Forschenden fest: Mit maßgeschneiderten Nanotexturen lassen sich überraschend vielseitige Verbesserungen erreichen. Diese Ergebnisse sind nicht nur für Tandemzellen aus Perowskit- und Silizium wertvoll, sondern auch für Leuchtdioden auf Perowskit-Basis.
P. Tockhorn, J. Sutter, A. Cruz, et al.
Nano-optical designs for high-efficiency monolithic perovskite–silicon tandem solar cells.
Nat. Nanotechnol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-022-01228-8
25.10.2022Federal Minister of Education and Research in Adlershof

10.10.2022Interview mit Dr. Sven Ramelow zum Physiknobelpreis 2022
 |
| Dr. Sven Ramelow |
Dr. Sven Ramelow leitet seit 2016 die Emmy Noether-Nachwuchsgruppe "Quanten-Bildgebung und Spektroskopie im Mittleren Infrarot". Zuvor hat er nach seinem Studium an der HU beim Ehrendoktor der HU, Prof. Anton Zeilinger, an der Universität Wien promoviert und als Post-Doc mit ihm an Experimenten zur Verletzung der Bellschen Ungleichung gearbeitet, für die unter anderem der diesjährige Physik-Nobelpreis verliehen wird. Weitere Stationen waren die University of Queensland (Brisbane, Australien) und die Cornell University (Ithaca, USA), bevor er zurück zur Humboldt-Universität kam. Er ist seit 2017 Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof.
Martin Bogner, IRIS Adlershof:
Lieber Herr Dr. Ramelow, der Nobelpreis in Physik 2022 wurde an Prof. Alain Aspect, Dr. John Clauser und Prof. Anton Zeilinger "für Experimente mit verschränkten Photonen, Nachweis der Verletzung der Bellschen Ungleichungen und Pionierarbeit in der Quanteninformationswissenschaft" vergeben. Hat es Sie überrascht, das Prof. Zeilinger den Nobelpreis erhalten hat?
Dr. Sven Ramelow: Jein. Es wurde ja seit über 10 Jahren immer wieder vermutet und man konnte online sogar darauf Wetten abschließen. Zu Recht! Aber wenn es dann tatsächlich passiert, ist das natürlich für den Moment eine sehr schöne, positive Überraschung.
Das Thema hört sich kompliziert an - was sind denn verschränkte Photonen und die Bellsche Ungleichung?
Wenn man die Eigenschaften von zwei verschränkte Photonen jeweils an verschiedenen, weit entfernten Orten misst, können die Ergebnisse für bestimmte Messeinstellungen immer gleich sein. Dies ist erst einmal auch nichts Besonderes. Es könnte ja einfach so sein, dass die Photonen einfach mit jeweils gleichen Eigenschaften erzeugt und danach nur verteilt wurden.
Die beiden Photonen hätten sich also bei der Entstehung als verschränkte Photonen entschieden, welches z.B. Spin up und welches Spin down erhält?
Genau, das könnte man so vermuten. Man bezeichnet diesen Erklärungsversuch als "lokale, versteckte Variablen" oder "lokalen Realismus". Und er deckt sich ja auch zu 100% mit unseren Alltagserfahrungen: Dinge hätten "an sich" Eigenschaften, die unabhängig davon sind, ob ich diese messe oder anschaue. Allerdings wurde in den 1960er Jahren durch John Bell eine Art von Experiment vorgeschlagen, mit dem man diese Art der Erklärung sicher ausschließen kann. Und genau solche Experimente - heute spricht man von Bell-Tests bzw. Verletzung der Bellschen Ungleichungen - wurden von allen 3 Preisträgern erfolgreich durchgeführt.
Worin liegen denn die praktischen Herausforderungen bei einem solchen Versuchsaufbau?
Zunächst einmal benötig man natürlich ein Quelle von verschränkten Photonen. Heutzutage sind solchen Quellen bereits (für andere Zwecke - z.B. Quantenkryptographie) kommerziell erhältlich, aber zum Zeitpunkt der Pionier-Arbeiten der 3 Preisträger mussten diese aufwendig konstruiert und aufgebaut werden. Dann müssen die einzelnen Photonen an zwei möglichst weit entfernten Orten möglichst effizient gemessen werden - eine große messtechnische Herausforderung. Und zuletzt müssen die Messwinkel sehr schnell und vor allem zufällig verändert, sowie die Daten sehr aufwendig statistisch analysiert werden.
Wo kann man mehr dazu erfahren?
Prof. Zeilinger hat dazu einige sehr gut erklärende Bücher geschrieben, die auch allgemeinverständlich sind. Zudem gibt es in jedem Sommersemester seit ein paar Jahren am Institut für Physik die Vorlesung "Advanced Optical Sciences", bei der es bei einem der 2-3 Hauptthemen immer um solche Bell-Experimente geht.
Arbeiten Sie in Ihrer Nachwuchsgruppe auch an verschränkten Photonen?
Ich würde eher sagen wir arbeiten MIT verschränkten Photonen. Im Moment versuchen wir diese für bestimmte neue Anwendungen und sogar mögliche Produkte im Bereich der Mikroskopie und Spektroskopie nutzbar zu machen. Zum Beispiel arbeiten wir an einem Gerät für die Erkennung vom Mikroplastik-Partikeln in Abwasser, sowie einer neuen Art von Mikroskop für die Krebsdiagnostik. Die Grundlagenforschung dafür wurde übrigens erst 2014 in der Arbeitsgruppe von Prof. Zeilinger gemacht - damals noch ohne jegliche Absicht einer möglichen Anwendung, sondern wirklich aus reiner Neugier.
Ab wann schätzen Sie werde ich mit meinem Handy quantenverschlüsselte Textnachrichten verschicken?
Ich glaube nicht, dass das eine Anwendung von Quantenverschlüsselung sein wird. Aber vielleicht wird es in den nächste 5-10 Jahren andere geben - in Bereichen wo extreme Datensicherheit erforderlich ist.
Vielen Dank für das interessante Gespräch!
09.10.2022Ist die Welt noch zu retten? - Prof. Dr. Eva Unger im "Köpfe der Nachhaltigkeit"-Interview
Welche Ideen Forscher:innen für eine nachhaltige Zukunft haben, stellt das Nachhaltigkeitsportal humboldts17 in der Reihe „Köpfe der Nachhaltigkeit“ vor.
In der fünften Folge wurde Prof. Dr. Eva Unger, Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof, vorgestellt. Sie untersucht und entwickelt sogenannte Perowskit-Halbleiter, die in Solarzellen eingesetzt werden können und aus Sonnenlicht Strom produzieren und gibt Antworten auf die Frage:
„Wie können wir als Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler dabei mithelfen, dass Prozesse und Technologien schneller in die Anwendung kommen?“
05.10.2022Spitzen-Arbeitsbedingungen für die Spitzenforschung: Feierliche Eröffnung des IRIS-Forschungsbaus

Auf dem Campus Adlershof wurde der hochinstallierte IRIS‑Forschungsbau, gemeinsam finanziert von Bund, Land und Humboldt-Universität, während der Pandemie fertig gestellt und bezogen. Das Gebäude ist heute im Beisein der Senatorin für Wissenschaft, Gesundheit, Pflege und Gleichstellung und von HU-Präsidentin Julia von Blumenthal feierlich eröffnet worden. Der Forschungsbau ist Sitz des IRIS Adlershof und bietet mit Labor-, Büro- und Kommunikationsflächen auf rund 4.500 Quadratmetern optimale Bedingungen für die Zusammenarbeit von Arbeitsgruppen aus Physik und Chemie der Humboldt-Universität sowie mit Kooperationspartnern aus außeruniversitären Forschungsinstituten und der Wirtschaft.
Wissenschaftssenatorin Ulrike Gote erklärt: „Der hochmoderne Forschungsbau liegt inmitten von zahlreichen Instituten und Unternehmen im Wissenschafts- und Technologiepark Adlershof. In dieser Lage und mit seinen weitläufigen Laborbereichen bietet er den rund 160 Mitarbeiterinnen und Mitarbeitern optimale Bedingungen für die Forschung und Entwicklung hybrider Systeme für Elektronik, Optoelektronik und Photonik. Der Forschungsbau ist ein wichtiger Baustein für die herausragende Wissenschafts- und Forschungslandschaft Berlins.“
„Der IRIS-Forschungsbau stellt eine herrausragende Verbesserung der Forschungsinfrastruktur auf dem Campus Adlershof und eine große Bereicherung für Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler, Studierende, sowie für unsere Partner am Standort Berlin-Adlershof dar“, sagt HU-Präsidentin Julia von Blumenthal anlässlich der Eröffnung.
„Durch die integrative Architektur mit Verbund- wie Speziallaboren werden physikalische, chemische, material- und ingenieurswissenschaftliche, sowie IT- und AI-Methoden hier zusammengeführt. Davon erhoffen sich alle Beteiligten vor Ort, wie auch unsere strategischen internationalen Kooperationspartner erhebliche Innovationsschübe“, sagt Prof. Dr. Jürgen P. Rabe, langjähriger Direktor des IRIS Adlershof.
Im IRIS-Forschungsbau lernen und forschen Mitarbeiterinnen und Mitarbeiter unterschiedlicher Disziplinen zusammen an der Entwicklung neuartiger hybrider Materialien. Hybrid bedeutet dabei, dass etwa anorganische Halbleitermaterialien mit organischen Materialien auf einer Nanoskala zusammengebracht werden, um neue Materialien mit besseren oder auch völlig neuen Funktionalitäten zu entwickeln.
Als Herzstück des Gebäudes hat das IRIS-Team ein großes Verbundlabor mit einem integrierten Reinraumtrakt errichten lassen. Hier werden Arbeitsmethoden aus Physik und Chemie zusammengeführt. Darüber hinaus verfügt das neue Gebäude über hochspezialisierte Labore, in denen Forschende die hier entwickelten, neuen Materialien auf Herz und Nieren prüfen. Ein Highlight ist ein elektromagnetisch abgeschotteter Raum mit entkoppeltem Fundament, in dem eines der modernsten Transmissionselektronenmikroskope der Welt steht.
Die Anordnung der Labore und Büros sowie die großzügigen Kommunikationsflächen im IRIS- Forschungsbau schaffen beste Voraussetzungen, damit die unterschiedlichen Disziplinen sich austauschen und voneinander lernen können. Der Bau befindet sich in unmittelbarer Nähe der Institute für Physik und Chemie der Humboldt-Universität. Er schlägt nicht nur eine Brücke zwischen unterschiedlichen Disziplinen, sondern auch zwischen Theorie und Experiment, verbindet Grundlagenforschung, anwendungsorientierte Forschung und Hightech-Unternehmen. Hier forschen auch Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler aus außeruniversitären Einrichtungen wie dem Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie (HZB) und dem Fritz-Haber-Institut der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft. Vergangenes Jahr haben das HZB, zwei Max-Planck-Institute und die HU begonnen, ein gemeinsames Forschungslabor für Katalyse, das CatLab, im IRIS-Forschungsbau aufzubauen. Im Fokus der Forschung des CatLab steht Grüner Wasserstoff.
Eine Aufzeichnung der Eröffnungsfeier können Sie auf Youtube abrufen:
16.09.2022FAIRmat in the Adlershof Journal
 Physics professor Claudia Draxl coordinates the FAIRmat consortium, whose goal is to store not only the final results of materials science publications but also all other measurement data. In the current issue of the Adlershof Journal, she reveals why it is so important for materials researchers to process and exchange their measurement data with each other and what role the predecessor project NOMAD plays in this.
Physics professor Claudia Draxl coordinates the FAIRmat consortium, whose goal is to store not only the final results of materials science publications but also all other measurement data. In the current issue of the Adlershof Journal, she reveals why it is so important for materials researchers to process and exchange their measurement data with each other and what role the predecessor project NOMAD plays in this.to the online article...
30.08.2022"Non-Standard Models" - an entertaining and informative Youtube-Channel
Ever wondered how physicists come up with new theories? How were theorists able to predict such complex phenomena, years before they were observed experimentally? Come with us and step into the world of theoretical physics!
Non-Standard Models is a YouTube channel that provides entertaining and informative answers to research questions beyond the Standard Model, like “do extra dimensions exist and why would we need them?” or “what if the Higgs boson is actually a composite particle?”.
 This social media project was initiated by the doctoral students of the Research Training Group 2575 "Rethinking Quantum Field Theory". They create the appealing animations themselves and thus make the explanations easy to understand for physics students, but also for interested laypeople. It launched at the Lange Nacht der Wissenschaften 2022 in Berlin, and in the future further interviews with PIs and doctoral candidates of the GRK will appear.
This social media project was initiated by the doctoral students of the Research Training Group 2575 "Rethinking Quantum Field Theory". They create the appealing animations themselves and thus make the explanations easy to understand for physics students, but also for interested laypeople. It launched at the Lange Nacht der Wissenschaften 2022 in Berlin, and in the future further interviews with PIs and doctoral candidates of the GRK will appear.more on YouTube, Instagram (w/out log-in) and TikTok
08.08.2022 "Integrability, dualities and deformations" conference at IRIS Adlershof

Last week the second edition of the conference "Integrability, dualities and deformations" took place at IRIS Adlershof. This conference brought together 75 expert theoretical physicists working on integrable models, worldsheet dualities, non-commutative field theory, and the gauge/gravity correspondence, to discuss the latest developments in their fields, find new connections between these related areas, and share exciting insights. In addition to 18 great talks, you could find participants excitedly discussing their computations in various spots around and in front of the IRIS building until late each day. The talks were also livestreamed to YouTube, and recordings of the individual talks will be made available in the coming weeks.
For more details see the conference website: https://indico.cern.ch/event/1139791/
02.08.2022"Modeling Materials at Realistic time Scales via Optimal Exploitation of Exascale Computers and Artificial Intelligence" Workshop and Hands-on Tutorial successfully completed
 |
| Prof. Matthias Scheffler opens the joint workshop and hands-on tutorial |
During the week of 25-29 July, the successful workshop and hands-on tutorial on Modeling Materials at Realistic time Scales via Optimal Exploitation of Exascale Computers and Artificial Intelligence took place. The event was hosted by IRIS Adlershof and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and was a collaboration between them and the Pritzker School of the University of Chicago, CECAM, NOMAD, ECAM and MICCOM.
During the first three days from 25 to 27 July, leading experts from various fields gave talks on computational applications and related artificial intelligence methods in relation to advances in materials science. On the evenings of 25 and 26 July, there were dinners with poster sessions for further scientific and collective exchange. The afternoon of 27 July was followed by an excursion to a graffiti tour at Teufelsberg followed by dinner.
The 28th and 29th of July were then used for tutorials with hands-on examples focusing on the simulation of molecular dynamics.
01.08.2022Dr. Sven Rammelow was awarded an Eistein Junior Fellowship
 The experimental physicist and head of the Emmy Noether junior research group "Nonlinear Quantum Optics", Dr. Sven Ramelow, is doing research in the project "Sensors with entangled photons in the middle infrared" at IRIS Adlershof and the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. His approach is based on quantum-based measurements with so-called undetected photons: a new method in which entangled photon pairs are used to collect measurement information in different infrared ranges without using infrared lasers or detectors. The first industry-related applications are already in the development phase with the participation of the researcher.
The experimental physicist and head of the Emmy Noether junior research group "Nonlinear Quantum Optics", Dr. Sven Ramelow, is doing research in the project "Sensors with entangled photons in the middle infrared" at IRIS Adlershof and the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. His approach is based on quantum-based measurements with so-called undetected photons: a new method in which entangled photon pairs are used to collect measurement information in different infrared ranges without using infrared lasers or detectors. The first industry-related applications are already in the development phase with the participation of the researcher.
Sven Ramwlow has now been awarded an Einstein Junior Fellowship by the Einstein Foundation Berlin. We congratulate him warmly and look forward to continued good cooperation.
19.07.2022Niels Helle-Meyer electedVice President for Finance, Human Resources and Operations
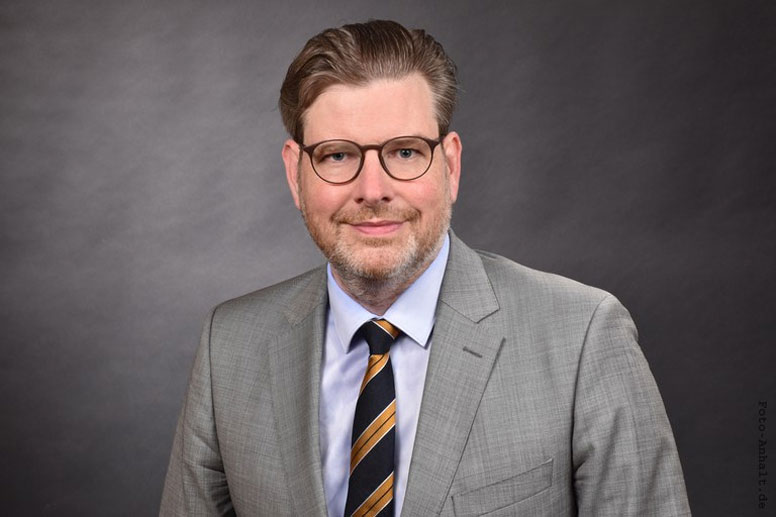

Niels Helle-Meyer has been Chancellor of the Europa Universität Viadrina in Frankfurt (Oder) since 2017. Before that, the lawyer was chancellor and director of Zeppelin Universität Friedrichshafen and director of the Naturwissenschaftlich-Technischen Akademie in Isny for five years. From 2006 to 2012 he was founding chancellor of HafenCity Universität Hamburg. (more...)
IRIS Adlershof congratulates and looks forward to a successful cooperation.
20.06.2022"Women in Natural Science School 2022 – Energy for (your) future" successfully completed
 IRIS Member Prof. Caterina Cocchi, together with Dr. Zsuzsanna Heiner and Dr. Petra Metz organized and carried out the WiNS School 2022 in Blossin, Brandenburg (June 10 – 13, 2022). About 30 women of 14 different nationalities from all career levels who are active in different areas of natural sciences – from astrophysics to biochemistry, and from environmental science to mechanical engineering – spent together four days in the nature to discuss about scientific and technological challenges in the field of energy production, storage, and consumption. The scientific program, consisting of a balanced mix between invited talks and oral contributions from the participants, was complemented by a one-day seminar on career development, personal empowerment, and community building. Two sessions dedicated to science communication augmented this rich agenda.
IRIS Member Prof. Caterina Cocchi, together with Dr. Zsuzsanna Heiner and Dr. Petra Metz organized and carried out the WiNS School 2022 in Blossin, Brandenburg (June 10 – 13, 2022). About 30 women of 14 different nationalities from all career levels who are active in different areas of natural sciences – from astrophysics to biochemistry, and from environmental science to mechanical engineering – spent together four days in the nature to discuss about scientific and technological challenges in the field of energy production, storage, and consumption. The scientific program, consisting of a balanced mix between invited talks and oral contributions from the participants, was complemented by a one-day seminar on career development, personal empowerment, and community building. Two sessions dedicated to science communication augmented this rich agenda.
The participants of this event are now part of the WiNS network and have committed themselves to act as role models for the next generation of female scientists.
Some impressions from the participants:
This weekend was so inspiring, thanks you all! – Josefin, undergraduate student
Thank you for organizing such an excellent event! These days are the highlight in my career and in my life as well! – Sarah, doctoral candidate
Thank you for providing us this platform and opportunity to explore ourselves! – Namita, Assistant Professor
more...
15.06.2022Laura Orphal and Pablo Hernández López were elected young scientist representatives
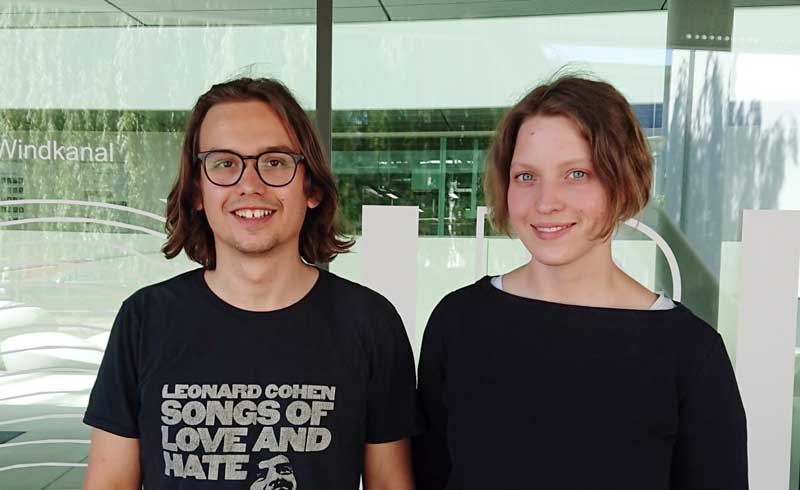 |
| Pablo Hernández López & Laura Orphal-Kobin, the newly elected junior scientists representatives |
The junior scientists of IRIS Adlershof have elected today Ms. Laura Orphal-Kobin as their representative in the IRIS bodies and Mr. Pablo Hernández López as her deputy. Thus, the young scientists are represented in the IRIS general meetings as well as in the IRIS Council with the right to speak, propose and vote.
Laura Orphal-Kobin is a PhD student in the group of Dr. Tim Schröder within the graduate school "Berlin School of Optical Sciences and Quantum Technologies" and is doing research on the optimization of diamond nanostructures.
Pablo Hernández López is a PhD student in the group of Dr. Sebastian Heeg and is doing research on one- and two-dimensional new materials. He is a member of the graduate school "Advanced Materials".
IRIS Adlershof congratulates Laura and Pablo on their election and is looking forward to a good collaboration!
08.06.2022The IOP–Humboldt Postdoctoral Fellowship in Physics
Nominations are open for postdoctoral fellowships between two cities, Berlin and Beijing, as part of a joint physics program between the Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences (IRIS Adlershof) of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU Berlin) and the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, (IOP) Beijing.
FELLOWSHIP PROGRAM
The prestigious two-year research fellowships are intended for exceptional early-career scientists, in preparation for an independent career in research at the frontier of condensed matter physics, quantum materials or device physics. Successful candidates will spend one year in Berlin and one in Beijing at the research groups of their choice, supported by up to 4,500 EUR/month.
The selected fellows will be appointed from August 2022 onwards. A first networking event is programmed in Berlin. Fellows will work at the Campus Adlershof of HU Berlin and the IOP Zhongcuancun Beijing Campus. The fellows have the possibility to visit and interact with associated Partners at the Max Born Institute, the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin and its Electron Storage Ring BESSY II, the Freie Universität Berlin, at the Leibniz-Institut für Kristallzüchtung or the Fritz-Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society.
The initial call includes the following topics and participating groups:Condensed Matter Theory
Prof. Claudia Draxl, Prof. Sheng Meng, Prof. Hongming Weng, Prof. Chen Fang, Prof. Xinguo Ren, Prof. Jiangping Hu, Prof. Zhong Fang, Prof. Tao Xiang, Prof. Matthias Scheffler, Prof. Caterina Cocchi
Ultrafast Laser Spectroscopy
Prof. Zhiyi Wei, Prof. Jianing Chen
Photoemission Spectroscopy and Surface Science
Prof. Norbert Koch, Prof. Tian Qian, Prof. Xingjiang Zhou, Prof. Jiandong Guo
Optoelectronic Devices and Quantum Transport
Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil, Prof. Thomas Schröder, Prof. Guangyu Zhang, Prof. Yongqing Li
Scanning Probe Microscopy
Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe, Prof. Carlos-Andres Palma, Prof. Kui Jin, Prof. Shuheng Pan, Prof. Hong-Jun Gao
Quantum Information
Prof. Tim Schröder, Prof. Oliver Benson, Prof. Li Lu
Electron Microscopy
Prof. Christoph Koch, Prof. Xuedong Bai
ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA
- Commitment to a one-year research stay at IOP followed by a further year at IRIS Adlershof, HU Berlin. Special cases committing to one-year at IRIS Adlershof followed by a further year at IOP will be considered.
- A PhD degree in physics, chemistry, mathematics, or materials, obtained no more than five years prior to the application deadline.
- Previous international experience, such as conference talks, research stays abroad and so on.
HOW TO APPLY
Applicants should send their CV and one publication (in PDF format), along with a cover letter and two reference letters to: fellowshipsphysik.hu-berlin.de. Only candidates specifying two or more preferred host research groups in Berlin and Beijing will be considered.- 2022 Program closing date: June 30th, 2022.
- 2023 Program closing date: November 30th, 2022.
DECISION
Decision will be made by a joint committee from IOP and HU Berlin. The decision announcements will be sent from July 2022 onwards.The HU Berlin and IOP specifically encourage qualified female scholars to apply.
08.06.2022Oliver Dumele funded by the BMBF project "BattFutur".

Due to its importance for a large number of different fields of application, such as electromobility, stationary energy storage, household appliances and high-performance tools, battery technology is a key technology for Germany as a business location, which can, for example, contribute to the federal government's obvious climate protection goals.
In order to be able to survive in global competition, the training and further education of young scientists in the field of battery research is necessary. For this purpose, the BMBF launched the “BattFutur” funding program in 2020.
IRIS-member Oliver Dumele will start his grant in this program in July 2022. His research on the synthesis of sustainable organic energy materials will be funded by € 1.62 million.
We wish Oliver Dumele every success in his important research project!
03.06.2022IRIS-fellow Archana Manoharan has successfully defended her dissertation on "X-ray Absorption Spectra of Kesterite-based Materials Studied from First Principles"

Solar energy is a reliable energy source to meet the fast-growing energy demand of today’s world. An absorber layer is the core of the solar cell device which absorbs sunlight and transports the resulting charge carriers to the electrical contacts. The kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) is a promising candidate which consists of earth abundant and non-toxic elements. CZTS has attracted much interest due to its high absorption coefficient of about ~1x10-4cm-1 and optimal bandgap of 1.4 eV. It is challenging to however, understand the electronic properties of this complex quaternary structure.
In her thesis Archana Manoharan tried to understand the electronic properties of CZTS. X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) is a powerful tool for this purpose. Interpreting XANES of complex materials is nontrivial and thus requires theoretical modeling. Here, all her calculations are performed using an all-electron full-potential augmented plane-wave method as implemented in the exciting code. The accurate description of the core level excitations was performed by a two-step procedure. First, the electronic structure was calculated by solving the Kohn-Sham (KS) equation of density functional theory (DFT). The absorption spectra including elecron-hole (e-h) was described by the solution of the Bethe-Salpeter equation (BSE) of many-body perturbation theory (MBPT) using the KS states as starting point.
The discrepancies between the calculated and measured spectra in CZTS however, remained an open question. For this purpose, she demonstrated the influence of defect complexes on the excited state properties of CZTS. First, the core level shifts upon the defect formation is understood as they are sensitive to chemical environment. The spectral signatures are obtained for the selected inequivalent sulfur sites. A detailed analysis of the impact of the local chemical environment is performed. From the insight gained from this analysis, the nature of the defects dominating the measured spectra are determined.
IRIS Adlershof supported this research with a fellowship, so Archana could focus on finalizing the project and getting the results ready for publication.
She sucessfully defended her thesis on June 3rd, 2022. Congratulation!
01.06.2022The chemist Prof. Robert Schlögl to be new president of the Humboldt Foundation
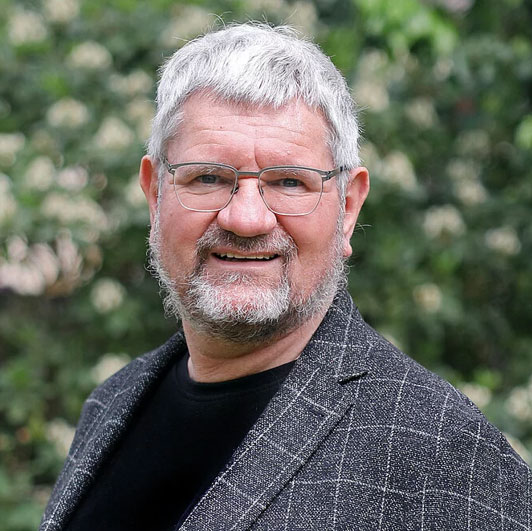 Robert Schlögl, Director at the Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society, and Honorary professor at the Chemistry department of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin will take office on 1 January 2023.
Robert Schlögl, Director at the Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society, and Honorary professor at the Chemistry department of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin will take office on 1 January 2023.
Born in 1954, Robert Schlögl is an internationally recognised and well-connected scientist. His research focus is energy conversion processes and catalysts. As an expert for energy systems of the future and the complex challenges arising in connection with transitioning the current energy system to renewable forms of energy, he also has a wealth of experience in the area of political consulting and science communication. As part of a joint catalysis research laboratory operated by the Helmholtz Center for Materials and Energy Berlin (HZB) and the two Max Planck Institutes FHI and CEC, a large working group led by Prof. Schlögl and Professors Reuter and Roldán is cooperating closely with IRIS Adlershof, thus benefiting from the up-to-date-infrastructure of the new IRIS research building.
We wish Mr. Schlögl every success in his new position and look forward to continued good cooperation.
more…
30.05.2022Nakib Protik awarded with a Humboldt Research Fellowship
 Dr. Nakib Protik has been awarded an Alexander von Humboldt Research Fellowship for Postdocs. He received his PhD in physics from Boston College (USA) in 2019 and then did research at Harvard University (USA) and at the Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (Spain).
Dr. Nakib Protik has been awarded an Alexander von Humboldt Research Fellowship for Postdocs. He received his PhD in physics from Boston College (USA) in 2019 and then did research at Harvard University (USA) and at the Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (Spain).
As a research fellow of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Dr. Protik will now be working in the group of Prof. Claudia Draxl, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, on improving the parameter-free description of the interactions of charge and heat carriers with neutral, charged, and magnetic impurities in quantum materials. This work will connect to a broad range of applications spanning heat harvesting to spintronics.
We congratulate Dr. Protik on successfully acquiring the research grant and wish him every success in his work. Welcome at IRIS Adlershof, Nakib!
18.05.2022Opening of the AdMaLab at IRIS Adlershof
Last Thursday, 12 May 2022, representatives of INAM e.V. and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin welcomed numerous guests from business, politics, research and teaching to the opening event of the incubator programme "AdMaLab - The Berlin Materials and Hardware Lab" in the research building of IRIS Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität.

As part of the "Berlin Startup Stipendim" funding programme, the Berlin Senate Department for Economics, Energy and Public Enterprises has provided INAM e.V. and its cooperation partners with around 1.1 million euros to set up an incubator programme tailored to material science start-ups.
>At the festive opening event, the AdMaLab team led by Oliver Hasse, Managing Director of the Innovation Network for Advanced Materials (INAM) e.V., and Prof. Dr. Emil List-Kratochvil, Deputy Director of IRIS Adlershof and Head of the Hybrid Devices Research Group, were able to welcome Michael Biel, Berlin's State Secretary for Economics, Prof. Dr. Christoph Schneider, Vice President for Research at the Universität zu Berlin, representatives of the first participating start-ups and numerous international guests from business, research, education and politics in the IRIS Adlershof research building.
The statements by the dignitaries are available in German.09.05.2022New production method for flexible, durable anodes with high capacity-to-weight
 A team of researchers from Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, the Leibniz-Institut für Polymerforschung Dresden (IPF) e. V., and the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have made an anode with superior performance for portable battery applications, close to limits of theoretical capacity. Uniquely, the obtained anodes are flexible without surface reconstruction or crack formation, and they survive heat shocks without performance-loss.
A team of researchers from Humboldt Universität zu Berlin, the Leibniz-Institut für Polymerforschung Dresden (IPF) e. V., and the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) have made an anode with superior performance for portable battery applications, close to limits of theoretical capacity. Uniquely, the obtained anodes are flexible without surface reconstruction or crack formation, and they survive heat shocks without performance-loss.
27.04.2022FAIR research data in materials sciences
 |
| How the FAIRmat consortium works (Copyright: FAIRmat) |
The lifestyle of our society is largely determined by the achievements of condensed matter physics, chemistry and material sciences. Touch screens, batteries, electronics or implants: Many new products in the fields of energy, environment, health, mobility and information technology are largely based on improved or even novel materials. These fields generate enormous amounts of data every day, which is a new raw material - and is therefore a gold mine in itself. However, a prerequisite for this is that these data are comprehensively characterized and made available to science.
06.04.2022WISTA visiting IRIS Adlershof
On Tuesday, April 5, 2022, the management and the supervisory board of our site partner WISTA Management GmbH visited the new research building of IRIS Adlershof. After a brief introduction by IRIS director Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe, there was a guided tour through some of the laboratories in the research building. The guests were allowed to lend a hand themselves at the glove box cluster of the network laboratory and they were able to see individual atoms at the NION-TEM. In particular, the State Secretary (StS) for Science, Ms. Armaghan Naghipour, and the State Secretary for Economic Affairs, Mr. Michael Biel, showed great interest in our research.
 |
||||
| IRIS Director Jürgen P. Rabe, IRIS Managing Director Nikolai Puhlmann and Dean Prof. Caren Tischendorf discuss current issues with WISTA Managing Director Roland Sillmann and the WISTA Supervisory Board members in the network laboratory of the research building. |
||||
 |
 |
 |
||
| Dr. Ligorio provides insights into current science at the large glass window in the foyer of the IRIS research building. | StS Armaghan Naghipour advances research at the glove box. | StS Michael Biel, StS Armaghan Naghipour, and WISTA Managing Director Roland Sillmann (from left to right) are shown individual atoms. | ||
28.03.2022Michael J. Bojdys: "Ukraine: how can the scientific community help scholars at risk?"

In the first 19 days following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine on February 24, 2022, 6,300 Ukrainian scientists moved abroad. Michael J. Bojdys, member of IRIS Adlershof, has been a member of the Advisory Board of the "Young Scientists" at the World Economic Forum (WEE) since 2018. In the WEE agenda he and his colleagues have summarized the experiences of the Young Scientists at the WEF as "academic ambassadors" and offer pathways for leveraging the international science community and inspire action ( #StandWithScholarsAtRisk ). They have identified four key areas where collaborative action can offer support to Ukraine scientist:
- Fund opportunities for research networks,
- Hire academics at risk,
- Hire technical staff and workers at risk,
- Engage directly with authorities.
04.03.2022Bremsstrahlung of black holes and neutron stars from quantum field theory

Fig 1: Visualization of the gravitational Bremsstrahlung from the scattering of two black holes (BSc thesis O. Babayemi)
When two massive objects (black holes, neutron stars, or stars) fly past each other, the gravitational interactions not only deflect their orbits, but also produce gravitational radiation, or gravitational bremsstrahlung, analogous to electromagnetism. The resulting gravitational waves of such a scattering event were calculated at leading order in Newton's gravitational constant in the 1970s using traditional methods of general relativity in an extensive series of four papers. Bremsstrahlung events are still out of reach for the current generation of gravitational-wave detectors because the signal is non-periodic and typically less intense. Nevertheless, they are interesting targets for future searches with future terrestrial and space-based observatories.
In the Quantum Field Theory lab around IRIS Adlerhof-member Prof. Plefka, a new approach to determining these waveforms (Fig. 1) and the deflections using methods of perturbative quantum field theory was recently developed, which proves to be significantly more efficient than the traditional approaches. It is based on a hybrid quantum field theory, in which the black holes (or stars) are idealized as point particles and interact with the gravitational field. The calculation is then based on a systematic diagrammatic expansion using Feynman graphs. I.e. the methods that were originally developed for the scattering of elementary particles can now also be used in astrophysical scenarios.
With this innovative method - the "Worldline Quantum Field Theory“ approach - our understanding of this fundamental physical process was recently significantly extended resulting in a series of three publications in the Physical Review Letters. In [1], the results from the 1970s were reproduced in a far more efficient way; this only required the calculation of three Feynman graphs (Fig. 2). In [2] the waveform could be extended to the case of rotating black holes and neutron stars. In a recent publication [3], the scattering angles and deflections in momenta and rotations due to the scattering process at the next-next-leading order of the gravitational constant were determined for the first time. Elaborated techniques for calculating Feynman integrals were used here. Interestingly, the rotational degrees of freedom of the black holes are described in this new formulation with a supersymmetric world line theory [4], which was originally developed in extensions of the Standard Model of particle physics.
This research was performed in the context of the DFG Research Training Group 2575 "Rethinking Quantum Field Theory“, where innovations in quantum field theory are developed in cooperation with the Max-Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics and the Helmholtz-Centre DESY.
Publikations:
| [1] | Classical Gravitational Bremsstrahlung from a Worldline Quantum Field Theory G. U. Jakobsen, G. Mogull, J. Plefka, and J. Steinhoff Phys. Rev. Lett. 126 (2021) 201103 arxiv: 2101.12688 OPEN  ACCESS ACCESS |
[3] | Conservative and radiative dynamics of spinning bodies at third post-Minkowskian order using worldline quantum field theory G. U. Jakobsen and G. Mogull erscheint in PRL arxiv: 2201.07778 OPEN  ACCESS ACCESS |
|
| [2] | Gravitational Bremsstrahlung and Hidden Supersymmetry of Spinning Bodies G. U. Jakobsen, G. Mogull, J. Plefka, and J. Steinhoff Phys. Rev. Lett. 128 (2022) 011101 arxiv: 2106.10256 OPEN  ACCESS ACCESS |
[4] | SUSY in the sky with gravitons G. U. Jakobsen, G. Mogull, J. Plefka, and J. Steinhoff JHEP 2201 (2022) 027 arxiv: 2109.04465 OPEN  ACCESS ACCESS |
Further Informationen:
Videos on Youtube (from BSc thesis of O. Babayemi)
Prof. Dr. Jan Plefka
Spokesperson RTG2575 „Rethinking Quantum Field Theory“
Dept. of Physics & IRIS Adlershof, Group Quantumfield- and Stringtheory
Email: jan.plefkahu-berlin.de
Tel: +49 (0)30 2093 66409
Secr.: +49 (0)30 2093 66413
http://qft.physik.hu-berlin.de
https://www2.hu-berlin.de/rtg2575/
17.02.2022Incubation Programme for innovators in ADVANCED MATERIALS

We will be considering applications for programmes starting on
- 1 April 2022 (application deadline: 28 February 2022) and
- 1 June 2022 (application deadline: 30 April 2022)
15.02.2022Julia von Blumenthal zur nächsten Präsidentin der HU gewählt
Prof. Dr.  Julia von Blumenthal ist am 15.2.2022 vom Konzil der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) mit 44 Ja-Stimmen bei 12 Nein-Stimmen und 2 ungültigen Stimmen zur neuen Präsidentin der HU gewählt worden. Sie hat die Wahl angenommen. "Ich danke dem Konzil und dem Kuratorium der Humboldt-Universität für das in mich gesetzte Vertrauen. Ich freue mich darauf, diese verantwortungsvolle Aufgabe zu übernehmen. Als Universität ist es unsere Aufgabe, Studierenden das Wissen und die Fähigkeiten zu vermitteln, die sie brauchen, um die Gesellschaft der Zukunft mitzugestalten. Mit exzellenter Forschung tragen wir dazu bei, die Herausforderungen von heute und die Fragen von morgen zu beantworten.", so von Blumenthal.
Julia von Blumenthal ist am 15.2.2022 vom Konzil der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) mit 44 Ja-Stimmen bei 12 Nein-Stimmen und 2 ungültigen Stimmen zur neuen Präsidentin der HU gewählt worden. Sie hat die Wahl angenommen. "Ich danke dem Konzil und dem Kuratorium der Humboldt-Universität für das in mich gesetzte Vertrauen. Ich freue mich darauf, diese verantwortungsvolle Aufgabe zu übernehmen. Als Universität ist es unsere Aufgabe, Studierenden das Wissen und die Fähigkeiten zu vermitteln, die sie brauchen, um die Gesellschaft der Zukunft mitzugestalten. Mit exzellenter Forschung tragen wir dazu bei, die Herausforderungen von heute und die Fragen von morgen zu beantworten.", so von Blumenthal.
Seit Oktober 2018 ist Julia von Blumenthal Präsidentin der Europa-Universität Viadrina Frankfurt (Oder). Zuvor war sie Dekanin der Kultur-, Sozial- und Bildungswissenschaftlichen Fakultät der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin und hat seit 2009 eine Professur am Institut für Sozialwissenschaften im Lehrbereich Innenpolitik der Bundesrepublik Deutschland der Humboldt-Universität Berlin (derzeit beurlaubt).
Vorraussichtlich zu Beginn des Wintersemesters 2022/23 wird sie Interims-Präsident Peter Frensch ablösen.
08.02.2022Many workshops for doctoral candidates by Berlin University Alliance and the Humboldt Graduate School
In the next months many workshop for interested doctoral candidates are offered. Please register in time!
 Berlin University Alliance Events:
Berlin University Alliance Events:Career Day 2022 - Berlin University Alliance
You are still considering what job is a match for you and don’t know where to start looking? Save the date for our virtual “Career Day 2022 for Doctoral Candidates – New Horizons" offered by the Berlin University Alliance! This event will introduce young scientists to a variety of career tracks inside and outside academia to give support in making informed and suitable career decisions.
Several World Cafés will provide an interactive space for exchanging experiences, sharing knowledge and networking with professionals from various fields. During Round Tables you can join our special discussions on pursuing a career in academia or how the transition to the wider job market can succeed. In January 2022 you will find further information and the complete programon our website.
Datum: 22.02.2022
Target Group: Doctoral Candidates in all years
Format: Online
Language: English
Participation is free of charge
-------------------------------------------------------
Erfolgreich in die Promotion – Berlin University Alliance Online-Retreat
Offen für alle Promovierenden der Berlin University Alliance
Für alle, die in Berlin mit der Promotion beginnen, bietet die Berlin University Alliance einen zweitägigen Retreat an. Dieser Retreat wird im April 2022 noch einmal Online stattfinden. Du wirst während des Retreats in kleinen Workshops Techniken lernen, die Dir helfen, gut vorbereitet in Deine Promotion zu starten und kannst Dich mit anderen Promovierenden der HU, FU, TU und Charité austauschen und vernetzen. Vielleicht lernst Du hier sogar Personen kennen, die Dich bis zum Abschluss Deiner Promotion begleiten? Der Graduate Studies Support der Berlin University Alliance freut sich auf Deine Teilnahme!
Datum: 05./06.04.2022
Zielgruppe: Promovierende aller Fachrichtungen in den ersten sechs Monaten ihrer Promotion
Format: Online über Konferenz-Tool Lounjee und in Gathertown
Sprache: Deutsch
Die Teilnahme ist kostenfrei (inkl. Verpflegung und Unterbringung)
-------------------------------------------------------
Kick Off your Doctorate – Berlin University Alliance Online-Retreat
Open to all Doctoral Candidates within the Berlin University Alliance
For all those starting their doctorate in Berlin, the Berlin University Alliance offers a two-day retreat. In April 2022, this retreat will be held again online. During the retreat, you are going to learn techniques that will help you to kick off your doctorate and you can meet and network with other doctoral candidates from HU, FU, TU and Charité. Maybe you will even get to know people who will accompany you until the completion of your doctorate? The Graduate Studies Support of the Berlin University Alliance is looking forward to your participation!
Datum: 07./08.04.2022
Target Group: Doctoral candidates in all disciplines in the first six months of their doctorate
Format: Online via conference tool Lounjee and in Gathertown
Language: English
Participation is free of charge (incl. food and lodging)
 Humboldt Graduate School Workshops:
Humboldt Graduate School Workshops:Planning the Completion of your Dissertation
Open to all Doctoral Candidates within the Berlin University Alliance
Trainer: Mr. Mark Edwards
Date: 07. + 09.03.2022; 09:00–12:00
Target Group: Candidates in last year of doctorate
Language: English
Participation is free of charge.
-------------------------------------------------------
Scientific Writing & Publishing (Life Sciences & Natural Sciences)
Open to all Doctoral Candidates within the Berlin University Alliance
Trainer: Dr. Martina Michalikova
Date: 11.03.; 18.03.; 25.03.; 01.04.2022; 09:00–13:00
Target Group: Candidates from Life Sciences & Natural Sciences in all years of doctorate
Language: English
Participation is free of charge.
-------------------------------------------------------
Disputationstraining
Offen für alle Promovierenden der Humboldt-Universität
Trainer: Dr. Nele Rother
Date: 31.03.2022 und 01.04.2022; 09:00-16:00
Target Group: Promovierende in der Abschlussphase (alle Fachrichtungen)
Language: Deutsch
Die Teilnahme ist kostenfrei.
-------------------------------------------------------
Presenting Science Online
Open to Doctoral Candidates from Member Programs, Associated Programs and Cooperations
The workshop can then be attended by others, if it is not fully booked 14 days before beginning.
Trainer: Ms. Millie Baker
Date: 23.–25.02.2022; 10:00–15:00
Target Group: Candidates in the 1st and 2nd year of doctorate
Language: English
The workshop can then be attended, if it is not fully booked 14 days before beginning.
-------------------------------------------------------
Grant Application Writing
Open to Doctoral Candidates from Member Programs, Associated Programs and Cooperations
The workshop can then be attended by others, if it is not fully booked 14 days before beginning.
Trainer: Dr. Sabine Preusse
Date: 28.03.; 29.03.; 04.04.; 05.04.2022; 09:00–12:30
Target Group: Candidates in 2nd and 3rd year of doctorate
Language: English
02.02.2022Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin appoints Eva Unger to professorship
 IRIS Adlershof-member Eva Unger was now appointed as W2 professor at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Prof. Dr. Eva Unger leads a research group at HZB. She develops scalable technologies for the production of perovskite semiconductors for low-cost and highly efficient solar cells.
IRIS Adlershof-member Eva Unger was now appointed as W2 professor at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Prof. Dr. Eva Unger leads a research group at HZB. She develops scalable technologies for the production of perovskite semiconductors for low-cost and highly efficient solar cells.
Prof. Dr Eva Unger works since 2016 as a scientist at HZB, with affiliation at Lund University in Sweden. After building up her research team as part of a BMBF-funded junior research group, she is now head of the department "Solution Processing for Hybrid Materials and Devices" at HZB. The Unger team is developing manufacturing processes to deposit semiconductor layers of perovskite on larger surfaces. They are working on functional inks for the deposition of perovskite semiconductors and are very active in the analysis of film growth processes and the combinatorial synthesis methods. In addition to large-area perovskite solar cell prototypes, Unger's team is working with other research groups at Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin on large-area tandem solar modules that combine perovskite with silicon layers. Eva Unger is also involved in Open Science and Open Data projects and is building a database for perovskite solar cells together with many international partners.
Eva Unger was appointed to a W2 S professorship at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin at the end of January, made possible by the Helmholtz Association's funding programme for the initial appointment of excellent female scientists. In the summer semester, she will offer a specialisation course on "The Chemistry of Solar cells".
IRIS Adlershof cordially congratulates Professor Eva Unger and anticipates with pleasure a further fruitful cooperation.
18.01.2022Professor Jürgen P. Rabe re-elected as director of IRIS Adlershof
 The IRIS General Assembly re-elected Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe as the director of IRIS Adlershof and Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil as well as Prof. Norbert Koch as his deputies for the third IRIS funding phase (Nov. 01, 2020 - Oct. 31, 2024). Prof. Claudia Draxl, Prof. Stefan Hecht and Prof. Matthias Staudacher have been elected as members of the IRIS Council. All elections were unanimous. After Dr. Julian Miczajka has moved to the Max Planck Institute for Physics, Dr. Sven Ramelow temporarily takes on the tasks of the junior representative in the IRIS Council.
The IRIS General Assembly re-elected Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe as the director of IRIS Adlershof and Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil as well as Prof. Norbert Koch as his deputies for the third IRIS funding phase (Nov. 01, 2020 - Oct. 31, 2024). Prof. Claudia Draxl, Prof. Stefan Hecht and Prof. Matthias Staudacher have been elected as members of the IRIS Council. All elections were unanimous. After Dr. Julian Miczajka has moved to the Max Planck Institute for Physics, Dr. Sven Ramelow temporarily takes on the tasks of the junior representative in the IRIS Council.IRIS Adlershof congratulates all council members on their election and wishes them every success in their responsible tasks.
22.12.2021Printing an electronic rainbow – Combination of colour printing and chemical tunability enables printed spectrometer
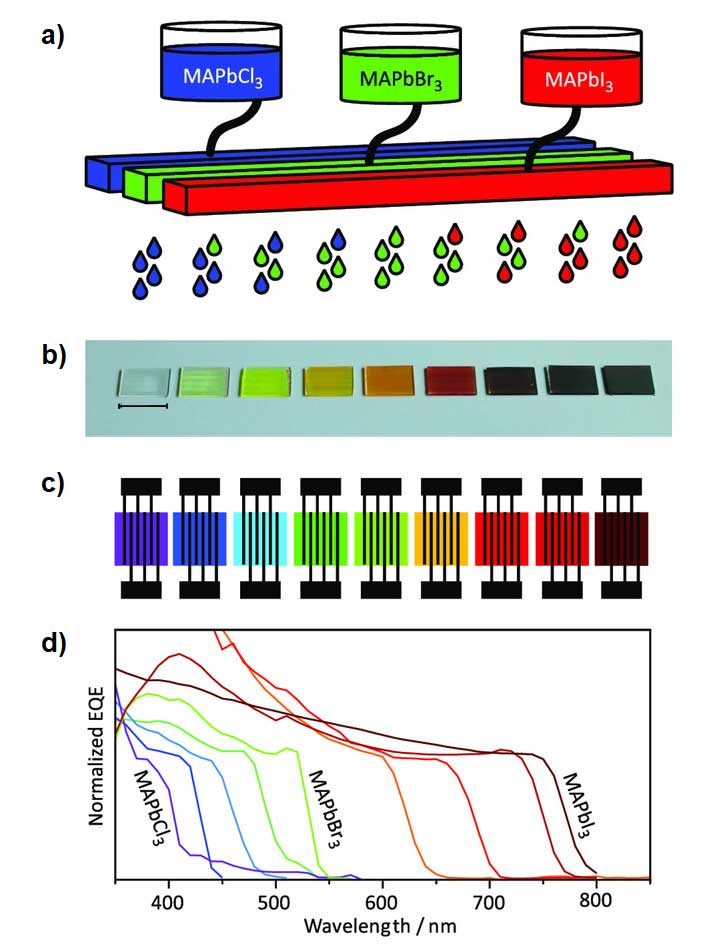
Researchers from Innovation Lab HySPRINT at Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) have used an advanced inkjet printing technique to produce a large range of photodetector devices based on a hybrid perovskite semiconductor. By mixing of only three inks, the researchers were able to precisely tune the semiconductor properties during the printing process. Inkjet printing is already an established fabrication method in industry, allowing fast and cheap solution processing. Extending the inkjet capabilities from large area coating towards combinatorial material synthesis opens the door for new possibilities for the fabrication of different kind of electronic components in a single printing step.
Wonder material metal halide perovskites
Metal halide perovskites are fascinating to researchers in academia and industry with the large range of possible applications. The fabrication of electronic components with this material is particularly appealing, because it is possible from solution, i.e. from an ink. Commercially available salts are dissolved in a solvent and then deposited on a substrate. The group around Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil, member of IRIS Adlershof and head of a joint research group at HZB and HU, focusses on building these types of devices using advanced fabrication methods such as inkjet printing. Researcher at HZB have already used inkjet printing to fabricate solar cells and LEDs made from perovskites. The inkjet capabilities were further expanded in 2020, when the group of Dr. Eva Unger first used a combinatorial approach to inkjet printing, to print different perovskite compositions in search of a better solar cell material.
Now, in this current work, the team around Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil found an exciting application for a large perovskite series within wavelength-selective photodetector devices. “Combinatorial inkjet printing cannot only be used to screen different compositions of materials for solar cell materials,” he explains, “but also enables us to fabricate multiple, separate devices in a single printing step.” Looking towards an industrial process, this would enable large scale production of multiple electronic devices. Combined with printed electronic circuits, the photodetectors would form a simple spectrometer: paper thin, printed on any surface, potentially flexible, without the need of a prism or grid to separate the incoming wavelengths.
Emil List-Kratochvil is Professor of Hybrid Devices at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, member of IRIS Adlershof and head of a Joint Lab founded in 2018 that is operated by HU together with HZB. In addition, a team jointly headed by List-Kratochvil and HZB scientist Dr. Eva Unger is working in the Helmholtz Innovation Lab HySPRINT at HZB on the development of coating and printing processes for hybrid perovskites. For a few days she is also a member of IRIS Adlershof.
Using Combinatorial Inkjet Printing for Synthesis and Deposition of Metal Halide Perovskites in Wavelength‐Selective PhotodetectorsV.R.F. Schröder, F. Hermerschmidt, S. Helper, C. Rehermann, G. Ligorio, H. Näsström, E.L. Unger, and E.J.W. List-Kratochvil
Adv. Eng. Mater. (2021) 2101111 OPEN
 ACCESS
ACCESSDOI: 10.1002/adem.202101111
more...
15.12.2021Prof. Ulf Leser becomes IRIS member
 We are delighted to welcome Prof. Dr. Ulf Leser as a member of IRIS Adlershof.
We are delighted to welcome Prof. Dr. Ulf Leser as a member of IRIS Adlershof.
He is a full professor at the Institute for Computer Science at Humboldt-Universiät zu Berlin. His main research interests are biomedical data management and text mining, infrastructures for large-scale scientific data analysis, and statistical Bioinformatics, with a focus on cancer research.
He is speaker of the Collaborative Research Center "Foundations of Workflows for Large-Scale Scientific Data Analysis (FONDA)" and of the collaborative research project "Comprehensive Data Integration for Precision Oncology (PREDICT)". From 2014-2019, he was speaker of the Research Training Group "Service-oriented Architectures for Health Care Systems (SOAMED)". Furthermore, he currently is principal investigator in the interdisciplinary graduate schools "Berlin School of Integrative Oncology (BSIO)" and "Computational Methods for Precision Oncology (CompCancer)", in the "Heibrids graduate school an Data Science", the research unit "Beyond the Exome", and the Einstein Center for Digital Future Berlin (ECDF).
IRIS Adlershof is looking forward to a good and fruitful collaboration.
10.12.2021Kultusministerkonferenz und DZLM vereinbaren Zehnjahres-Programm für den Mathematikunterricht
Die Kultusministerkonferenz verabschiedete am 9. Dezember 2021 einstimmig das umfassende Zehnjahres-Programm „QuaMath - Unterrichts- und Fortbildungs-Qualität in Mathematik entwickeln“ zur Stärkung der mathematischen Bildung in Deutschland. Sie reagiert auf das Problem, dass nur knapp die Hälfte aller Jugendlichen die mathematischen Kompetenzen erreicht, die die Kultusministerkonferenz (KMK) in ihren Regelstandards festgelegt hat und fördert damit eine wegweisende Weiterentwicklung des Mathematikunterrichts.
IRIS Adlershof-Mitglied Professor Dr. Jürg Kramer, Abteilungsdirektor am IPN, und ehemaliger Leiter des DZLM, sieht in dem QuaMath-Programm einen bildungspolitischen Meilenstein: „Die Herausforderungen im Mathematikunterricht wurden identifiziert und auch wissenschaftlich nachgewiesen. Die Bündelung vorhandener Ressourcen mit erheblichen zusätzlichen Mitteln durch die Kultusministerkonferenz zeigt, dass sie die Probleme aktiv angeht. In enger Kooperation der Mathematik-Verantwortlichen der Länder mit der Fortbildungsforschung und -praxis konnte das Programm nun über Ländergrenzen hinweg etabliert werden. Denn nur in Zusammenarbeit kann erkannt werden, was wirklich gebraucht wird.“
Das QuaMath-Programm wird vom Deutschen Zentrum für Lehrerbildung Mathematik (DZLM) am Leibniz-Institut für die Pädagogik der Naturwissenschaften und Mathematik (IPN) forschungsbasiert entwickelt und gemeinsam mit den Ländern umgesetzt. Vor allem mit Anregungen zur Unterrichtsentwicklung, fachdidaktisch fundierten Fortbildungsmaßnahmen und durch die Vernetzung aller Beteiligten soll das Programm mehr als 10.000 Schulen erreichen.
Für das QuaMath-Programm erhält das DZLM ab 2023 eine Fördersumme in Höhe von 17,6 Mio. Euro für die ersten 5,5 Jahre. Die Länder investieren zudem jährlich weitere 5,5 Mio. Euro für Länderkoordination sowie Multiplikatorinnen und Multiplikatoren. mehr...
IRIS Adlershof gratuliert ganz herzlich zu diesem wunderbaren Erfolg!
08.12.2021IRIS Adlershof is strengthened by three new members
The IRIS Council (IRIS-Rat) decided to offer other scientists full membership in IRIS Adlershof. We are very pleased that our offer has been accepted and we can introduce you to:

Dr. Eva Unger is head of the new department Solution processes for hybrid materials and components at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin and has been working closely with IRIS Adlershof for some time as part of the Joint Lab GenFab. In particular, she is interested in scalable deposition methods of high value semiconductors such as metal halide perovskites and a deeper understanding of layer formation. Eva Unger has recently received call for a professorship at the Department of Chemistry at HU.
Theoretical physicist and materials scientist Professor Matthias Scheffler, head of the NOMAD Laboratory at the Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society and honorary professor at the Department of Physics at the HU, conducts research on fundamental aspects of the chemical and physical properties of surfaces as well as on methodological developments in artificial intelligence to solve fundamental problems in materials science. Since 2020, he leads the European Center of Excellence NOMAD and is Co-speaker of the NFDI consortium FAIRmat.
The physicist Julia Stähler is a professor at the Department of Chemistry of HU with a research focus on ultrafast spectroscopy on nanostructured materials, in particular also on inorganic/organic hybrid systems. She is a subproject leader in the Collaborative Research Center 951 “Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)”, one of the lighthouse projects of IRIS Adlershof.
There are also two more, but not entirely new members: Two previous junior members, Prof. Dr. Michael J. Bojdys and Dr. Valentina Forini, have received full membership, which means that IRIS Adlershof now has 27 full members.
IRIS Adlershof warmly congratulates its new members and is looking forward to a fruitful cooperation.
07.12.2021IRIS Adlershof was able to win three new junior members
IRIS Adlershof is delighted to announce that three promising young scientists, namely Dr. Oliver Dumele, Dr. Nichol Furey, and Dr. Sebastian Heeg, will be joining as junior members.

Oliver Dumele is head of a Liebig junior research group at the Department of Chemistry at HU. He is an organic synthetic chemist with expertise in supramolecular chemistry and self-assembly systems. He believes that 2D layered structures are fascinating supramolecular platforms.
Nichol Furey is a 'Freigeist' fellow of the Volkswagen Foundation at the Institute for Physics at HU and at the IRIS Adlershof. She researches the algebraic structure of elementary particle physics as well as octonions and the standard model of particle physics.
Sebastian Heeg heads an Emmy Noether junior research group at the Institute for Physics at HU. He is interested in the investigation of low-dimensional solid-state systems, for example graphenes and nanotubes, with optical spectroscopy.
IRIS Adlershof warmly congratulates its new junior members and is looking forward to a good and fruitful collaboration.
06.12.2021IRIS Adlershof will be extended until 2024
 The Board of Trustees (Kuratorium) of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has decided to extend IRIS Adlershof until October 31, 2024. It follows a corresponding proposal by the Academic Senate of the HU, which is based on the successful evaluation of IRIS Adlershof by an external commission of experts.
The Board of Trustees (Kuratorium) of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has decided to extend IRIS Adlershof until October 31, 2024. It follows a corresponding proposal by the Academic Senate of the HU, which is based on the successful evaluation of IRIS Adlershof by an external commission of experts.
We are very pleased to continue the previous successful interdisciplinary scientific research!
03.12.2021IRIS Adlershof and INAM support start-ups in material sciences with the incubator "AdMaLab – The Berlin Hardware and Materials Lab"
 The State of Berlin is providing the Innovation Network for Advanced Materials (INAM e.V.) and its cooperation partners, such as IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, around 1.1 million EUR to set up an incubator programme specifically tailored to material science start-ups. In addition to accompanied access to the high-quality equipped and newly opened research building of IRIS Adlershof and the Innovation Lab HySPRINT at Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, scholarships will be provided to enable the founders to dedicate themselves to the development of their business ideas and products.
The State of Berlin is providing the Innovation Network for Advanced Materials (INAM e.V.) and its cooperation partners, such as IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, around 1.1 million EUR to set up an incubator programme specifically tailored to material science start-ups. In addition to accompanied access to the high-quality equipped and newly opened research building of IRIS Adlershof and the Innovation Lab HySPRINT at Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, scholarships will be provided to enable the founders to dedicate themselves to the development of their business ideas and products.
Starting Friday, 3 December 2021, 12:00 noon, founders with a focus on new materials can apply for a place in the incubator programme. More information on the application process is provided at www.inam.berlin/admalab. In addition to the innovative activities in the lab, the selected startups receive an intensive mentoring and training programme which is supported by Humboldt Innovation GmbH and experts from various specialist areas. On 15 December 2021 at 10 a.m., the project partners will provide more detailed information about the incubator programme in a webinar. Interested parties can register here.
With the Berlin Startup Stipendium, which provides the grant, the State of Berlin has launched a funding programme to turn innovative ideas into products for those willing to start a business. With the funding from the European Social Fund and the State of Berlin, scholarship holders can advance their business ideas in various subject areas. Over 120 innovative startup projects have already been supported. This success can now be expanded further with the AdMaLab into the field of materials science.
23.11.2021Scholarships for the Transition from Master's to Doctorate
As part of the Excellence Strategy, the Humboldt-Universität once again awards Humboldt Research Track Scholarships.
The six-months scholarship aims at outstanding Master's students as well as graduates who plan to pursue a doctorate and helps recipients to prepare for their doctoral thesis. It provides a funding of 800 EUR per month. To enable more prospective doctoral candidates with disabilities or chronic illnesses to prepare for a doctorate, applications from this target group will be given particular consideration.
The current application period runs until 15 January 2022 for funding starting 1 April 2022.
more...
19.10.2021Stefan Hecht elected as a Fellow of the European Academy of Sciences
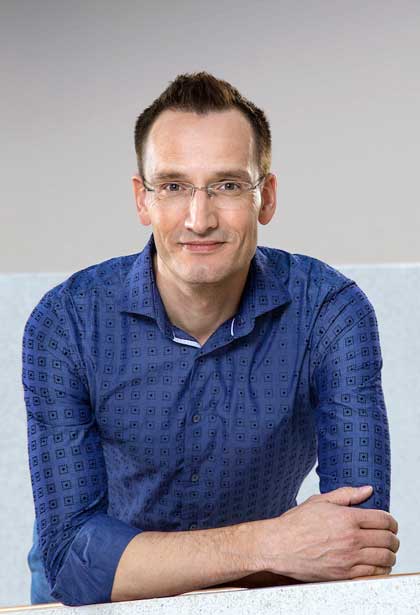 The European Academy of Sciences (EURASC) has elected Prof. Stefan Hecht, Ph.D., Director of the DWI - Leibniz-Institute for Interactive Materials, Guestprofessor at the Department of Chemistry of HU Berlin and founding member of IRIS Adlershof, as a Fellow.
The European Academy of Sciences (EURASC) has elected Prof. Stefan Hecht, Ph.D., Director of the DWI - Leibniz-Institute for Interactive Materials, Guestprofessor at the Department of Chemistry of HU Berlin and founding member of IRIS Adlershof, as a Fellow.
 The EURASC is dedicated to scientific excellence as well as cutting-edge basic research and interdisciplinary collaboration, which is the basis for all scientific and technological innovation. It is a non-profit and independent association of the most renowned European scientists engaged in cutting-edge research and the development of advanced technologies with more than 770 members in various disciplines, among them Nobel laureates.
The EURASC is dedicated to scientific excellence as well as cutting-edge basic research and interdisciplinary collaboration, which is the basis for all scientific and technological innovation. It is a non-profit and independent association of the most renowned European scientists engaged in cutting-edge research and the development of advanced technologies with more than 770 members in various disciplines, among them Nobel laureates.
"It is a very special honor to be part of this illustrious circle. The election reaffirms both the recognition of our research and its socio-economic benefits," explains Stefan Hecht. In particular, his recent results and successes in the field of 3D printing, more specifically the development of xolography, reflect this achievement. The process is based on the light-induced curing of a transparent high-viscosity resin mixture. However, the curing only occurs at points where two different colors thus wavelengths of light cross. The crossing (X) light rays thereby produce the entire (holos) object in a print (graphy), hence the name "xolography".
IRIS Adlershof is very pleased about this special award and warmly congratulates its member.
more...
15.10.2021Sparking electroluminescence in poly(triazine imide) films
 A team of researchers from King’s College London, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, and Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), headed by Prof. Michael J. Bojdys, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, has investigated the synthesis, structure, optical properties of poly(triazine imide), a member of the family of graphitic carbon nitrides. Their progress on material quality and processing allowed for construction of the first single layer, organic light emitting device (OLED) with a solution-processed graphitic organic material as a metal-free emission layer.
A team of researchers from King’s College London, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg, and Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), headed by Prof. Michael J. Bojdys, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, has investigated the synthesis, structure, optical properties of poly(triazine imide), a member of the family of graphitic carbon nitrides. Their progress on material quality and processing allowed for construction of the first single layer, organic light emitting device (OLED) with a solution-processed graphitic organic material as a metal-free emission layer.
Organic semiconductors have sparked great interest in academic and industrial circles over the last decades, because of their advantageous properties such as (i) a high absorption coefficient compared to conventionally used silicon as well as (ii) less energy intensive production, and (iii) composition from earth-abundant elements. Progress in this field of research promises new, cost- and energy-efficient technologies in consumer electronics, smart packaging, and flexible light-emitters.
Hitherto explored organic semiconductors often suffer from degradation processes and defects especially when electrochemically altered (“doped”), due to dopant drift and migration or due to oxidation when exposed to atmospheric conditions. The unique properties of poly(triazine imide) enable the research to address the issues that plague conventional organic semiconductors. Poly(triazine imide) is a very stable under heat and air. Furthermore, the graphitic morphology of poly(triazine imide) allows exfoliation of the material into thin, solution-processable layers, while at the same time reducing migration and drift of chemically bonded dopants.
“With the improved material quality, we are now able to dive deeper into the more delicate features of this material, such as the electronic structure and vibration modes. This will greatly improve our understanding of this material, as well as related materials, and help us improving OLED performance and think about future, high-value applications of poly(triazine imide).”, says David Burmeister, PhD student at bojdysLAB.
This work was published in:
“Optimized synthesis of solution-processable crystalline poly(triazine imide) with minimized defects for OLED application” Burmeister, D.; Tran, H. A.; Müller, J.; Guerrini, M.; Cocchi, C.; Plaickner J.; Kochovski, Z.: List-Kratochvil, E.; Bojdys,* M. J. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202111749
10.10.2021Successful project start of the NFDI consortium FAIRmat
 One week old now, the NFDI consortium FAIRmat, led by HU professor Claudia Draxl, who is a member of IRIS-Adlershof. She looks back on the project start with satisfaction:
One week old now, the NFDI consortium FAIRmat, led by HU professor Claudia Draxl, who is a member of IRIS-Adlershof. She looks back on the project start with satisfaction:
08.07.2021 Prof. Jan Plefka elected to the Senate of the DFG
 The General Assembly of the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG) elected on the 7th of July four new members to the Senate of the largest research funding organization and central self-governing body of science in Germany at its meeting during the virtual DFG Annual Meeting today. Five Senate members were elected for a further term of office. The Senate is the central scientific body that discusses and decides on all DFG matters of major importance, unless they are reserved for the Joint Committee.
The General Assembly of the German Research Foundation (Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, DFG) elected on the 7th of July four new members to the Senate of the largest research funding organization and central self-governing body of science in Germany at its meeting during the virtual DFG Annual Meeting today. Five Senate members were elected for a further term of office. The Senate is the central scientific body that discusses and decides on all DFG matters of major importance, unless they are reserved for the Joint Committee.The Senate has a total of 39 members. Of these, 36 are elected by the General Assembly; they are also the scientific members of the Joint Committee.
Jan Plefka, who is a professor at the physics department of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and IRIS Adlershof, was elected for the field of theoretical physics. He has already been a member of the Senate Committee for DFG Collaborative Research Centers since 2016.
We congratulate Jan Plefka warmly and wish him much joy and success in this new area of responsibility!
02.07.2021FAIRmat: Lifting the treasure trove of materials data

Prosperity and lifestyle of our society are very much governed by achievements of condensed-matter physics, chemistry, and materials science, because new products for the energy, environment, health, mobility, IT sectors, for example, largely rely on improved or even novel materials. The enormous amounts of research data produced every day in this field therefore represent the treasure trove of the 21st century. This treasure trove is, however, of little value, if these data are not comprehensively characterized and made available. How can we refine this feedstock, in other words, turn data into knowledge and value? For this, a FAIR data infrastructure is a must.

FAIRmat Spokesperson Claudia Draxl
FAIRmat Deputy Spokesperson Matthias Scheffler from the Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society explains: “We interpret the acronym FAIR in a forward looking way: Research data should be Findable and Artificial-Intelligence Ready. This new perspective will advance scientific culture and practice."

FAIRmat Deputy Spokesperson
Matthias Scheffler (FHI Berlin)
FAIRmat covers a wide range of research fields in physics and related areas, consequently basic concepts and measuring techniques, working style, and research data are extremely diverse and heterogeneous. This renders the need for a FAIR data infrastructure as extremely pressing. FAIRmat promotes the efficient sharing of research data (sharing is caring!) and its preparation for reuse and analysis by Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools, enabling a new level, a new quality of science.
For this, FAIRmat follows a bottom-up approach, which is oriented towards the needs of scientists. The consortium is already receiving great support from the community, being well integrated into the Condensed Matter Section of the German Physical Society, the Max Planck Society (e.g., Big-Data Network, CPTS), a large number of universities and institutes as well as various international activities (for example RDA, GO FAIR, EOSC). FAIRmat is based on Claudia Draxl’s and Matthias Scheffler's extensive experience with the world's largest computational materials science data infrastructure, the Novel Materials Discovery (NOMAD) Laboratory, which is online since 2014.

FAIRmat Spokesperson Claudia Draxl (HU Berlin) and
Deputy Spokesperson Matthias Scheffler (FHI Berlin)
discuss with Peter Frensch (Vice President for Research
HU Berlin) at the Berlin Science Week 2020 how the dis-
covery of new materials can enable the the production of
new, more powerful technologies and products.
Video of the panel discussion „Sharing is Caring!
Mit FAIRem Datenmanagement und KI die Materialien
der Zukunft finden"
©Christina Färber
To find out more about FAIRmat, click here.
To join the FAIRmat team, click here.
04.06.2021Lichtblick für die Quantenforschung
Ein IRIS-Forschungsteam und seine Partner haben erstmals die Teilchenaustauschphase von Photonen direkt gemessen.
Die Teilchen, denen das Forscherteam auf der Spur ist, sind schwer zu fassen. Die Physiker untersuchen die Quantenteilchen der elektromagnetischen Wellen, auch Photonen genannt, aus denen Licht besteht. „Dass Photonen bosonisch sind, konnte bislang nur durch indirekte Messungen und mathematische Berechnungen gezeigt werden“, sagt Kurt Busch. „In unserem jüngsten Experiment haben wir die Teilchenaustauschphase von Photonen erstmals direkt gemessen und haben damit einen direkten Beleg für ihren bosonischen Charakter erbracht.“
Das Experiment etabliert eine neue Methode zur Erzeugung und Zertifizierung von Quanten-Zuständen von Licht. Dies ist sehr wichtig im neuen Gebiet der Quanteninformationsverarbeitung, auf deren Basis derzeit neuartige, wesentlich leistungsfähigere Computer entwickelt werden.
more...
19.05.2021New video about the RTG 2575 online
A great example of successful promotion of early-career researchers at IRIS Adlershof is the Research Training Group 2575 “Rethinking Quantum Field Theory. RTG members give an insight into their research:
12.05.2021NFDI Consortium FAIRmat recommended for funding

 A team led by Claudia Draxl, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, has reached a key milestone: The FAIRmat consortium, which Draxl constituted, was recommended for funding by the NFDI expert panel of the German Research Foundation (DFG) on May 10. This is an important success in the three-stage application process to establish the National Research Data Infrastructure (NFDI). FAIRmat applied together with 16 other consortia in October 2020 and already received positive feedback at the beginning of the year on the virtual review that took place in December 2020. The final funding decision will be made by the Joint Science Conference (GWK) in early July. The aim of the national research data infrastructure (NFDI) is to systematically manage scientific and research data, provide long-term data storage, backup and accessibility, and network the data both nationally and internationally. FAIRmat represents the interests of experimental, theoretical and computational condensed matter physics and materials science.
A team led by Claudia Draxl, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, has reached a key milestone: The FAIRmat consortium, which Draxl constituted, was recommended for funding by the NFDI expert panel of the German Research Foundation (DFG) on May 10. This is an important success in the three-stage application process to establish the National Research Data Infrastructure (NFDI). FAIRmat applied together with 16 other consortia in October 2020 and already received positive feedback at the beginning of the year on the virtual review that took place in December 2020. The final funding decision will be made by the Joint Science Conference (GWK) in early July. The aim of the national research data infrastructure (NFDI) is to systematically manage scientific and research data, provide long-term data storage, backup and accessibility, and network the data both nationally and internationally. FAIRmat represents the interests of experimental, theoretical and computational condensed matter physics and materials science.
IRIS Adlershofcongratulates and keeps its fingers crossed!
06.05.2021Launch of the first Einstein Research Unit of the Berlin University Alliance on the topic of quantum computing
 Quantum computers are seen as one of the key technologies of the 21st century. Can they revolutionize the computational capacity of computers? Which new insights do they offer for high energy physics or quantum chemistry? These are the questions on which the first Einstein Research Unit (ERU) of the Berlin University Alliance (BUA) will be focusing. The interdisciplinary research team of the partners Free University of Berlin, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Technical University of Berlin and Charité - Universitätsmedizin, which includes IRIS Adlershof members Prof. Dr. Oliver Benson and Dr. Tim Schröder, has made it its task to explore the potential of the quantum digital transformation. They will combine expertise in theoretical and experimental physics, applied mathematics, computer science and machine learning in a unique way. The Einstein Research Unit „Perspectives of a quantum digital transformation: Near-term quantum computational devices and quantum processors“ will initially receive two million Euros in funding over the next three years.
Quantum computers are seen as one of the key technologies of the 21st century. Can they revolutionize the computational capacity of computers? Which new insights do they offer for high energy physics or quantum chemistry? These are the questions on which the first Einstein Research Unit (ERU) of the Berlin University Alliance (BUA) will be focusing. The interdisciplinary research team of the partners Free University of Berlin, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Technical University of Berlin and Charité - Universitätsmedizin, which includes IRIS Adlershof members Prof. Dr. Oliver Benson and Dr. Tim Schröder, has made it its task to explore the potential of the quantum digital transformation. They will combine expertise in theoretical and experimental physics, applied mathematics, computer science and machine learning in a unique way. The Einstein Research Unit „Perspectives of a quantum digital transformation: Near-term quantum computational devices and quantum processors“ will initially receive two million Euros in funding over the next three years.
More information can be found here.
29.04.2021Call for Applications: Marga Faulstich-Programme for HU-women wanting to launch a company (in German) - Apply until May 16!
 Bis zum 16. Mai 2021 haben HU-Frauen* mit Gründungsvorhaben die Möglichkeit, sich für das Marga Faulstich-Programm zu bewerben. Das Programm findet von Juni bis November 2021 statt. Es werden gezielt Wissenschaftlerinnen*, Doktorandinnen*, Post-Doktorandinnen* und Studentinnen* der Humboldt Universität zu Berlin motiviert und empowert, ihre Geschäftsidee weiterzuentwickeln und bis zur Marktreife auszuarbeiten. Den Teilnehmerinnen wird auf ihrem Gründungsweg neben einer Mentoring-Partnerschaft mit einer erfolgreichen Unternehmerin, Know-how vermittelt, Beratung und Coaching angeboten sowie Strategien für die Zukunft aufgezeigt. Im Bereich der Gründungsberatung steht mit der Humboldt-Innovation GmbH, einer Tochtergesellschaft der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, eine starke Kooperationspartnerin zur Seite.
Bis zum 16. Mai 2021 haben HU-Frauen* mit Gründungsvorhaben die Möglichkeit, sich für das Marga Faulstich-Programm zu bewerben. Das Programm findet von Juni bis November 2021 statt. Es werden gezielt Wissenschaftlerinnen*, Doktorandinnen*, Post-Doktorandinnen* und Studentinnen* der Humboldt Universität zu Berlin motiviert und empowert, ihre Geschäftsidee weiterzuentwickeln und bis zur Marktreife auszuarbeiten. Den Teilnehmerinnen wird auf ihrem Gründungsweg neben einer Mentoring-Partnerschaft mit einer erfolgreichen Unternehmerin, Know-how vermittelt, Beratung und Coaching angeboten sowie Strategien für die Zukunft aufgezeigt. Im Bereich der Gründungsberatung steht mit der Humboldt-Innovation GmbH, einer Tochtergesellschaft der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, eine starke Kooperationspartnerin zur Seite.
More information regarding the programme and the application process can be found here.
13.04.2021A Group of researchers with participation of IRIS Adlershof achieves real-time optical distance sensing of nanoparticles with precision of 2.8 nanometers
Calculated self-interference of a single nanoparticle
placed on a mirror substrate with a silica layer as the
spacer. (i), (ii) and (iii) show different cuts through the
far-field patterns of oriented dipoles oscillating along
the x,y and z-axis, respecitvely
Sub-diffraction limited localization of fluorescent emitters is a major goal of microscopy imaging. It is of key importance for so-called super-resolution, a technique that was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2014. A cooperation of researchers in Australia, China, the USA and IRIS Adlershof have now demonstrated ultra-precise localization and tracking of fluorescent nanoparticles dispersed on a mirror. The approach is based on self-interference patters of the nanoparticles. These patterns can be picked up by a sensitive camera and subsequently compared to numerical simulations.
In this way, it was possible to localize individual particles with an accuracy of only 2.8 nm.
Additionally, the localization can be performed rapidly, and a single particle can be followed with a 50Hz frame rate. This is much faster than other comparable methods. A special benefit of this new approach is its high photo-stability and sensitivity, e.g. to temperature and PH. Therefore, the novel technique may be used for high-resolution multimodality single-particle tracking and sensing.
You can find out more about this here.
Axial Localization and Tracking of Self-interference Nanoparticles by Lateral Point Spread Functions
Y. Liu, Z. Zhou, F. Wang, G. Kewes, S. Wen, S. Burger, M. Ebrahimi Wakiani, P. Xi, J. Yang, X. Yang, O. Benson, and D. Jin
Nat. Commun. 12 (2021) 2019, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-22283-0
01.04.2021Stijn van Tongeren, Emanuel Malek and Markus Krutzik join IRIS Adlershof as junior membersStijn van Tongeren, Emanuel Malek and Markus Krutzik join IRIS Adlershof as junior members
IRIS Adlershof is delighted to announce that three leaders of Junior Research Groups, namely Dr. Stijn van Tongeren, Dr. Emanuel Malek, and Dr. Markus Krutzik will be joining IRIS Adlershof as junior members.



Since 2019, Dr. Markus Krutzik is leading the „Joint Lab Integrated Quantum Sensors“ at the Ferdinand-Braun-Institut, Leibniz-Institut für Höchstfrequenztechnik, where he has already been working as a guest researcher since 2017. Additionally, he has been a group leader at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin since 2015, working on Quantum Sensors and Optical Technologies for Space Applications. His research focuses on the devlopment of the next generation of chip-scale quantum sensors for real world applications. Krutzik finished his doctoral studies at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin in 2014. He then worked as a Postdoctoral researcher at the Cold Atom Laboratory of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory between 2014 and 2015, where he continued to work as a Technical Consultant between 2016 and 2018.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates its new members and is looking forward to a fruitful collaboration.
24.03.2021Erik Panzer receives the 2020 Hermann Weyl Prize

Erik Panzer, former junior researcher at IRIS Adlershof, who is now doing research at University of Oxford, has been awarded the 2020 Hermann Weyl Prize of the International Colloquium on Group Theoretical Methods in Physics for “his pioneering achievements in the calculation of amplitudes in gauge theories, for developing new mathematical structures that exploit the language of symmetries, and for his contribution to the description of important physical phenomena present in nature.”
Panzer received his PhD in 2015 from Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin under the mentorship of IRIS Adlershof member Dirk Kreimer. Between 2015 and 2020, he then worked as a Post-Doctoral Research Fellow at the University of Oxford, where he then became a Royal Society Research Fellow in October 2020. His research interests include Feynman integrals, hyperlogarithms, (elliptic) polylogarithms, (elliptic) multiple zeta values, motivic periods, combinatorial Hopf algebras, renormalization, and Dyson–Schwinger equations.
The Weyl Prize recognizes young scientists who have performed top-level original work in the area of understanding physics through symmetries.
IRIS congratulates.
03.03.2021Successful collaboration with industry in joint paper on inkjet-printed electrodes in OLEDs
Researchers in the HySPRINT joint lab Generative Manufacturing Processes for Hybrid Components (GenFab) of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) and Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) have successfully implemented an ink produced by the Berlin-based company OrelTech in solution-processed organic light emitting diodes.

The OLEDs incorporating the OrelTech
ink illuminating under strain.
After inkjet printing the particle-free silver ink, an argon plasma is used to reduce the silver ions in the ink to metallic silver. “Because this process takes place at a low temperature, it is suitable for use with temperature-sensitive substrates, such as flexible plastic foils,” explains Dr. Konstantin Livanov, co-founder and CTO of OrelTech. The researchers fabricated organic light-emitting diodes employing the silver ink as a transparent conductive electrode on the flexible substrate PET. The resulting devices show comparable light output characteristics to those based on the otherwise widely used indium tin oxide (ITO). Crucially, however, the silver electrodes showed superior stability to ITO upon mechanical bending. Dr. Felix Hermerschmidt, senior researcher in the joint lab of HU and HZB, confirms, "The OLEDs based on the OrelTech ink remain intact at a bending radius at which the OLEDs based on ITO show breakage and fail.” This opens up several application opportunities of the printed devices. The work has been published in the journal Flexible and Printed Electronics and is available Open Access. GenFab, led by Prof. List-Kratochvil, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, is moving into laboratories and offices in the new IRIS research building for further research and development work.
Publication:
ITO-free OLEDs utilizing inkjet-printed and low temperature plasma-sintered Ag electrodes,
M. Hengge, K. Livanov, N. Zamoshchik, F. Hermerschmidt, and E..J. W. List-Kratochvil
Flex. Print. Electron. 6 (2021) 015009.
DOI: 10.1088/2058-8585/abe604
25.01.2021HZB and Humboldt University agree to set up a catalysis research laboratory
Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) have signed a cooperation agreement with the aim of establishing a joint research laboratory for catalysis in the IRIS research building of HU in Adlershof. The IRIS research building offers optimal conditions for the research and development of complex material systems.
 Catalysts are the key to many technologies and processes needed to build a climate-neutral economy. A hotspot for catalysis research has been developing in Berlin's research landscape for some time. As part of the Excellence Initiative, new clusters such as UniSysCat have been created in which established research institutes bundle their activities and the chemical industry is involved through the BASCat laboratory. An important field of research is the production of "green" hydrogen: in order to produce hydrogen and synthetic fuels in a climate-neutral way using renewable energies, innovative catalysts are needed. The recently launched CatLab project, which is funded as part of the Hydrogen Strategy, is pursuing completely new approaches based on thin-film technologies that promise real leaps in innovation.
Catalysts are the key to many technologies and processes needed to build a climate-neutral economy. A hotspot for catalysis research has been developing in Berlin's research landscape for some time. As part of the Excellence Initiative, new clusters such as UniSysCat have been created in which established research institutes bundle their activities and the chemical industry is involved through the BASCat laboratory. An important field of research is the production of "green" hydrogen: in order to produce hydrogen and synthetic fuels in a climate-neutral way using renewable energies, innovative catalysts are needed. The recently launched CatLab project, which is funded as part of the Hydrogen Strategy, is pursuing completely new approaches based on thin-film technologies that promise real leaps in innovation.
IRIS laboratories equipped for catalysis research
To further promote catalysis research in Berlin, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and HZB have now signed another cooperation agreement. Part of the IRIS labo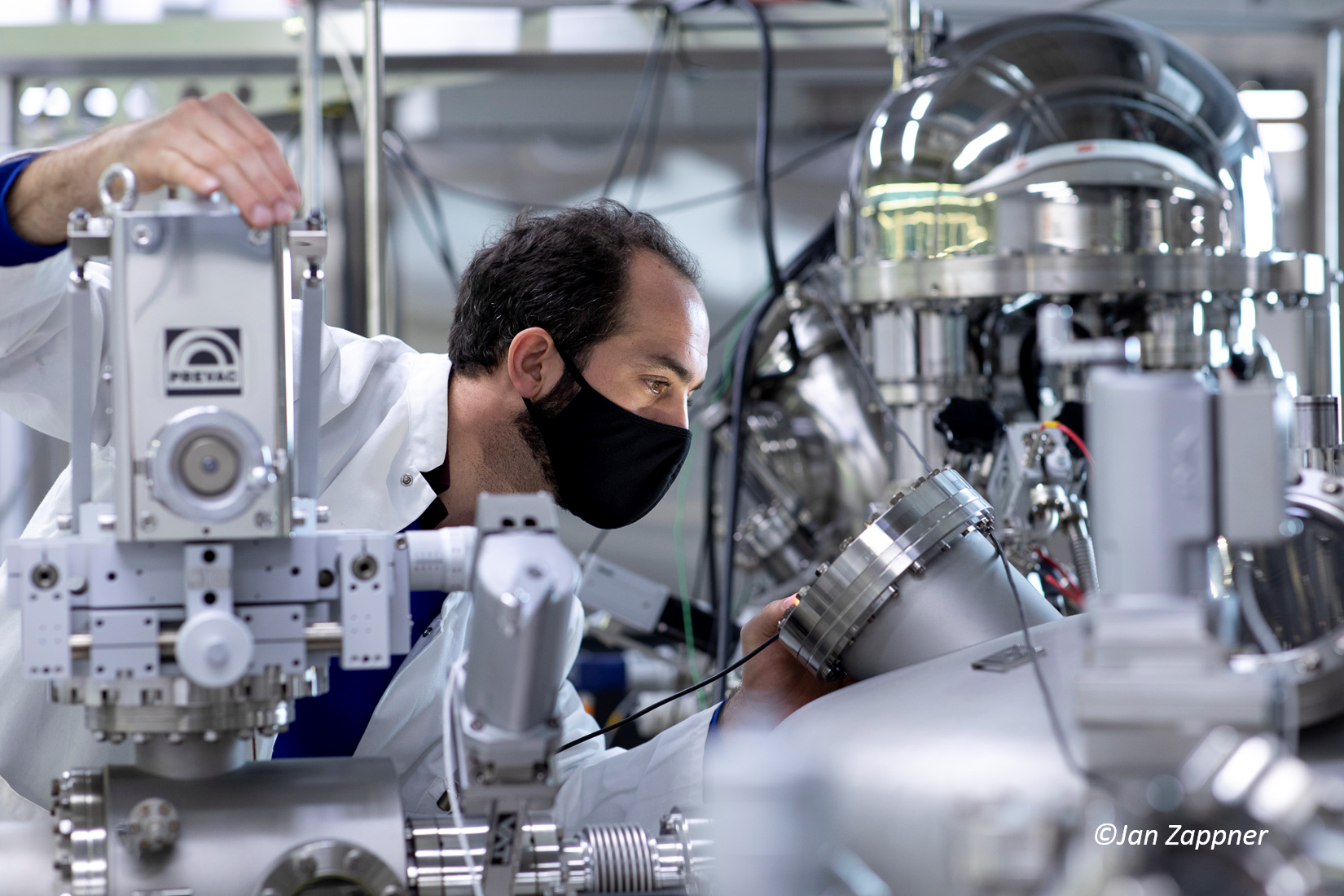 ratories in Berlin-Adlershof will be additionally equipped for the development and investigation of heterogeneous catalyst systems. IRIS Adlershof stands for Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences. With approximately 4,500 square metres of state-of-the-art laboratory, office and communication space, the IRIS research building offers optimal conditions for the research and development of complex material systems. An open-plan laboratory is planned for the installation of laboratory reactors to determine the catalytic activity and selectivity of the material systems. To study catalysts in action, electron microscopes will be set up in the basement. In addition, in-operando investigation methods such as X-ray diffraction, photoelectron, Raman and UV-vis spectroscopy will be used, which will be completed by the high-end analysis options of the neighbouring synchrotron radiation source BESSY II of the HZB. Close cooperation is also planned in the field of thin-film technology, using additive manufacturing processes and nanostructuring and synthesis methods.
ratories in Berlin-Adlershof will be additionally equipped for the development and investigation of heterogeneous catalyst systems. IRIS Adlershof stands for Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences. With approximately 4,500 square metres of state-of-the-art laboratory, office and communication space, the IRIS research building offers optimal conditions for the research and development of complex material systems. An open-plan laboratory is planned for the installation of laboratory reactors to determine the catalytic activity and selectivity of the material systems. To study catalysts in action, electron microscopes will be set up in the basement. In addition, in-operando investigation methods such as X-ray diffraction, photoelectron, Raman and UV-vis spectroscopy will be used, which will be completed by the high-end analysis options of the neighbouring synchrotron radiation source BESSY II of the HZB. Close cooperation is also planned in the field of thin-film technology, using additive manufacturing processes and nanostructuring and synthesis methods.
Innovations through interdisciplinary cooperation
In the IRIS research building, experts from different disciplines work closely together for a deep physical-chemical understanding of complex interfaces. This forms an excellent basis for the development of energy materials. The arrangement of the laboratories and offices as well as the spacious communication areas create the best conditions for the different disciplines to exchange ideas and learn from each other.
Cooperation agreement is also legally innovative
The cooperation between the HU and the HZB on the catalysis research laboratory is being structured on a public-law basis for the first time due to the recent amendment to the Berlin Higher Education Act on cooperation between scientific institutions. The procedure for recording, evaluating and documenting mutual cooperation contributions is simpler and less bureaucratic. This allows researchers to concentrate on their core task – doing science.
18.01.2021Stefan Hecht elected into the National Academy of Science and Engineering
 The National Academy of Science and Engineering (acatech) has elected the chemist Stefan Hecht as one of its new members. With him and the mathematician Jürg Kramer, IRIS-Adlershof is prominently represented in acatech. Hecht is very grateful about the election to the National Academy of Science and Engineering: “For me, it means recognition and motivation at the same time. I am looking forward to develop technological solutions and recommendations for pressing future topics together with well-known colleagues ”, says the chemist. As a new acatech member, he will be particularly active in the field of materials science.
The National Academy of Science and Engineering (acatech) has elected the chemist Stefan Hecht as one of its new members. With him and the mathematician Jürg Kramer, IRIS-Adlershof is prominently represented in acatech. Hecht is very grateful about the election to the National Academy of Science and Engineering: “For me, it means recognition and motivation at the same time. I am looking forward to develop technological solutions and recommendations for pressing future topics together with well-known colleagues ”, says the chemist. As a new acatech member, he will be particularly active in the field of materials science.
As a national academy funded by the federal and state governments, acatech represents the sciences and engineering at home and abroad and conducts an active, science-based dialogue on future technology-related issues. The focus is on:
• Scientific recommendations
• Knowledge transfer and networking between science and business
• Promotion of young researchers in technical professions
• International representation of technical sciences.
The members of the academy are elected into the academy based on their outstanding academic achievements and their high reputation. Acatech currently has more than 400 members from engineering, natural sciences, medicine, as well as from the humanities and social sciences.
more...
08.01.2021Humboldt-Prize for IRIS Young Reseracher Aron Vanselow
Award for one of the best 2020 Masters theses at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
The prize, which is awarded annually to only a few of M.Sc. Students of the entire University for “excellent academic achievements” that are moreover especially related to the “Humboldtian Ideals”, honours the thesis of Mr. Vanselow on “Mid-infrared frequency-domain optical coherence tomography with undetected photons”. The corresponding publication is published in the latest issue of Optica, The Optical Society's journal for high-impact research, and is displayed as an IRIS Adlerhof research highlight:
Frequency-domain optical coherence tomography with undetected mid-infrared photons
A. Vanselow, P. Kaufmann, I. Zorin, B. Heise, H. M. Chrzanowski, S. Ramelow
Optica 12 (2020) 1729, DOI:10.1364/OPTICA.400128
Mr. Vanselow did his work in the group “Nonlinear Quantum Optics”, led by Dr. Sven Ramelow, who is a Young Research Group Leader of IRIS Adlershof. It's already the second award for his thesis after the "Quantum Futur Award".
IRIS Adlershof warmly congratulates the young award winner.
06.01.2021Interview with the "Magician of the Octonions" in the Adlershof Journal
 Nichol Furey has been researching at IRIS Adlershof for half a year and turns to the fundamentals of quantum field theory with an unusual approach. In the current issue of the Adlershof Journal, she explains how she would like to find the 'theory of everything'
Nichol Furey has been researching at IRIS Adlershof for half a year and turns to the fundamentals of quantum field theory with an unusual approach. In the current issue of the Adlershof Journal, she explains how she would like to find the 'theory of everything'
to the online article...
29.12.2020Xolography as new volumetric 3D printing method
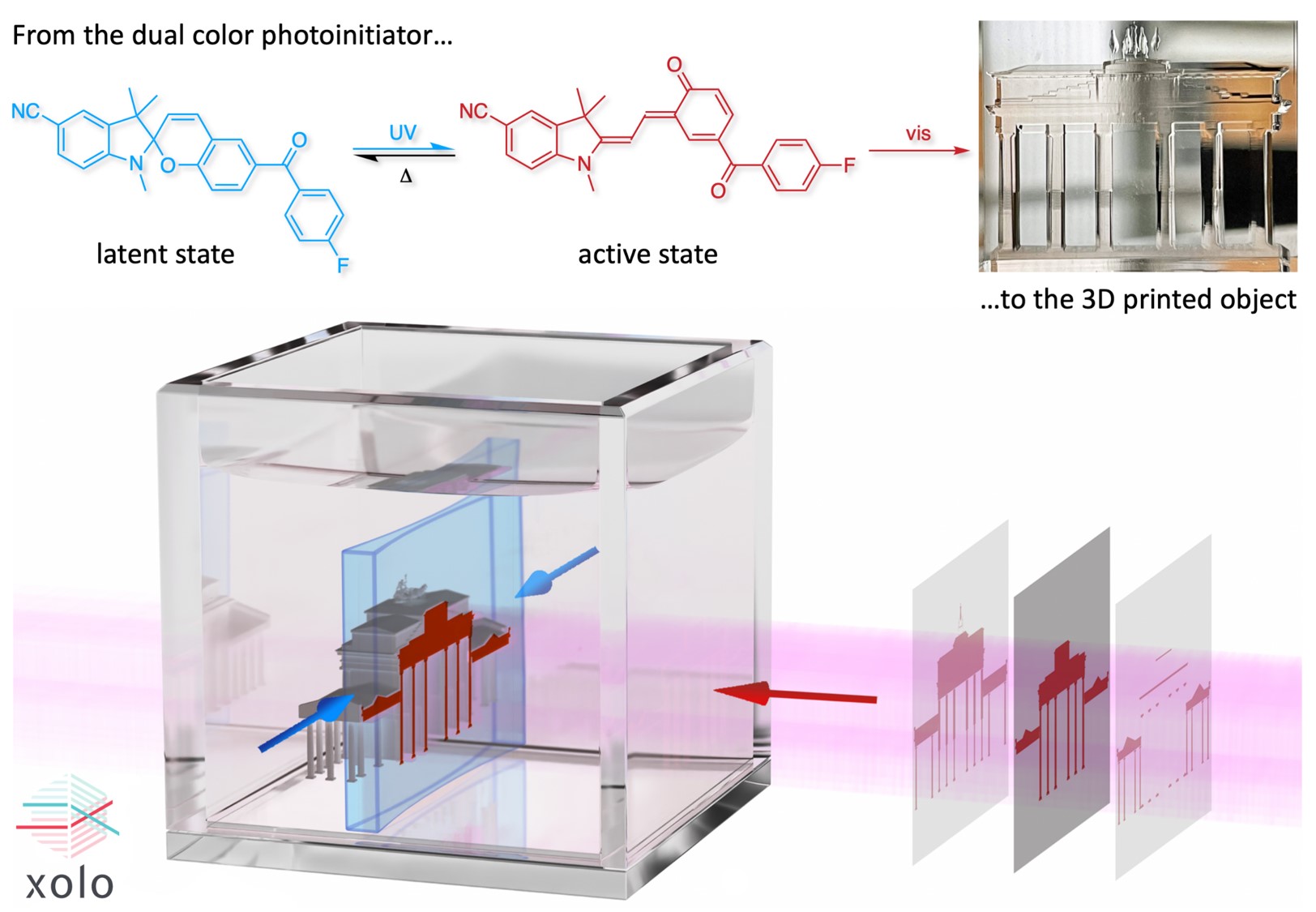 It looks like science fiction but in fact could be the future of 3D printing: A blue slice of light wanders through a liquid, while light projections emerge through the window of a glass vessel. Resembling the replicator of the Star Trek spaceships, the desired object materializes. What used to take hours soon floats in the liquid in the vessel, is then removed, and cured under UV light.
It looks like science fiction but in fact could be the future of 3D printing: A blue slice of light wanders through a liquid, while light projections emerge through the window of a glass vessel. Resembling the replicator of the Star Trek spaceships, the desired object materializes. What used to take hours soon floats in the liquid in the vessel, is then removed, and cured under UV light.
The underlying process – xolography – was developed by a team led by chemist Stefan Hecht from IRIS Adlershof, physicist Martin Regehly, and the founder Dirk Radzinski in the startup company xolo GmbH in Berlin Adlershof over the past two years. For the first time, they now describe their unique method in the renowned journal Nature.
Their invention is based on Hecht’s specialty: photoswitchable molecules, which only at the intersection (xolography) of light rays of two different colors allow precise curing of the starting material in the entire volume (holos). In combination with a new printing process (xolography) based on a laser-generated light sheet and projected cross-sectional images, the desired objects are generated from virtual 3D models.
In contrast to conventional 3D printing, in which the objects are created layer by layer, the advantages of xolography are the significantly higher build speed that is due to the higher efficiency of combining two linear one-photon processes as opposed to non-linear two-photon stereolithography. The faster build speed does not compromise for resolution and thus smooth surfaces can be created. Moreover, fully assembled multicomponent systems can be fabricated in just one step.
Hecht is amazed “to see how fast this has been moving from an idea to xolo’s first prototype printer, the XUBE. Working in a highly interdisciplinary team including chemists, physicists, materials scientists, and software developers with a clear focus and dedication, we have been able to develop xolography as a powerful new method.” He is excited about the many opportunities ahead: “The beauty is our method’s versatility as we can print hard as well as soft objects. This should have major implications for the future manufacturing of optical, (micro)fluidic, and biomedical devices.”“
Xolography for linear volumetric 3D printing
M. Regehly, Y. Garmshausen, M. Reuter, N.F. König, E. Israel, D.P. Kelly, C.-Y. Chou, K. Koch, B. Asfari, and S. Hecht
Nature 588 (2020) 620, DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-3029-7
17.12.2020Hi-Accuracy – Micro level developments driving great innovations in display technologies
Hi-Accuracy is an ambitious EC Horizon 2020 funded project that aims to develop new ways to produce high-resolution displays, improving how they are used in existing technologies and creating exciting new opportunities for new applications. It commenced in April 2020 and is coordinated by the Austrian non-profit research institute Joanneum Research Forschungsgesellschaft mbH.
In a joint approach, 11 project partners from 6 European countries are developing new printable materials and innovative additive fabrication processes to create next generation display technologies. Materials such as quantum dots (QD), novel organic semiconductors and conductive inks that can be produced at low cost with minimal environmental impact are being developed. Hi-Accuracy will employ a variety of deposition, and new additive fabrication processes, such as electro-static jetting (ESJET), reverse-offset printing (ROP), nano-imprint lithography (NIL), Vapour Deposition (ESAVD) and assisted ion deposition (AAID) to deliver the speed and accuracy required to successfully produce the structures commercially. Hi-Accuracy’s printed structures will be manufactured in a range of resolutions on flexible substrates that could be applied to virtually any surface. These technologies will utilise printed electronics down to µm size, for Organic Large Area Electronics (OLAE), Thin Film Transistor (TFT) and Display Applications.
The end goal for these advances is the development of cost effective, adaptable and more sustainable printed QD based displays with greater resolution and brightness than is currently possible. The three year Hi-Accuracy project is focused on producing a small scale ‘proof of concept’ display screen. But it is anticipated that longer term applications of the technology will be on larger, high-resolution displays for use in venues including transport hubs, civic centres, sports stadia, exhibition halls and road side information and advertising signage. At the other end of the scale it is expected that the Hi-Accuracy’s lightweight, ultra high definition displays will become the basis of personal devices including smart watches, phones, virtual reality headsets and augmented reality screens, as well as being used as Point of Sale displays and digital vehicle dashboards. Centro Ricerche FIAT (CRF) is a Hi-Accuracy partner and has proposed exciting in-car applications of this kind such as the futuristic Chrysler Portal concept.
The global market for printed, flexible and organic electronics is projected to grow annually by about 8.5% to a value exceeding $77billion (US) by 2029, and Hi-Accuracy aims to place Europe at the heart of this growth.
Dr. Pufinji Obene of Precision Varionic International, a UK based Hi-Accuracy consortium partner, said ‘with input from our industry partners, SONY, Huawei and Polar, this innovative project aims to produce a highly marketable display technology, which will be the catalyst for improvements to existing devices, including mobile phones, making the use of screens more immersive and engaging for us all.’
The Hi-Accuracy consortium is: Joanneum Research forschungsgesellschaft mbH, Bionanonet Forschungsgesellschaft mbH, Centro Ricerche Fiat SCpA, Dycotec Materials Ltd, Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Polymer Research IAP, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Interuniversitair Micro-Electronica Centrum, NeuDrive Ltd, Precision Varionic International Ltd, Teknologian tutkimuskeskus VTT Oy, University College London
To learn more about these innovations, as well as details about the partner organisations, click here.
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No. 862410
17.12.2020Digital tools for sensors and quanta
 As part of the programme „Digitalisation in the sciences”, the Ministry of Science of Lower Saxony provides funding to the tune of 4.5 million Euros for five research projects at the University of Oldenburg for three years.
As part of the programme „Digitalisation in the sciences”, the Ministry of Science of Lower Saxony provides funding to the tune of 4.5 million Euros for five research projects at the University of Oldenburg for three years.
Together with their partners, the researchers at the University of Oldenburg plan to explore the „nanoworld” using new digital tools as well develop new systems to automatically analyse data from satellites or environmental sensors using artificial intelligence.
One of the principal investigators of the projects is the physicist Caterina Cocchi, who leads a research group on theoretical solid-state physics at the University of Oldenburg and who is also a member of IRIS Adlershof.
Her project SMART – „Simulations meet experiments on the nanoscale: Opening up the quantum world to artificial intelligence“ – aims at uncovering quantum mechanical processes using innovative methods from computational and ultrafast physics. One such process of particular interest to the researchers is the interaction of light and matter at the scale of just a few nanometres.
more...
30.11.2020The Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOP) and IRIS Adlershof start a joint PostDoc program

.gif) The Institute of Physics (IOP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and the IRIS Adlershof of the Humboldt University in Berlin have now established a joint PostDoc program and launched a first round of applications. The prestigious two-year research fellowships are intended for exceptional early-career scientists, in preparation for an independent career in research at the frontier of condensed matter physics, quantum materials or device physics. Successful candidates will spend one year in Beijing and one in Berlin at the research groups of their choice. The application deadline is February 28, 2021.
The Institute of Physics (IOP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and the IRIS Adlershof of the Humboldt University in Berlin have now established a joint PostDoc program and launched a first round of applications. The prestigious two-year research fellowships are intended for exceptional early-career scientists, in preparation for an independent career in research at the frontier of condensed matter physics, quantum materials or device physics. Successful candidates will spend one year in Beijing and one in Berlin at the research groups of their choice. The application deadline is February 28, 2021.
more...
25.11.2020German Centre for Mathematics Teacher Education (DZLM) will be sustained
 The German Centre for Mathematics Teacher Education (DZLM) will be a part of the newly established department “Subject-related knowledge transfer” at the Leibniz Institute for Science and Mathematics Education (IPN) in Kiel. The DZLM is a network of nine universities under the direction of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. For ten years it has been developing, implementing and researching nationwide effective offers for further education for multipliers, teachers and daycare specialists in mathematics. The DZLM was initiated by the Deutsche Telekom Stiftung, from which it has so far been financed with more than ten million euros.
The German Centre for Mathematics Teacher Education (DZLM) will be a part of the newly established department “Subject-related knowledge transfer” at the Leibniz Institute for Science and Mathematics Education (IPN) in Kiel. The DZLM is a network of nine universities under the direction of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. For ten years it has been developing, implementing and researching nationwide effective offers for further education for multipliers, teachers and daycare specialists in mathematics. The DZLM was initiated by the Deutsche Telekom Stiftung, from which it has so far been financed with more than ten million euros.
"The work of the DZLM has shown that advanced trainers need far more skills than just being very good teachers in their subjects," explains the previous director of the DZLM and future director of the new IPN department, Professor Jürg Kramer, who is also a member of IRIS Adlershof. “Our approach is therefore to qualify further trainers not only in terms of further training methodology and adult pedagogy, but also very specifically on subject-specific questions relating to the content and learning processes of teachers in further training. In this way, they are much better able to support teachers and educational specialists effectively in their daily work. We are very pleased that we can now continue this work at the IPN "
IRIS Adlershof warmly congratulates and looks forward to continued good cooperation.
more...
18.11.2020Berlin becomes a center for national high-performance computing
 The Joint Science Conference of the federal and state governments (GWK) is establishing a total of eight centers for “National High-Performance Computing” (HPC), one of them in Berlin. To this end, the Zuse-Institute Berlin (ZIB) was approved for funding as the centre for scientific computing of the Berlin University Alliance (BUA), the cluster of excellence comprising of the three major universities Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Technische Universität Berlin as well as the Charité – University Hospital Berlin. Prof. Alexander Reinefeld, scientific director at the Zuse-Institute and member of IRIS Adlershof delightedly says: „The funding to the tune of approximately 72 million euros affords the Zuse-Institute planning security for the acquisition, modernisation and operation of HPC systems for the next ten years, of which the university research, in particular in Berlin and therefore at IRIS Adlershof, will surely profit.“ He adds, „that the financial support provided by the state of Berlin and the Federation will also be used to provide expert counseling to make the efficient usage of the complex supercomputers easier for the scientists.“
The Joint Science Conference of the federal and state governments (GWK) is establishing a total of eight centers for “National High-Performance Computing” (HPC), one of them in Berlin. To this end, the Zuse-Institute Berlin (ZIB) was approved for funding as the centre for scientific computing of the Berlin University Alliance (BUA), the cluster of excellence comprising of the three major universities Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Technische Universität Berlin as well as the Charité – University Hospital Berlin. Prof. Alexander Reinefeld, scientific director at the Zuse-Institute and member of IRIS Adlershof delightedly says: „The funding to the tune of approximately 72 million euros affords the Zuse-Institute planning security for the acquisition, modernisation and operation of HPC systems for the next ten years, of which the university research, in particular in Berlin and therefore at IRIS Adlershof, will surely profit.“ He adds, „that the financial support provided by the state of Berlin and the Federation will also be used to provide expert counseling to make the efficient usage of the complex supercomputers easier for the scientists.“
IRIS Adlershof cordially congratulates and is looking forward to continued fruitful collaboration.
18.11.2020Joachim Sauer receives Bunsen-Denkmünze 2020
 The German Bunsen-Society for Physical Chemistry honours Joachim Sauer, professor at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin as well as former and founding member of IRIS Adlershof, in recognition of his seminal work. The Bunsen-Denkmünze has been awarded since 1908 to "personalities who advanced the goals of physical chemistry through scientific or practical achievments in an extraordinary way".
The German Bunsen-Society for Physical Chemistry honours Joachim Sauer, professor at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin as well as former and founding member of IRIS Adlershof, in recognition of his seminal work. The Bunsen-Denkmünze has been awarded since 1908 to "personalities who advanced the goals of physical chemistry through scientific or practical achievments in an extraordinary way".
IRIS Adlershof cordially congratulates Prof. Sauer.
more...
13.11.2020Implementation of Flexible Embedded Nanowire Electrodes in Organic Light‐Emitting Diodes
 Researchers in the HySPRINT joint lab Generative manufacturing processes for hybrid components (GenFab) of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) and Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) have developed together with the Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT) a method to produce flexible transparent electrodes based on silver nanowires. Specifically, the nanowires are spray coated and embedded within a polymer resin on top of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate.
Researchers in the HySPRINT joint lab Generative manufacturing processes for hybrid components (GenFab) of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) and Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) have developed together with the Austrian Institute of Technology (AIT) a method to produce flexible transparent electrodes based on silver nanowires. Specifically, the nanowires are spray coated and embedded within a polymer resin on top of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate.
The researchers fabricated organic light-emitting diodes employing the developed ITO‐free nanowire electrodes. These show considerably higher luminance values at the same efficacy compared to their ITO‐based counterparts. As Dr. Theodoros Dimopoulos, senior scientist at AIT, points out, "Replacing ITO in optoelectronic devices is a key area of research and this work shows the possibilities of doing so without loss in performance."
GenFab, led by IRIS Adlershof member Prof. List-Kratochvil, is moving in laboratory rooms in the new IRIS-research building for further development.The work has been published in physica status solidi rapid research letters and is featured on the cover of the November 2020 issue of the journal.
Publication
Lukas Kinner, Felix Hermerschmidt, Theodoros Dimopoulos, and Emil J. W. List-Kratochvil
Implementation of Flexible Embedded Nanowire Electrodes in Organic Light‐Emitting Diodes
Phys. Status Solidi RRL 14 (2020) 2000305
20.10.2020The future of bio-medicine?
Researchers from Humboldt University and the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC) built the first infrared based microscope with quantum light. By deliberately entangling the photons, they succeeded in imaging tissue samples with previously invisible bio-features.
Researchers of the Emmy Noether Junior Research Group "Nonlinear Quantum Optics" of the physics department and IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and of the Experimental and Clinical Research Center (ECRC), a joined institution from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and Max Delbruck Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association, are featured on the cover of ‘Science Advances’ with their new experiment. For the first time they successfully used entangled light (photons) for microscope images. This very surprising method for quantum imaging with undetected photons was only discovered in 2014 in the group of the famous quantum physicist Anton Zeilinger in Vienna. The first images show tissue samples from a mouse heart.
The team uses entangled photons to image a bio-sample probed by ‘invisible’ light without ever looking at that light. The researchers only use a normal laser and commercial CMOS camera. This makes their MIR microscopy technique not only robust, fast and low noise, but also cost-effective - making it highly promising for real-world applications. This use of quantum light could support the field of biomedical microscopy in the future.
 Quantum microscopy of a mouse heart. Entangled photons allow for the making of a high-resolution mid-IR image, using a visible light (CMOS) camera and ultralow illumination intensities. In the picture, absorption (left) and phase information (right) from a region in a mouse heart. The yellow scale bar corresponds to 0.1 mm which is about the width of a human hair.
Quantum microscopy of a mouse heart. Entangled photons allow for the making of a high-resolution mid-IR image, using a visible light (CMOS) camera and ultralow illumination intensities. In the picture, absorption (left) and phase information (right) from a region in a mouse heart. The yellow scale bar corresponds to 0.1 mm which is about the width of a human hair.
Current camera detection is unequivocally dominated by silicon based technologies. There are billions of CCD (charge coupled device) and CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) sensors in digital cameras, mobile phones or autonomous vehicles. These convert light (photons) into electrical signals (electrons). But like our human eyes, these devices cannot see the important mid-IR range. This wavelength range is very important for biological science, containing valuable bio-chemical information that allows researchers to tell different biomolecules apart. The few camera technologies that exist at these crucial wavelengths are very expensive, noisy and subject to export restrictions. That is why the huge potential mid-IR light has for the life sciences so far remained unfulfilled. But researchers have proposed a new solution: “Using a really counterintuitive imaging technique with quantum-entangled photons allows us to measure the influence of a sample on a mid-IR light beam, without requiring any detection of this light” explains Inna Kviatkovsky, the lead author of the study.
There is also no conversion or so-called ‘ghost-imaging’ involved, but the technique relies on a subtle interference effect: first a pair of photons is generated by focusing a pump laser into a nonlinear crystal. This process can be engineered, such that one of the photons will be in the visible range and the other one in the MIR (invisible). The MIR photon probes the sample and is together with the visible photon and the laser sent back to the crystal. Here, quantum interference takes place - between the possibilities of the photon pair being generated on this first pass, and the possibility of not being generated on the first pass, but instead on the second pass through the crystal. Any disturbance, i.e. absorption caused by the sample, will now affect this interference and intriguingly this can be measured by only looking at the visible photons. Using the right optics one can build a mid-IR microscope based on this principle, which the team showed for the first time in their work.
“After a few challenges in the beginning, we were really surprised how well this works on an actual bio-sample.” Kviatkovsky notes. “Also we shine only extremely low powers of mid-IR light on the samples, so low, that no camera technology could directly detect these images.” While this is naturally only the first demonstration of this microscopy technique, the researchers are already developing an improved version of the technique. The researchers envisage a mid-IR microscope powered by quantum light that allows the rapid measurement of the detailed, localized absorption spectra for the whole sample. “If successful this could have a wide range of applications in label-free bio-imaging and we plan to investigate this with our collaboration partners from ECRC”, Dr. Sven Ramelow, group leader at the physics department and IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, explains.
The research was funded by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) within the Emmy-Noether-Program.
Publication:
Inna Kviatkovsky, Helen M. Chrzanowski, Ellen G. Avery, Hendrik Bartolomaeus, and Sven Ramelow
„Microscopy with undetected photons in the mid-infrared.“
Veröffentlichung: 14. Oktober 2020 in Science Advances Issue 42, p. xxx
15.09.2020IRIS-Nachwuchsforscher Michael Kathan receives prestigious award for photochemistry
 For his outstanding dissertation "Photoswitching Reactivity: From remote-controlled to light-driven chemical systems", Dr. Michael P. Kathan was awarded the Albert Weller Prize on September 14, 2020. This is the second award after the Friedrich Hirzebruch PhD award 2020.
For his outstanding dissertation "Photoswitching Reactivity: From remote-controlled to light-driven chemical systems", Dr. Michael P. Kathan was awarded the Albert Weller Prize on September 14, 2020. This is the second award after the Friedrich Hirzebruch PhD award 2020.
Michael Kathan, born in 1988, studied chemistry at the Free University of Berlin and ETH Zurich, where he dealt with fluorine chemistry and strained aromatics. After completing his master's degree at the Free University of Berlin, he began his doctoral thesis in 2015 in the working group of IRIS member Prof. Stefan Hecht at the Humboldt University in Berlin, funded by the German National Academic Foundation.
Michael Kathan's research focus was on the control of chemical reactivity and adaptive materials with light:
In an innovative way, he used light as a tool to control the course of chemical reactions and to control material properties. The focal point of Michael Kathan's dissertation is the development of the concept of "photo reversal", in which the chemical behavior of molecules can be fundamentally changed by the dosed irradiation with light of different colors. In their justification, the jury emphasized that Kathan had impressively managed to span the spectrum from the physicochemical basics to the manufacture of intelligent materials and new, sustainable concepts that address socially relevant issues. His research opens up access to cost-effective sensor materials that indicate, for example, the freshness of highly perishable foods. The light-controlled assembly and dismantling of plastic materials also promises progress in the area of sustainable recycling of mixtures of different plastic products.
The GDCh and the German Bunsen Society awarded the Albert Weller Prize on September 14, 2020 at the digital 27th Lecture Conference on Photochemistry. This year, the award is shared by two young researchers: in addition to Michael Kathan, it was awarded to Yusen Luo, who did her doctorate at Leibniz-IPHT and the University of Jena and is now a post-doc at the Institute for Chemistry and Pharmacy at the University of Erlangen.
Kathan's research has already resulted in several publications in relevant specialist media. Since completing his dissertation in January 2019, Michael Kathan has been working on molecular motors as a postdoc with Prof. Ben Feringa at the University of Groningen, Netherlands.
We congratulate you!
11.09.2020First quantum measurement of temperature in a living organism
The exact measurement of temperature with highest spatial resolution in living organisms is of great importance in order to be able to investigate metabolic processes precisely. However, such a measurement was previously impossible due to the lack of precise and reliable nano thermometers or nano temperature probes. An international research team led by Prof. Oliver Benson, member of IRIS Adlershof, and Prof. Masazumi Fujiwara from Osaka City Universitity has now developed a quantum sensor that is only a few nanometers in size and has been able to measure temperature changes in a nematode after administration of a pharmacological substance. The results pave the way for diverse applications of the novel quantum sensors in biomedical research, e.g. for taking high-resolution thermal images.
Scheme of the experiment: With the help of laser light (green), the characteristic microwave resonance line (in orange: microwave antenna) of nanodiamonds in a nematode (typical length 1 mm) can be recorded under a microscope. Since this depends on the temperature, a temperature change can be measured very precisely and locally. (©Masazumi Fujiwara, Osaka City University, e-mail to Oliver Benson)
Further Information:
In their experiment, the scientists used small diamonds with a diameter of a few 10 nanometers (1 nanometer = 1 millionth of a millimeter). These nanodiamonds contain luminous (fluorescent) quantum defects that can be observed under an optical microscope. With the help of radiated microwaves one can change the brightness of the luminous quantum defects. At a very specific microwave frequency, the defects appear a little darker. This so-called resonance frequency depends on the temperature. The researchers were now able to determine the shift in the resonance frequency very precisely and thus precisely determine the temperature change at the location of the nanodiamonds.
The nanodiamonds were inserted into a nematode (C. elegans). C. elegans is a very well understood model system and is examined in a large number of biophysical and biochemical experiments. By administering a certain pharmacological substance, the mitochondria, the “power stations” of the cells, could be stimulated to increased activity in individual cells of the worm. This then showed up as a slight local temperature increase of a few degrees.
The researchers were fascinated by the results of the experiment. "I never would have thought that the new methods of quantum technology would work so well even in living organisms," said Masazumi Fujiwara, professor at Osaka City University. "With these promising results, we are very confident that quantum sensing will establish in biochemistry and biomedicine. "adds Prof. Oliver Benson from Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. The research teams are now working on further improving and automating their measuring method so that it can be easily integrated into standard microscopy setups.
Funding:
Osaka City University Strategic Research Grant. Murata Science Foundation.
JSPS-KAKENHI (20H00335, 16K13646, 17H02741, 19K14636, 17H02738).
MEXT-LEADER program. Sumitomo Research Foundation.
Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (FOR 1493).
Contact:
Oliver Benson
Nano-Optik
Institut für Physik und IRIS Adlershof der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
Newtonstraße 15
12489 Berlin
030 2093 4711
oliver.bensonphysik.hu-berlin.de
First quantum measurement of temperature in a living organism
M. Fujiwara, S. Sun, A. Dohms, Y. Nishimura, K. Suto, Y. Takezawa, K. Oshimi, L. Zhao, N. Sadzak, Y. Umehara, Y. Teki, N. Komatsu, O. Benson, Y. Shikano, and E. Kage-Nakadai,
Science Advances (2020). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba9636
09.09.2020The Research Training Group 2575 “Rethinking Quantum Field Theory” starts its work.
.png) The Research Training Group 2575 “Rethinking Quantum Field Theory”, funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), has started its work. Due to the pandemic, the hiring of the first two cohorts was delayed until autumn 2020. In October, however, the Research Training Group (RTG) will start with 15 doctoral students from 10 countries and two postdocs. The RTG will deal with pressing theoretical questions and key innovations in quantum field theory that go beyond established methods. “Quantum field theory is a highly developed formalism of theoretical physics for the description of interacting many-body systems. Nevertheless, fundamental questions are still open, especially in relation to gravity, and in recent years fascinating, almost revolutionary innovations have emerged here, which are being further researched within the our new graduate school, ”says the spokesman Prof. Dr. Jan Plefka, head of the Quantum Fields and String Theory group at the Institute of Physics. However, the pandemic continues to make work difficult. “Fortunately, we theorists are almost fully operational in the home office with a laptop, paper and pencil, Mathematica and Zoom. What is missing, however, is the spontaneous exchange between us, for example in the common room over coffee or at lunch, where new ideas often arise. Every meeting is now planned. ”All courses, colloquia and seminars of the RTG will also have to be held virtually in the winter semester 2020/21. It is also currently unclear whether the first retreat in November can be held as planned. “The organization is in full swing. The first conference in particular is very important to us, in order to give everyone involved the opportunity to get to know each other in an informal setting, "explains PD Dr. Oliver Bär, the coordinator of the GRK.
The Research Training Group 2575 “Rethinking Quantum Field Theory”, funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG), has started its work. Due to the pandemic, the hiring of the first two cohorts was delayed until autumn 2020. In October, however, the Research Training Group (RTG) will start with 15 doctoral students from 10 countries and two postdocs. The RTG will deal with pressing theoretical questions and key innovations in quantum field theory that go beyond established methods. “Quantum field theory is a highly developed formalism of theoretical physics for the description of interacting many-body systems. Nevertheless, fundamental questions are still open, especially in relation to gravity, and in recent years fascinating, almost revolutionary innovations have emerged here, which are being further researched within the our new graduate school, ”says the spokesman Prof. Dr. Jan Plefka, head of the Quantum Fields and String Theory group at the Institute of Physics. However, the pandemic continues to make work difficult. “Fortunately, we theorists are almost fully operational in the home office with a laptop, paper and pencil, Mathematica and Zoom. What is missing, however, is the spontaneous exchange between us, for example in the common room over coffee or at lunch, where new ideas often arise. Every meeting is now planned. ”All courses, colloquia and seminars of the RTG will also have to be held virtually in the winter semester 2020/21. It is also currently unclear whether the first retreat in November can be held as planned. “The organization is in full swing. The first conference in particular is very important to us, in order to give everyone involved the opportunity to get to know each other in an informal setting, "explains PD Dr. Oliver Bär, the coordinator of the GRK.
The graduate college is supported by 13 principal investigators and includes all working groups in theoretical particle physics at the Institute of Physics. Further cooperation partners are the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics and the Helmholtz Center DESY. “The scientific breadth is what makes the GRK so attractive. It offers young academics many opportunities to think outside the box of their own project, "explains deputy spokesman Prof. Dr. Agostino Patella." It is the stated aim of the RTG to train doctoral candidates comprehensively and broadly, and thus to provide an ideal basis for a career in science. "
Quantum field theory as the unification of quantum mechanics and special relativity represents one of the main intellectual achievements of the last century. These theoretical advances, closely connected with experimental observations, led to the standard model of elementary particle physics. With the experimental discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012, we now have an empirically validated and mathematically consistent theory up to the highest energy scales. Nevertheless, a series of terrestrial experiments, as well as the astrophysically proven existence of dark matter and energy, indicate that the Standard Model cannot be the final theory of nature. At the same time, pressing theoretical questions such as the structure of quantum gravity, the hierarchy problem or the discovery of dualities between different quantum field theories force established formulations to be reconsidered. More recently, crucial innovations have been achieved in quantum field theory that have led to a serious rethinking of its basic principles. These include new methods of perturbation theory, dualities and hidden symmetries, the prominent role of effective field theories, modern methods for scattering amplitudes and the gradient flow in lattice field theory. The further development of these methods and concepts of modern quantum field theory – or simply the rethinking quantum field theory -represent the common basis of this graduate school. These demands result in a challenging qualification program that is based on the current state of research.
More information can be found here.
05.09.2020New junior research group “Exploring the landscape of string theory flux vacua using exceptional field theory” as part of the Emmy-Noether-Programme of the German Research Foundation
 Since August Dr. Emanuel Malek has been establishing a junior research group on “Exploring the landscape of string theory flux vacua using exceptional field theory” at the Physics Department of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. His group will receive more than 1.2 million euros in funding over 6 years from the Emmy-Noether-Programme of the German Research Foundation. After finishing his doctoral studies at the University of Cambridge in 2014, Dr. Malek spent one year as a Postdoctoral Fellow at the University of Cape Town, followed by a three-year-long stay as a Research Fellow at the Ludwig Maximilian University Munich. He subsequently worked at the Max-Planck-Institute for Gravitational Physics in Potsdam for two years. At Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Dr. Malek will continue his work on the field of theoretical physics and closely collaborate with Prof. Dr. Jan Plefka, Prof. Dr. Matthias Staudacher and Dr. Olaf Hohm, all of whom are members of IRIS Adlershof.
Since August Dr. Emanuel Malek has been establishing a junior research group on “Exploring the landscape of string theory flux vacua using exceptional field theory” at the Physics Department of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. His group will receive more than 1.2 million euros in funding over 6 years from the Emmy-Noether-Programme of the German Research Foundation. After finishing his doctoral studies at the University of Cambridge in 2014, Dr. Malek spent one year as a Postdoctoral Fellow at the University of Cape Town, followed by a three-year-long stay as a Research Fellow at the Ludwig Maximilian University Munich. He subsequently worked at the Max-Planck-Institute for Gravitational Physics in Potsdam for two years. At Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Dr. Malek will continue his work on the field of theoretical physics and closely collaborate with Prof. Dr. Jan Plefka, Prof. Dr. Matthias Staudacher and Dr. Olaf Hohm, all of whom are members of IRIS Adlershof.
Dr. Malek’s research group will develop new computational tools that allow us to obtain predictions from string theory for our universe. String theory is based on the idea that all matter is composed of tiny vibrating strings and is our best attempt at unifying the gravitational force with quantum mechanics. A key prediction of string theory is that the universe contains six additional spatial dimensions, on top of the three spatial dimensions we observe daily. While these extra dimensions are too small to be observed directly, their shape determines the particles and forces that we experience in our 3-dimensional universe. However, a large class of shapes for the extra dimensions, so-called flux compactifications, have long evaded a systematic study due to the lack of the right mathematical framework. By using and developing the new mathematical techniques of Exceptional Field Theory, Dr. Malek’s research group will, for the first time, systematically investigate the possible shapes of string theory’s extra dimensions, especially flux compactifications. The insights gained from this research are crucial for testing string theory experimentally in the future.
IRIS Adlershof wishes Dr. Malek much success in obtaining these goals and is looking forward to a fruitful collaboration.
26.08.2020Stefan Hecht elected as a member of the Academia Europaea
The Academia Europaea has accepted Prof. Stefan Hecht, already a member of IRIS Adlershof, as a new member. The Academy is based in London and was founded in 1988. It currently has more than 4,000 members, including 54 Nobel Prize winners.
The aim of the academy is to promote education and research in Europe and to strengthen interdisciplinary and international exchange in science. As an independent partner, the academy also advises governments and international organizations on scientific issues. The members are leading experts from the fields of chemistry, physics, biology, medicine, mathematics, computer science and technology, the social sciences and humanities as well as economics and law.
"The election to the chemistry section of the Academia Europaea is a great honor and I am very happy about this special personal recognition of my research," explains Stefan Hecht. His main focus is on macro- and supramolecular chemistry and organic material synthesis Interest in light-controlled and -driven processes as well as polymerisation on surfaces.
The chemistry section covers all areas of experimental and theoretical chemistry that deal with the study of matter and its properties. In addition, the members address the questions of how and why substances combine or separate to form other substances and how substances interact with energy. The section forms the interface to other disciplines and related areas of pharmacy, chemical process engineering and materials science, where research is primarily concerned with chemical aspects and less with clinical or engineering issues.
“Membership gives me an excellent network that I would like to use for interdisciplinary exchange in the future. It is a privilege to be able to participate in the advisory work of the academy in setting the political course ”, says Stefan Hecht.
21.08.2020Valentina Forini at the podcast of Einstein Foundation
 With the new podcast series #AskDifferent, the Einstein Foundation Berlin is expanding its science-communication portfolio. Funded scientists and academics affiliated with the foundation give personal insights into their highly specialized field of work and their path of life.
With the new podcast series #AskDifferent, the Einstein Foundation Berlin is expanding its science-communication portfolio. Funded scientists and academics affiliated with the foundation give personal insights into their highly specialized field of work and their path of life.
In episode # 2 You will be challenged, the physicist Valentina Forini, member of IRIS Adlershof as well as Lecturer at City University of London, talks about her two passions:
She first graduated in classical piano. Looking for an additional challenge, she decided to study physics. Today, Forini conducts research in string and quantum field theory as an Einstein Junior Fellow at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. She told us what drove her to follow this path - and why we need more female role models in top-notch science.
19.08.2020Wissenschaft als Katalysator des Wandels – „Lebendiger Blog“ weltweit gestartet
Am Juni 2020 begann ein internationales Team von gut 30 Wissenschaftler*innen die Arbeit an einem in seiner Art bislang einzigartigen gemeinsamen Text
Unter den Autor*innen aus Wissenschaftsinstitutionen weltweit war Fraser Stoddart, der 2016 den Nobelpreis für Chemie erhielt. Die Forschenden gingen der Frage nach: Wie soll unser "Zuhause“ in der Wissenschaft aussehen? Ihre Antwort, kurzgefasst: bunt, spannend und exzellent. Die gemeinsame Überzeugung, die dem Text vorangestellt wurde: "Vielfalt wertzuschätzen, das führt zu wissenschaftlicher Exzellenz, zu Fortschritt und ist vor allem richtig“.
Für ihre Arbeit am Artikel schlossen sich die Autoren spontan über soziale Medien und durch Echtzeit-Kommunikation zu ad-hoc-Teams zusammen.
Michael J.Bojdys, Juniormitglied von IRIS Adlershof, brachte verschiedene Verlagshäuser zur gemeinsamen Publikation des Artikels zusammen. Die Bereitschaft dort war wegen des universellen Charakters der angesprochenen Probleme groß, so Bojdys:
"Dieses Stück sprach für sich selbst, es brauchte nicht allzu viel Überzeugung. Wenn die Leute nicht bereit sind, den moralistischen Argumenten zu folgen, dass dieses Stück zur rechten Zeit kommt und wichtig ist, dann doch wenigstens, dass dieser Aufsatz Aufmerksamkeit erzeugen wird. Und das wird er, da bin ich mir sicher."
Vor allem aber hätten die Autoren hart daran gearbeitet, einen Ton des Fortschritts und der Zusammenarbeit zu finden, und nicht der Konfrontation. "Wir wählten die Sprache eines positiven Ausblicks, wie ein wissenschaftliches Miteinander aussehen könnte. Das ist es, was die Verleger letztlich überzeugt hat."
Ausgangspunkt für den Blog "Diverse Views in Science" sind drei Fragen, die Wissenschaftler*innen aus der ganzen Welt aus ihrer Perspektive beantworten:
- Welche wissenschaftlichen Probleme werden die Trends im kommenden Jahrzehnt bestimmen?
- Wie erleben Sie in Ihrem Leben, in Ihrem Labor und in Ihrem Gastland Vielfalt, Gerechtigkeit und Inklusion?
- Was ist Ihre Botschaft an die nächste Generation von Wissenschaftlern, und was sind Ihre Tipps für ihren Erfolg?
Dieser Blog ist eine lebendige, wachsende Sammlung von Ideen, wie Wissenschaftler*innen zusammen leben und arbeiten sollten.
Die ersten Fragen und Antworten dienten als Grundlage für den Aufsatz „A diverse view of science to catalyse change“. Dieser wurde am 17. August 2020 veröffentlicht in den Zeitschriften Nature Chemistry, Chemical Science, Journal of the American Chemical Society, Angewandte Chemie International Edition, Canadian Journal of Chemistry und Croatica Chemica Acta.
17.08.2020Appointment of Prof. Dr. Jan Lüning
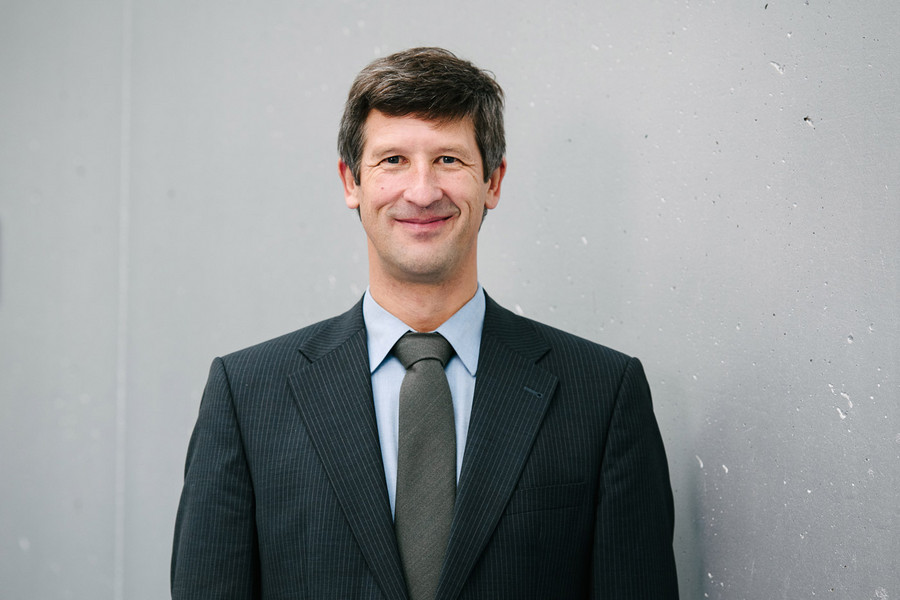

The Department of Physics and IRIS Adlershof are delighted about the appointment of Prof. Dr. Jan Lüning to the W3-S professorship "Electronic properties of materials / X-ray analysis" at the Physics Department of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Since June 1st, 2019, Mr. Lüning has also been Scientific Director for the "Matter" department at the Helmholtz Center Berlin (HZB). He is an internationally recognized expert in research with synchrotron radiation who, before joining the HZB, also did research at Marie-Curie University in Paris and at the synchrotron in Stanford.
IRIS Adlershof warmly congratulates Jan Lüning and is looking forward to a good cooperation.
13.08.2020Dr. Michael J. Bojdys now at King's College London

Dr. Michael J. Bojdys, ERC Junior Research Group Leader at Humboldt-Universität's Chemistry department and member of IRIS Adlershof, is now moving to King's College London. There he will hold the position of a Reader in Chemistry. He will continue to be a member of IRIS Adlershof. Before his time at Humboldt-Univerität zu Berlin, Dr. Bojdys had worked at Charles University Prague, TU Berlin as well at the University of Liverpool.
IRIS Adlershof warmly congratulates, wishes Dr. Bojdys good luck in his new job and looks forward to continued good cooperation.
20.07.2020Prof Christoph Koch elected as director of the department of physics
 Professor Christoph T. Koch, PhD was elected new director of the Department of Physics of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Prof. Koch has been at HU since 2015 and focuses on the development of new methods in quantitative transmission electron microscopy and their application to materials science problems. He has been a member of IRIS Adlershof since 2016 and is a member of the research building commission. Prof. Dr. Heiko Lasker was elected as his deputy. IRIS Adlershof congratulates them both and wishes them every success in their new role.
Professor Christoph T. Koch, PhD was elected new director of the Department of Physics of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Prof. Koch has been at HU since 2015 and focuses on the development of new methods in quantitative transmission electron microscopy and their application to materials science problems. He has been a member of IRIS Adlershof since 2016 and is a member of the research building commission. Prof. Dr. Heiko Lasker was elected as his deputy. IRIS Adlershof congratulates them both and wishes them every success in their new role.
01.07.2020Turning science fiction into science fact
Everything revolves around IRIS Adlershof in the current issue of the WISTA-magazine "Potenzial". In the following three articles different areas of IRIS Adlershof are introduced:
Turning science fiction into science fact
Professor Jürgen P. Rabe, director of the Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences IRIS Adlershof, about building bridges, joint labs, and a new research building
A hub for basic research, teaching, and industrial application
How the Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences IRIS Adlershof supports many different technology start-ups
Focusing on advanced materials
A graduate school in Adlershof offers top qualification and turns teams into families
More information can be found here.
15.06.2020Conference on a FAIR Data Infrastructure for Materials Genomics was a Big Success
539 participants from 33 countries and 6 continents: the Conference on a FAIR Data Infrastructure for Materials Genomics was a big success. IRIS Adlershof members were also involved.
With the five plenary speakers:
- Barend Mons (Leiden University, Co-Leader of the GO-FAIR Initiative, President of CODATA - The FAIR Guiding Principles in Times of Crisis),
- Claudia Draxl (Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, IRIS Adlershof, FAIR-DI e.V. - New Horizons for Materials Research - Role of FAIR Data),
- York Sure-Vetter (Director of the NFDI Directorate, KIT - The German Research Data Infrastructure: Concepts, Challenges and Chances),
- James Warren (Director of the Materials Genome Program, NIST - The US Material Genome Initiative and the Materials Data Infrastructure), and
- Tong-Yi Zhang (Director of the Materials Genome Institute, Shanghai University - From Data to Knowledge: Data Driven Discovery of Formulas),
as well as 28 renown invited speakers, essentially all worldwide leading experts were present. In addition, numerous young scientists presented their research at a poster session and two satellite workshops on Data Acquisition in Angle-Resolved Photoemission Spectroscopy and NFDI@Teaching. IRIS Adlershof member Christoph Koch was involved in the latter as speaker, he also acted as one of the moderators.
High-resolution videos of all the 33 talks and the discussions as well as the poster pitch videos are available on the conference website, on the NOMAD Laboratory YouTube Channel and on KouShare.
The conference was organized by FAIR-DI e.V., an association dedicated to building a worldwide data infrastructure for big data from material science, engineering, and astronomy that follows the FAIR principles.
15.06.2020Printed perovskite LEDs – an innovative technique towards a new standard process of electronics manufacturing
.jpg)
© Claudia Rothkirch/HU Berlin
A team of researchers from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has succeeded for the first time in producing light-emitting diodes (LEDs) from a hybrid perovskite semiconductor material using inkjet printing.This opens the door to broad application of these materials in manufacturing many different kinds of electronic components.The scientists achieved the breakthrough with the help of a trick: "inoculating" (or seeding) the surface with specific crystals.
Microelectronics utilise various functional materials whose properties make them suitable for specific applications. For example, transistors and data storage devices are made of silicon, and most photovoltaic cells used for generating electricity from sunlight are also currently made of this semiconductor material. In contrast, compound semiconductors such as gallium nitride are used to generate light in optoelectronic elements such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs). The manufacturing processes also different for the various classes of materials.
Transcending the materials and methods maze
.jpg)
Major work on the printable perovskite-LEDs was carried out here.
© HZB/Phil Dera
Hybrid perovskite materials promise simplification – by arranging the organic and inorganic components of semiconducting crystal in a specific structure. “They can be used to manufacture all kinds of microelectronic components by modifying their composition“, says Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil, head of a Joint Research Group at HZB and Humboldt-Universität. What's more, processing perovskite crystals is comparatively simple. “They can be produced from a liquid solution, so you can build the desired component one layer at a time directly on the substrate“, the physicist explains.
First solar cells from an inkjet printer, now light-emitting diodes too
Scientists at HZB have already shown in recent years that solar cells can be printed from a solution of semiconductor compounds – and are worldwide leaders in this technology today. Now for the first time, the joint team of HZB and HU Berlin has succeeded in producing functional light-emitting diodes in this manner. The research group used a metal halide perovskite for this purpose. This is a material that promises particularly high efficiency in generating light – but on the other hand is difficult to process. “Until now, it has not been possible to produce these kinds of semiconductor layers with sufficient quality from a liquid solution“, says List-Kratochvil. For example, LEDs could be printed just from organic semiconductors, but these provide only modest luminosity. “The challenge was how to cause the salt-like precursor that we printed onto the substrate to crystallise quickly and evenly by using some sort of an attractant or catalyst“, explains the scientist. The team chose a seed crystal for this purpose: a salt crystal that attaches itself to the substrate and triggers formation of a gridwork for the subsequent perovskite layers.
Significantly better optical and electronic characteristics
In this way, the researchers created printed LEDs that possess far higher luminosity and considerably better electrical properties than could be previously achieved using additive manufacturing processes. But for List-Kratochvil, this success is only an intermediate step on the road to future micro- and optoelectronics that he believes will be based exclusively on hybrid perovskite semiconductors. “The advantages offered by a single universally applicable class of materials and a single cost-effective and simple process for manufacturing any kind of component are striking“, says the scientist. He is therefore planning to eventually manufacture all important electronic components this way in the laboratories of HZB and HU Berlin. List-Kratochvil is Professor of Hybrid Devices at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and head of a Joint Lab founded in 2018 that is operated by HU together with HZB. In addition, a team jointly headed by List-Kratochvil and HZB scientist Dr. Eva Unger is working in the Helmholtz Innovation Lab HySPRINT on the development of coating and printing processes – also known in technical jargon as "additive manufacturing" – for hybrid perovskites. These are crystals possessing a perovskite structure that contain both inorganic and organic components.
The work was published in Materials Horizons, the journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry, in an article entitled:
„Finally, inkjet-printed metal halide perovskite LEDs – utilizing seed crystal templating of salty PEDOT:PSS“
Felix Hermerschmidt, Florian Mathies, Vincent R. F. Schröder, Carolin Rehermann, Nicolas Zorn Morales, Eva L. Unger, Emil. J. W. List-Kratochvil. DOI: 10.1039/d0mh00512f
Ralf Butscher
15.06.2020Development of high-resolution printing technologies - Start of the HI-ACCURACY project

The European project HI-ACCURACY with the involvement of the Hybrid Devices group at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, and coordinated by Joanneum Research, started on April 1st, 2020. HI-ACCURACY is funded by HORIZON 2020 research framework programme with a total volume of around 5 million euros and a project term of 36 months.
According to current estimates, the global market for printed, flexible and organic electronics amounts to 28.3 billion euros with an annual growth rate of >8%. This market is mainly dominated by the display industry, which is looking for new and innovative ways to increase screen resolution and incorporate new user interfaces throughout the display range. High-resolution printing technology is an important factor in achieving these goals.
HI-ACCURACY aims to produce structures with very high resolution up to the μm range and thus the next generation of large area production of flexible organic electronics. This goal is to be achieved through a unique range of advanced materials and printing inks combined with scalable, cost-effective printing and coating processes that require no or minimal vacuum. HI-ACCURACY will thus demonstrate the production of front and backplane structures with structure sizes approaching 1 μm that can operate at frequencies of >1MHz.
Further information on the project can be found here.
Further information on the work of the Hybrid Devices group can be found here.
08.06.2020Max Heyl receives the Fischer-Nernst Study Award of HU's Department of Chemistry
 This year's Fischer-Nernst Study Award of the Department of Chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has been awarded to Max Heyl for his Master's thesis work on the exfoliation and polymer-free transfer of TMDC monolayers using template-stripped gold substrates. Max Heyl has conducted this work as part of the Collaborative Research Center CRC 951 - "Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)", where he now also continues to working as a doctoral student in the Hybrid Device group of the Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil, who is a Deputy Director of IRIS Adlershof.
This year's Fischer-Nernst Study Award of the Department of Chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has been awarded to Max Heyl for his Master's thesis work on the exfoliation and polymer-free transfer of TMDC monolayers using template-stripped gold substrates. Max Heyl has conducted this work as part of the Collaborative Research Center CRC 951 - "Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)", where he now also continues to working as a doctoral student in the Hybrid Device group of the Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil, who is a Deputy Director of IRIS Adlershof.
Well deserved Max!
29.05.2020New Collaborative Research Centre „FONDA – Foundations of workflows for large- scale scientific data analysis“ at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
 The German Research Foundation (DFG) has approved a new Collaborative Research Centre (CRC) at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. The CRC 1404 entiteld „FONDA – Foundations of workflows for large- scale scientific data analysis“ will initially be funded for four years from July 1, 2020. Spokesperson of the CRC is Prof. Ulf Leser from the Department of Computer Science of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. The new research network focuses on the research of techniques, processes and tools that enable scientists to be more productive when creating and using data analysis workflows. Special emphasis is laid on portability, adaptability and reliability that are important for this goal. On the part of IRIS Adlershof, the professors Claudia Draxl, Christoph T. Koch and Alexander Reinefeld are involved in the new CRC.
The German Research Foundation (DFG) has approved a new Collaborative Research Centre (CRC) at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. The CRC 1404 entiteld „FONDA – Foundations of workflows for large- scale scientific data analysis“ will initially be funded for four years from July 1, 2020. Spokesperson of the CRC is Prof. Ulf Leser from the Department of Computer Science of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. The new research network focuses on the research of techniques, processes and tools that enable scientists to be more productive when creating and using data analysis workflows. Special emphasis is laid on portability, adaptability and reliability that are important for this goal. On the part of IRIS Adlershof, the professors Claudia Draxl, Christoph T. Koch and Alexander Reinefeld are involved in the new CRC.
We congratulate the successful applicants and wish the new project a good start.
more...
22.05.2020Fengshuo Zu receives 2019 Chinese Government Award
 Congratulations! Fengshuo Zu, former doctoral student in the group of Norbert Koch, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, received the “2019 Chinese Government Award for Outstanding Self-Financed Students Abroad” of the China Scholarship Council. Meanwhile Fengshuo is postdoc in the Koch group and investigates the electronic structure of metal halide perovskites for high-efficiency solar cells.
Congratulations! Fengshuo Zu, former doctoral student in the group of Norbert Koch, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, received the “2019 Chinese Government Award for Outstanding Self-Financed Students Abroad” of the China Scholarship Council. Meanwhile Fengshuo is postdoc in the Koch group and investigates the electronic structure of metal halide perovskites for high-efficiency solar cells.
Well deserved, Fengshuo!
19.05.2020Apply until June 1st, 2020! As part of the Excellence Strategy, the Humboldt-Universität once again awards Humboldt Research Track Scholarships

Funding for Master's students with strong research skills who plan to pursue a doctorate.
The Humboldt Research Track funding line is designed to support outstanding Master’s students from Humboldt-Universität who plan to pursue a doctorate. Graduates from other universities may also be funded if they pursue a doctorate at Humboldt-Universität. The program offers funding for the transition phase between the end of a Master’s program and the beginning of a doctorate. Requirements for funding are excellent academic results and an original, high-quality proposal of the doctoral project. Applications may already be submitted during the Master’s studies, but funding can only start after graduation. The scholarship helps recipients to focus on the preparation of their doctorate.
How much funding is provided?
Funding of 800 EUR per month is awarded for up to six months. Scholarship holders with children receive an additional 400 EUR a month for the first child, plus 100 EUR for each additional child. In exceptional cases, funding can be extended for up to an additional six months Monatlich 800 EUR Stipendium über sechs Monate, ggf. Familienzuschlag (gemäß Richtlinien der DFG), Verlängerung in Ausnahmefällen um weitere sechs Monate möglich.
What are the application deadlines?
The Humboldt Research Track Scholarships are awarded four times a year. Application periods are
1 June to 15 July for funding starting 1 October
1 September to 15 October for funding starting 1 February
1 December to 15 January for funding starting 1 April.
Further information is provided here.
30.04.2020Graduate School "Advanced Materials": First admission of members
.png) This April, the Graduate School "Advanced Materials" (GS-AM) admitted 22 doctoral students as members, from HU Berlin, FU Berlin, TU Berlin, and Potsdam Universität. The mission of GS-AM is to provide superior qualification for doctoral students across Berlin and Potsdam, in research on modern and emerging advanced materials for optics, electronics, and optoelectronics, as well as in transferable skills.
This April, the Graduate School "Advanced Materials" (GS-AM) admitted 22 doctoral students as members, from HU Berlin, FU Berlin, TU Berlin, and Potsdam Universität. The mission of GS-AM is to provide superior qualification for doctoral students across Berlin and Potsdam, in research on modern and emerging advanced materials for optics, electronics, and optoelectronics, as well as in transferable skills.
The spokesman of the graduate school, Professor Norbert Koch from the Department of Physics and IRIS Adlershof at HU explains: The research projects of our students are devoted to unraveling fundamental and applied aspects of 3D and 2D inorganic semiconductors, organic semiconductors, and their hybrids. During the current period of reduced access to the universities, GS-AM offers online-courses by professional trainers, on topics such as scientific writing/presentation, project management, and scientific leadership. We all hope that meeting in person will become possible eventually, but for the time being digital instruments are our key for interaction.
The next term of applications to GS-AM will be in the fall of 2020.
more information
27.04.2020Maximum capacities at the theoretical limit come from Adlershof
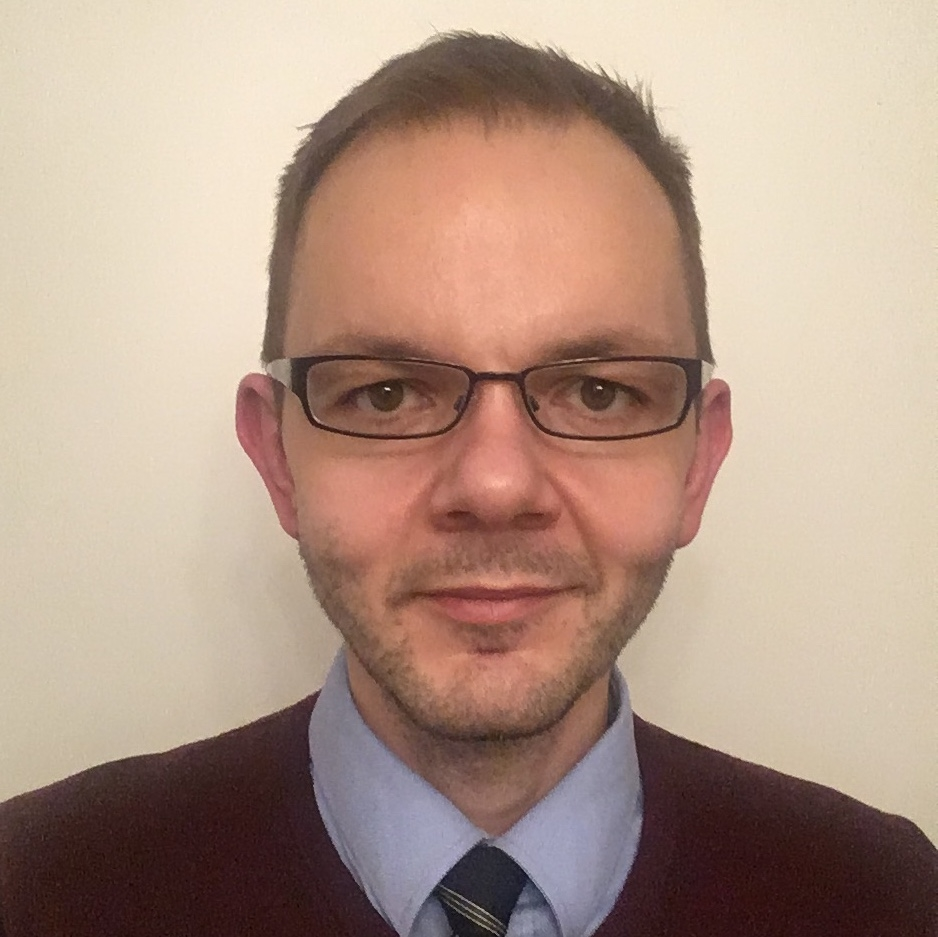 On April 27, the European Research Council (ERC) announces the recipients of the Proof of Concept (PoC) Grant scheme: one of them is Michael J. Bojdys, materials chemist and junior research group leader at IRIS Adlershof and the department of chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. This makes Bojdys one of the first two ERC PoC grantees in Berlin since the grant was established in 2018. This year’s second recipient is from the TU Berlin.
On April 27, the European Research Council (ERC) announces the recipients of the Proof of Concept (PoC) Grant scheme: one of them is Michael J. Bojdys, materials chemist and junior research group leader at IRIS Adlershof and the department of chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. This makes Bojdys one of the first two ERC PoC grantees in Berlin since the grant was established in 2018. This year’s second recipient is from the TU Berlin.
Proof of Concept Grants are exclusively awarded to researchers who already hold an ERC Grant and wish to move the output of their research towards the initial steps of pre-commercialisation.
 In the course of his ERC PoC Grant "Ultra-high energy storage Li-anode materials" (LiAnMAT) Michael Bojdys will develop together with VARTA Micro Innovation GmbH and the Adlershof start-up INURU GmbH, Li anode materials for high capacity applications.
In the course of his ERC PoC Grant "Ultra-high energy storage Li-anode materials" (LiAnMAT) Michael Bojdys will develop together with VARTA Micro Innovation GmbH and the Adlershof start-up INURU GmbH, Li anode materials for high capacity applications.
First promising results are part of a patent application of HU Berlin and the start-up incubator Humboldt Innovation GmbH: the capacity of the novel anodes exceeds that of commercially available anodes by a factor of 10-40.
Dr. Michael J. Bojdys
Head of the Functional Nanomaterials Group, Department of Chemistry and IRIS Adlershof, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
tel (D): +491774818190
m.j.bojdys.02cantab.net
http://bojdyslab.org/
23.04.2020„Die Wissenschaft bleibt nicht stehen“

Die Humboldt-Universität befindet sich derzeit aufgrund der Coronavirus-Pandemie – wie alle anderen Wissenschaftsbetriebe der Stadt – im Präsenznotbetrieb.Die Gebäude der Universität sind verschlossen – so auch das Institut für Chemie – und nicht alle Mitarbeiterinnen und Mitarbeiter der HU haben Zutritt. Der Chemiker und Forscher Michael Bojdys hält daher Kontakt zu seiner Arbeitsgruppe und seinen Studierenden über digitale Plattformen.
Die komplette Folge finden sie hier.
20.04.2020Technology Park Adlershof fights against Covid-19
Many businesses and schientific institutions are involved in the fight against the Coronavirus
Currently, more than 30 companies and scientific institutions in Adlershof are busy fighting the coronavirus. This is the result of a survey by the operating company WISTA Management GmbH. "In order to combat and contain the Covid-19 virus, we need suitable drugs and vaccines quickly," said Ramona Pop (Bündnis 90/Die Grünen), Senator for Economic Affairs. "Our Berlin locations of future innovations have excellent research skills for this. They are all making an important contribution to overcoming the corona crisis.”"
According to WISTA Managing Director Roland Sillmann, this commitment shows "that companies and institutions in such a diversified science and technology park as Berlin Adlershof are able to act flexibly and develop innovative forces very quickly, especially in times of crisis. This at least makes us confident that the Technology Park Adlershof can successfully overcome the current crisis in its entirety.” (Source: Der Tagesspiegel)
more...
01.04.2020Apply for support through the family fund of Humboldt-Universität
Für das Jahr 2020 können Mittel aus dem Familienfonds der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin beantragt werden.
Der Familienfonds wurde mit dem Ziel eingerichtet, bestimmte Maßnahmen zur noch besseren Förderung der Vereinbarkeit von Beruf, Studium und Familie an der HU finanziell zu unterstützen. Grundlage ist das umfassende Familienverständnis der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin entsprechend ihrem Leitbild als familiengerechte Hochschule.
Ab heute können sich alle Mitglieder der HU für die unterschiedlichen Programmlinien bewerben, sofern sie die jeweils genannten Voraussetzungen erfüllen. Anträge können vom 1. April bis zum 15. Mai 2020 gestellt werden (Ausschlussfrist).
Weitere Informationen finden Sie hier.
18.03.2020Apply until May 15th, 2020! As part of the Excellence Strategy, the Humboldt-Universität once again awards Humboldt Research Track Scholarships
Funding for Master's students with strong research skills who plan to pursue a doctorate.
The Humboldt Research Track funding line is designed to support outstanding Master’s students from Humboldt-Universität who plan to pursue a doctorate. Graduates from other universities may also be funded if they pursue a doctorate at Humboldt-Universität. The program offers funding for the transition phase between the end of a Master’s program and the beginning of a doctorate. Requirements for funding are excellent academic results and an original, high-quality proposal of the doctoral project. Applications may already be submitted during the Master’s studies, but funding can only start after graduation. The scholarship helps recipients to focus on the preparation of their doctorate.
How much funding is provided?
Funding of 800 EUR per month is awarded for up to six months. Scholarship holders with children receive an additional 400 EUR a month for the first child, plus 100 EUR for each additional child. In exceptional cases, funding can be extended for up to an additional six months Monatlich 800 EUR Stipendium über sechs Monate, ggf. Familienzuschlag (gemäß Richtlinien der DFG), Verlängerung in Ausnahmefällen um weitere sechs Monate möglich.
What are the application deadlines?
The Humboldt Research Track Scholarships are awarded four times a year. Application periods are
1 April to 15 May for funding starting 1 August
1 June to 15 July for funding starting 1 October
1 September to 15 October for funding starting 1 February
1 December to 15 January for funding starting 1 April.
Further information is provided here.
07.02.2020Flavie Davidson-Marquis supported by IRIS Adlershof fellowship

Our modern society depends on the efficient processing of information, but conventional electronic data processing is reaching its limits. We need new approaches to store and process large amounts of information. Quantum computing is the promising candidate, and quantum supremacy has already been shown in 2019.
If photons are used as qubits, they have to be controlled, slowed and stored, f.e. in a waveguide or a light-cage. Flavie Davidson-Marquis, a PhD-student in the group of Prof. Oliver Benson, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, is investigating a novel light-cage type waveguide: She explores the enhanced light-matter interaction resulting from cohabitation of caesium vapour and a guided field.
IRIS Adlershof supports this research with a fellowship, so Flavie can focus on finalizing the project and getting the results ready for publication.
06.02.2020Prof. Caterina Cocchi appointed W3 professorship at the University of Oldenburg
 The Ministry of Science and Culture of the State Niedersachsen, has appointed Professor Caterina Cocchi the W3 professorship "Theoretical Solid State Physics" at the Carl von Ossietzky University in Oldenburg. Ms. Cocchi, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, will move to her new position in Oldenburg at the beginning of the summer semester 2020. She will keep in touch with Humboldt-Universität as a visiting scientist, as project leader within the CRC 951 “HIOS”, as well as a member of IRIS Adlershof.
The Ministry of Science and Culture of the State Niedersachsen, has appointed Professor Caterina Cocchi the W3 professorship "Theoretical Solid State Physics" at the Carl von Ossietzky University in Oldenburg. Ms. Cocchi, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, will move to her new position in Oldenburg at the beginning of the summer semester 2020. She will keep in touch with Humboldt-Universität as a visiting scientist, as project leader within the CRC 951 “HIOS”, as well as a member of IRIS Adlershof.
We warmly congratulate Ms. Cocchi and wish her every success and all the best for her new position. We look forward to our further fruitful cooperation.
more...
11.12.2019Dr. Tim Schröder and Dr. Olaf Hohm, new members at IRIS Adlershof
 An essential prerequisite for quantum communication and technology is the transmission of quantum information over long distances, but far-reaching and stable networks can only be realized with quantum amplifiers. Dr. Tim Schröder conducts research on such amplifiers with the ERC project QUERP “Quantum Repeater Architectures Based on Quantum Memories and Photonic Encoding” and also attempts to combine complementary technologies from quantum communication: In a hybrid quantum repeater module, two different concepts, such as quantum memory in tin defect centers in diamond, and photonic cluster states are to be brought together.
An essential prerequisite for quantum communication and technology is the transmission of quantum information over long distances, but far-reaching and stable networks can only be realized with quantum amplifiers. Dr. Tim Schröder conducts research on such amplifiers with the ERC project QUERP “Quantum Repeater Architectures Based on Quantum Memories and Photonic Encoding” and also attempts to combine complementary technologies from quantum communication: In a hybrid quantum repeater module, two different concepts, such as quantum memory in tin defect centers in diamond, and photonic cluster states are to be brought together.
Dr. Olaf Hohm leads the ERC Consolidation Group “Symmetries and Cosmology”. He‘s developing a computational approach based on string theory, arguably the most promising candidate for a complete theory of quantum gravity. This approach might answer questions relating to the very early history of the Universe, and even test string theory on measurements of background radiation.
IRIS Adlershof welcomes its new members warmly and looks forward to a long and fruitful cooperation.
10.12.2019"Étoiles de l'Europe 2019" - iSwitch receives prestigious award from the French Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Innovation
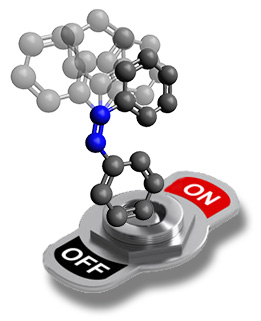 The Innovative Training Network iSwitch is awarded the "Étoiles de l'Europe" prize of the French Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Innovation for its outstanding and European-oriented research. With this, the project, in which IRIS Adlershof members Prof. Norbert Koch and Prof. Stefan Hecht were participating as Principle Investigators, now literally belongs to the shining "stars of Europe".
The Innovative Training Network iSwitch is awarded the "Étoiles de l'Europe" prize of the French Ministry of Higher Education, Research and Innovation for its outstanding and European-oriented research. With this, the project, in which IRIS Adlershof members Prof. Norbert Koch and Prof. Stefan Hecht were participating as Principle Investigators, now literally belongs to the shining "stars of Europe".
The award is given each year to twelve research and innovation projects initiated in France to reward and strengthen international cooperation in the field of science and technology at a European level. iSwitch was coordinated by Paolo Samorì, Professor at the University of Strasbourg, and since 2015 has brought together leading international research groups at the interface between chemistry, physics and engineering with the aim of educating and promoting the next generation of researchers in the emerging fields of materials science and nanoscience. The network consisted of 14 interdisciplinary academic and industrial partners from seven European countries (France, Germany, Belgium, Spain, Italy, Great Britain and Switzerland).
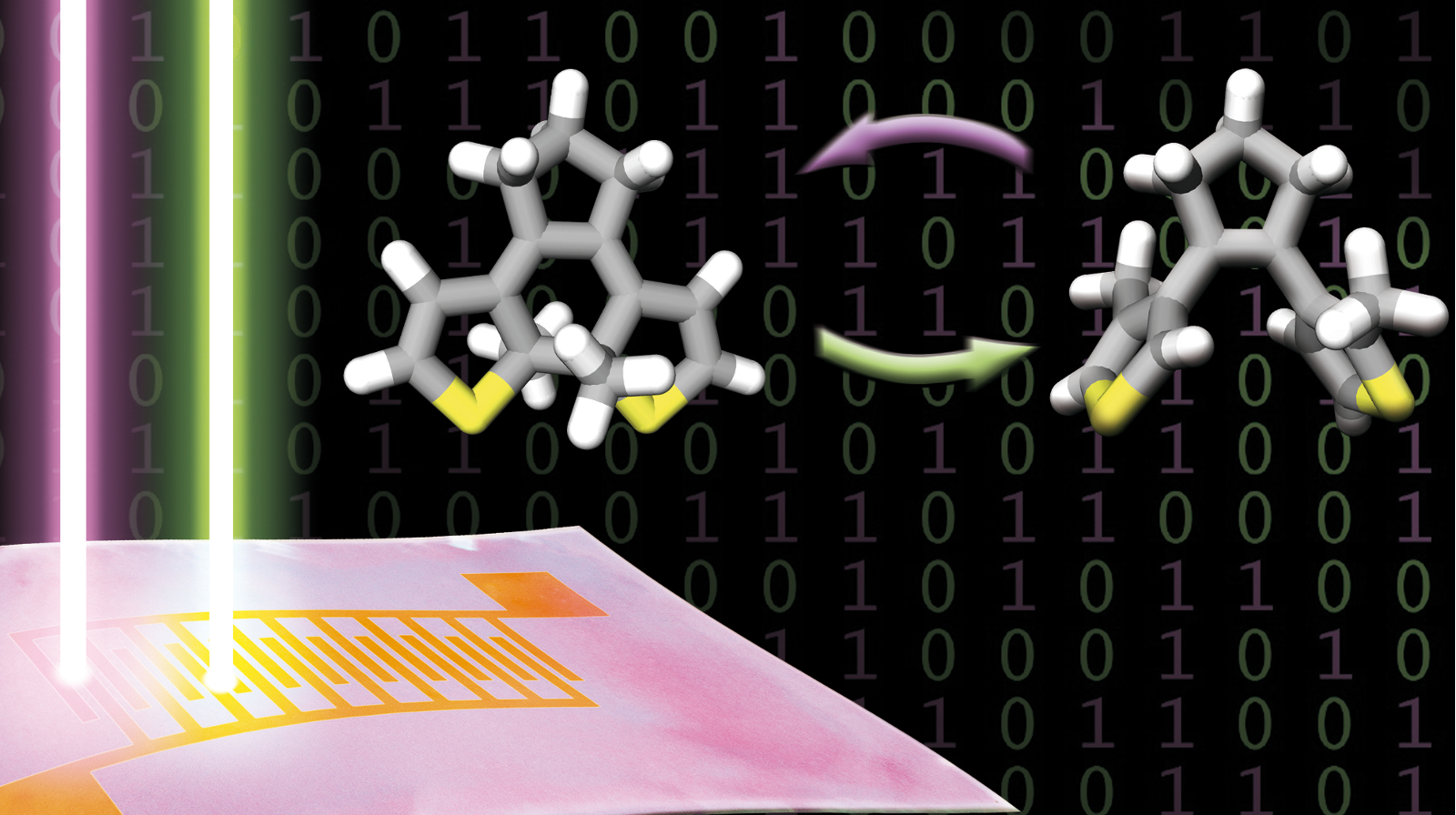 In December 2018, the project funded by the EU under Horizon2020 ended successfully: The iSwitch training program qualified its young scientists for employment with leading global companies such as Johnson & Johnson, universities of excellence or prestigious research institutions. In addition, the knowledge gained and technologies developed in the project have provided significant impetus in the research field of optoelectronic devices, for example for the manufacture of artificial retinae and smart textiles such as special clothing, which can measure temperature changes and then adapt shape and color.
In December 2018, the project funded by the EU under Horizon2020 ended successfully: The iSwitch training program qualified its young scientists for employment with leading global companies such as Johnson & Johnson, universities of excellence or prestigious research institutions. In addition, the knowledge gained and technologies developed in the project have provided significant impetus in the research field of optoelectronic devices, for example for the manufacture of artificial retinae and smart textiles such as special clothing, which can measure temperature changes and then adapt shape and color.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates the iSwitch team for this great success!
11.11.2019 DFG funds new Research Training Group „Rethinking Quantum Field Theory“
 The Research Training Group (RTG) "Rethinking Quantum Field Theory" is based in the Physics Department and the IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin(HU). From April 2020, it will be funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) for four and a half years with about 4 Mio Euro. The RTG will address urgent theoretical questions and significant innovations in quantum field theory (QFT) that go beyond established methods.
The Research Training Group (RTG) "Rethinking Quantum Field Theory" is based in the Physics Department and the IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin(HU). From April 2020, it will be funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) for four and a half years with about 4 Mio Euro. The RTG will address urgent theoretical questions and significant innovations in quantum field theory (QFT) that go beyond established methods.
Quantum field theory (QFT), the unification of quantum mechanics and special relativity, represents a major intellectual achievement of the past century. These innovations culminated in the formulation of the Standard Model (SM). With the discovery of the Higgs boson, the SM is an empirical validated and mathematically consistent theory valid up to highest energies. However, a number of terrestrial experiments exhibit significant tensions with the SM, while astrophysical observations require the existence of dark matter and energy showing that the SM is not the ultimate theory of particle physics. In addition, pressing theoretical issues as the quest for a quantum theory of gravity, the hierarchy problem and the discovery of dualities between different QFTs raise questions about the foundations of the SM and QFT in general. In recent years important innovations in QFT occurred leading the community to a serious rethinking of its core concepts. These include the methodology of perturbation theory, dualities and hidden symmetries, the prominent role of effective field theory in fundamental physics, modern on-shell methods for scattering amplitudes and the gradient flow methodology in lattice field theory. The further development of these methods and concepts of modern QFT leading to a deep rethinking of it provides the common basis of this proposed research training group (RTG). We designed a timely qualification program for the new generation of quantum field theorists. The RTG is headed by 12 principal investigators including senior and junior research group leaders, encompassing all groups working in theoretical high energy physics Humboldt University. Partners of the RTG are the Max-Planck-Insitute for Gravitational Physics and the Helmholtz Center DESY. IRIS Adlershof is involved with several members in the newly established RTG. These are RTG-spokesman Prof. Jan Plefka, Dr. Valentina Forini, Prof. Dirk Kreimer and Prof. Matthias Staudacher.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates the successful applicants and wishes a lot of success.
26.10.2019Lively participation in the symposium IRIS 2019: Best-Poster-Award for Dr. Benedikt Haas

The IRIS Symposium has firmly established itself as an annual highlight in the scientific life of IRIS Adlershof, and it has a growing interest far beyond the Adlershof location, as the annually increasing number of participants impressively demonstrates. This year, ideas for the further development of IRIS in the areas of 2D Based Heterostructures, Energy Conversion, Data Science, and Emerging Fields were in the focus of interest. These topics were introduced to an extremely open-minded audience of internationally renowned researchers.
The junior researchers had the opportunity to present their own research results during a poster competition to the invited speakers and the other participants of the symposium. The jury, consisting of the junior researchers Dr. Zsuzsanna Heiner and Dr. Felix Hermerschmidt, as well as the IRIS member Prof. Nicola Pinna, was visibly struggling to make the choice for the best poster.
 Finally, Dr. Benedikt Haas was able to prevail with a total of 33 competitors with his poster. Benedikt, PostDoc in the group „Structure Research and Electron Microscopy“, which is led by IRIS member Prof. Christoph T. Koch, received the Best Poster Award and a voucher for a travel allowance up to a maximum of 500 EUR for active participation in a scientific conference. Doctoral students Martin Rothe (AG Nanooptik) and Niklas Mutz (AG Hybride Bauelemente) were awarded second and third prize as well as book vouchers for their poster contributions. The event ended with grilled and drinks.
Finally, Dr. Benedikt Haas was able to prevail with a total of 33 competitors with his poster. Benedikt, PostDoc in the group „Structure Research and Electron Microscopy“, which is led by IRIS member Prof. Christoph T. Koch, received the Best Poster Award and a voucher for a travel allowance up to a maximum of 500 EUR for active participation in a scientific conference. Doctoral students Martin Rothe (AG Nanooptik) and Niklas Mutz (AG Hybride Bauelemente) were awarded second and third prize as well as book vouchers for their poster contributions. The event ended with grilled and drinks.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates the winners and thanks everyone who has contributed actively to the success of the symposium.
22.10.2019The best of both worlds: HU article on the importance of CRC 951 published
 "Getting to the bottom of the materials of the future" - in a newly published article, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin addresses the research of the CRC 951 - Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS), in which members of IRIS Adlershof are also involved.
"Getting to the bottom of the materials of the future" - in a newly published article, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin addresses the research of the CRC 951 - Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS), in which members of IRIS Adlershof are also involved.
The importance of the CRC’s theoretical und application-oriented research on materials is discussed, especially with regard to the indispensable use of optoelectronics in modern everyday life and the ever-increasing demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly materials.
Claudia Draxl’s SOLgroup and Emil List-Kratochvil’s Hybrid Devices Group are covered in detail. Both are members of IRIS Adlershof and professors at the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences of the HU, as is the spokesperson of HIOS, Norbert Koch.
The article can be found in the press portal of the HU. Here you can find the website of the CRC, which entered its third funding period in July this year. More information about the working group of Claudia Draxl can be found here, the working group of Emil List-Kratochvil here.
19.10.2019Workshop of the Institute of Physics (IOP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and IRIS Adlershof in Dongguan, Guangdong
 The Institute of Physics (IOP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and IRIS Adlershof want to intensify their scientific collaboration. After the first joint workshop at IRIS Adlershof on June 25./26. the second workshop took place at the IOP (SLAB) in Dongguan, Guangdong, followed up by visits of the IOP in Beijing and at the University of CAS (UCAS, North Campus). The focus of interest were priority subjects at both institutes, including 2D- and nano-materials, soft matter, hybrid electronic devices, photoemission, synchrotron research, and quantum information.
The Institute of Physics (IOP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and IRIS Adlershof want to intensify their scientific collaboration. After the first joint workshop at IRIS Adlershof on June 25./26. the second workshop took place at the IOP (SLAB) in Dongguan, Guangdong, followed up by visits of the IOP in Beijing and at the University of CAS (UCAS, North Campus). The focus of interest were priority subjects at both institutes, including 2D- and nano-materials, soft matter, hybrid electronic devices, photoemission, synchrotron research, and quantum information.
During their visit to Beijing, members of the Berlin delegation headed by IRIS Director Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe also met Academician Prof. Hongjun Gao, who will visit Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin on October 21, with an official delegation of IOP/CAS.
 Starting in November, Carlos-Andres Palma, Professor at the IOP, will regularly carry out research at IRIS Adlershof within the framework of a research fellowship granted by the Alexander von Humboldt. Furthermore, the participating institutes plan to regularly exchange students and scientists, establish a joint postdoctoral program, and implement joint scientific events.
Starting in November, Carlos-Andres Palma, Professor at the IOP, will regularly carry out research at IRIS Adlershof within the framework of a research fellowship granted by the Alexander von Humboldt. Furthermore, the participating institutes plan to regularly exchange students and scientists, establish a joint postdoctoral program, and implement joint scientific events.
04.10.2019Freigeist-Fellowship of the Volkswagen foundation for Dr. Nichol Furey
 The mathematicial physicist Nichol Furey (University of Cambridge) has been awarded a Freigeist Fellowship by the Volkswagen Foundation.
The mathematicial physicist Nichol Furey (University of Cambridge) has been awarded a Freigeist Fellowship by the Volkswagen Foundation.
These Fellowships are aimed at unusual and courageous lateral thinkers from all disciplines in the first four years following their doctorate. In order to become a Freigeist Fellow, the young researchers must not only possess outstanding specialist expertise, but also look beyond their own discipline and combine critical analytical skills with new perspectives and approaches.
At the IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Ms. Furey will study a special number system, the octaves, and would like to prove that the behavior of elementary particles can be predicted using this system. Her project "In-depth Study into the Algebraic Structure of Elementary Particle Physics" explores the question of whether there is a mathematical logic behind the inner processes of elementary particle physics.
Anyone interested in learning more about this exciting topic can experience Ms. Furey as invited speaker at the symposium IRIS 2019.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates the successful young scientist and looks forward to a fruitful cooperation.
more...
01.10.2019Humboldt Research Fellowship for Prof. Carlos-Andres Palma
 Professor Carlos-Andres Palma has been awarded a Humboldt Research Fellowship for Experienced Researchers. The fellowship provides funding for international experts to make extended research visits to Germany. At IRIS Adlershof and at the physics department of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Prof. Palma will contribute with expertise in ultrahigh-vacuum variable temperature, low-temperature atomic force microscopy (AFM) and complementary surface analytics. Together with Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe’s group and co-hosted by Prof. Norbert Koch’s group, he will explore nanographane materials and their phonon properties in the project entitled ‘Low-dimensional carbon sp3 materials at well-defined interfaces’, in collaboration with Prof. Klaus Müllen (MPI Mainz) and Prof. Thomas Frauenheim (University of. Bremen). The first publication from his fellowship "Edge Phonon Excitations in a Chiral Self-Assembled Supramolecular Nanoribbon" has been recently published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
Professor Carlos-Andres Palma has been awarded a Humboldt Research Fellowship for Experienced Researchers. The fellowship provides funding for international experts to make extended research visits to Germany. At IRIS Adlershof and at the physics department of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Prof. Palma will contribute with expertise in ultrahigh-vacuum variable temperature, low-temperature atomic force microscopy (AFM) and complementary surface analytics. Together with Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe’s group and co-hosted by Prof. Norbert Koch’s group, he will explore nanographane materials and their phonon properties in the project entitled ‘Low-dimensional carbon sp3 materials at well-defined interfaces’, in collaboration with Prof. Klaus Müllen (MPI Mainz) and Prof. Thomas Frauenheim (University of. Bremen). The first publication from his fellowship "Edge Phonon Excitations in a Chiral Self-Assembled Supramolecular Nanoribbon" has been recently published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters.
Carlos-Andres Palma (36) is associate professor of physics at the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS)–a leading research institute in condensed matter physics, contributing extensively to copper-and iron-based high-temperature superconductors, Weyl semimetals, the quantum anomalous Hall effect, topological insulators and related physics. Prior to joining the Institute of Physics, he worked at the TU Munich, the Max-Planck Institute for Polymer Research, ETH Zurich, University College London and the University of Strasbourg, where he completed his MSc and PhD in 2010.
His group is funded by the Thousand Youth Talent Plan, the CAS Instrument Development, the CAS Frontier Research Grant and Sino-German NSFC-DFG Grants. His research interests lie in the physics of precision molecular architectures at interfaces.
Anyone interested in learning more about Prof. Palma's exciting research can experience him as an invited speaker at the symposium IRIS 2019.
25.09.2019Quantum Futur Award 2019 for Aron Vanselow
 Aron Vanselow has been awarded the second prize of the Quantum Futur Award 2019 by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) for his master thesis on “Mid-infrared frequency-domain optical coherence tomography with undetected photons”. Mr. Vanselow did his work in the group “Nonlinear Quantum Optics”, led by Dr. Sven Ramelow, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof. Some results of this work were recently published in the journal Optics Letters and have already led to a patent.
Aron Vanselow has been awarded the second prize of the Quantum Futur Award 2019 by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) for his master thesis on “Mid-infrared frequency-domain optical coherence tomography with undetected photons”. Mr. Vanselow did his work in the group “Nonlinear Quantum Optics”, led by Dr. Sven Ramelow, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof. Some results of this work were recently published in the journal Optics Letters and have already led to a patent.
IRIS Adlershof warmly congratulates the young award winner.
more...
19.09.2019Royal Society of Chemistry Poster Prize for Valentin Reiter-Scherer
 Valentin Reiter-Scherer, doctoral student in the group of Jürgen P. Rabe, director of IRIS Adlershof was awarded the Royal Society of Chemistry Poster Prize at the Polydays 2019 of the Berlin-Brandenburg Association of Polymer Research (BVP) for his poster "Dynamic interactions of influenza A virus proteins hemagglutinin and neuraminidase with sialic acid revealed by Single Molecule Force Spectroscopy". Well deserved, Valentin!
Valentin Reiter-Scherer, doctoral student in the group of Jürgen P. Rabe, director of IRIS Adlershof was awarded the Royal Society of Chemistry Poster Prize at the Polydays 2019 of the Berlin-Brandenburg Association of Polymer Research (BVP) for his poster "Dynamic interactions of influenza A virus proteins hemagglutinin and neuraminidase with sialic acid revealed by Single Molecule Force Spectroscopy". Well deserved, Valentin!
05.09.2019ERC Starting Grant for Dr. Tim Schröder
 Dr. Tim Schröder, junior research group leader at the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and the Ferdinand-Braun-Institut, Leibniz-Institut fuer Höchstfrequenztechnik (FBH), was awarded an ERC Starting Grant and will receive EUR 1.5 million for five years.
Dr. Tim Schröder, junior research group leader at the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and the Ferdinand-Braun-Institut, Leibniz-Institut fuer Höchstfrequenztechnik (FBH), was awarded an ERC Starting Grant and will receive EUR 1.5 million for five years.
With his project QUERP "Quantum Repeater Architectures Based on Quantum Memories and Photonic Encoding", Mr. Schröder is researching the next generation of faster, safer and future-compatible communication at the interface of integrated quantum optics, communication and new material systems.
He can also use resources from IRIS Adlershof when working on this topic. We congratulate and look forward to the continuation of our good cooperation.
more...
19.07.2019Decision in the German Excellence Strategy
 The Berlin University Alliance has won funding as a group in the Universities of Excellence funding line of the German federal and state governments’ Excellence Strategy. The German Council of Science and Humanities announced the decision on July 19, 2019, in Bonn. The four Berlin partners – Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Technische Universität Berlin, and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin – submitted a joint proposal entitled Crossing Boundaries toward an Integrated Research Environment and in a highly competitive process were able to convince the reviewers of its feasibility.
The Berlin University Alliance has won funding as a group in the Universities of Excellence funding line of the German federal and state governments’ Excellence Strategy. The German Council of Science and Humanities announced the decision on July 19, 2019, in Bonn. The four Berlin partners – Freie Universität Berlin, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Technische Universität Berlin, and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin – submitted a joint proposal entitled Crossing Boundaries toward an Integrated Research Environment and in a highly competitive process were able to convince the reviewers of its feasibility.
more...
19.07.2019Article of IRIS junior research group leader Michael J. Bojdys published in Nature Communications
The IRIS junior research group leader Michael J. Bojdys and his international team have achieved a great success: Their article “Real-time optical and electronic sensing with a β-amino enone linked, triazine-containing 2D covalent organic framework” has been selected to be published in the renowned journal Nature Communications.
 Bojdys article deals with aromatic two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (2D COFs), which are a class of porous polymers that allow the precise incorporation of organic units into periodic structures.COFs can be chemically designed to incorporate particular surface functional groups which can be exploited to tune the optical and electronic properties. However, low stability towards chemical triggers has hampered their practical implementations.
Bojdys article deals with aromatic two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (2D COFs), which are a class of porous polymers that allow the precise incorporation of organic units into periodic structures.COFs can be chemically designed to incorporate particular surface functional groups which can be exploited to tune the optical and electronic properties. However, low stability towards chemical triggers has hampered their practical implementations.
Together with a team from the Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry of the Czech Academy of Sciences (Prague, Czech Republic), IRIS junior research group leader Michael J. Bojdys and his team from Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin have explored a new design principle for COFs that makes use of strong, overall conjugation and incorporation of donor-acceptor domains. In this study a new, a highly stable chemoresistant β-amino enone linked, triazine-containing COF was used as a real-time, reversible optical and electronic sensor for volatile acids and bases. The team was further able to conclude that the sensing capabilities of the COF was achieved by preferential protonation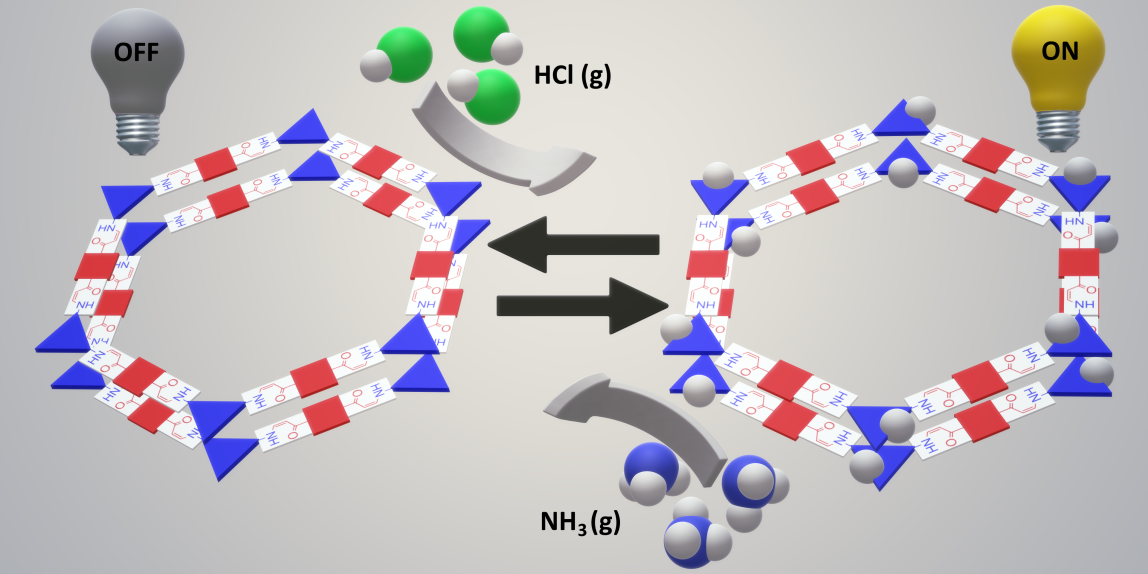 of the electron accepotor – a triazine ring in the structure – , resulting in an optical response visible to the naked eye and an increase of bulk electrical conductivity by two orders of magnitude. These findings demonstrate a powerful approach to design more practical sensors and switches, and take genuine advantage of the chemoresistant make-up, porous structure, and overall conjugation of fully-aromatic systems.
of the electron accepotor – a triazine ring in the structure – , resulting in an optical response visible to the naked eye and an increase of bulk electrical conductivity by two orders of magnitude. These findings demonstrate a powerful approach to design more practical sensors and switches, and take genuine advantage of the chemoresistant make-up, porous structure, and overall conjugation of fully-aromatic systems.
IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Michael J. Bojdys and his team on this successful study and its publication in Nature Communications!
Due to his great enthusiasm for the concept of IRIS Adlershof and the research carried out here, ERC-grant holder Bojdys joined the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and IRIS Adlershof in 2018 as leader of the junior research group “Functional Materials”. The group’s research aims at the development of metal-free, electronic components for transistors and sensors on the basis of functional materials made up of light, covalently-bonded atoms. At the heart of the project lies the challenge to transfer the control mechanisms and modularity known from molecular, organic chemistry to macroscopic structures.
Real-time optical and and electronic sensing with a β-amino enone linked, triazine-containing 2D covalent organic framework
R. Kulkarni, Y. Noda, D.K Barange, Y.S. Kochergin, P. Lyu, B. Balcarov, P. Nachtigall, and M.J. Bojdys
Nat. Commun 10 (2019) 3228
Click here for the press release of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin!
02.07.2019IRIS junior research group leader Michael J. Bojdys at the annual meeting of the new champions in Dalian (China)
 The European Research Council (ERC) brings pioneering science to the Annual Meeting of the New Champions (AMNC), also known as "Summer Davos", organised by the World Economic Forum (WEF) in Dalian, China, from 1 to 3 July. The 2019 edition will address the topic of "Leadership 4.0: Succeeding in a new era of globalization".
The European Research Council (ERC) brings pioneering science to the Annual Meeting of the New Champions (AMNC), also known as "Summer Davos", organised by the World Economic Forum (WEF) in Dalian, China, from 1 to 3 July. The 2019 edition will address the topic of "Leadership 4.0: Succeeding in a new era of globalization".
For the eighth year running, the ERC will take part with a delegation, composed of ERC President Prof. Jean-Pierre Bourguignon and ten ERC grantees, all leaders in their respective fields. Among these these ten ERC grantees is Dr. Michael J. Bojdys, junior research group leader at IRIS Adlershof and at the Chemistry Department of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
 Dr. Bojdys is pleased about the invitation to Dalian and summarizes his impressions: "The WEFfocused this year in particular on "Leadership 4.0" to deliver on sustainable development goals. The technology for sustainable electronics, smart energy storage, food security and healthier living is out there, sponsored by tax-payer's money via the ERC, for example, who are supporting my research. But most scientists lack the business literacy to bring their projects to the market. WEF and ERC identify the need for (1) better business training of scientists - that means: can you deliver an "elevator pitch" on the impact of your research on society? Can you make the same pitch to funders? (2) Better funding instruments to develop prototype devices - here, the ERC is leading with the ERC "Proof of Concept" grant scheme that pays not only for prototype development but also for a market study, and (3) how can we help scientists find the right type of funders for their pre-IPO [initital public offering] projects - an exciting new initiative by the ERC is the "Virtual Ventures Fair" that aims to bring scientists that succesfully resolved their "Proof of Concept" grants together with investors. I am particularly looking forward to work together with the new leadership of the ERC on the "Virtual Ventures Fair" project - if there's anything we know as scientists, then it is to contribute expert opinions via peer-review."
Dr. Bojdys is pleased about the invitation to Dalian and summarizes his impressions: "The WEFfocused this year in particular on "Leadership 4.0" to deliver on sustainable development goals. The technology for sustainable electronics, smart energy storage, food security and healthier living is out there, sponsored by tax-payer's money via the ERC, for example, who are supporting my research. But most scientists lack the business literacy to bring their projects to the market. WEF and ERC identify the need for (1) better business training of scientists - that means: can you deliver an "elevator pitch" on the impact of your research on society? Can you make the same pitch to funders? (2) Better funding instruments to develop prototype devices - here, the ERC is leading with the ERC "Proof of Concept" grant scheme that pays not only for prototype development but also for a market study, and (3) how can we help scientists find the right type of funders for their pre-IPO [initital public offering] projects - an exciting new initiative by the ERC is the "Virtual Ventures Fair" that aims to bring scientists that succesfully resolved their "Proof of Concept" grants together with investors. I am particularly looking forward to work together with the new leadership of the ERC on the "Virtual Ventures Fair" project - if there's anything we know as scientists, then it is to contribute expert opinions via peer-review."
more...
05.06.2019Organic electronics: a novel semiconductor from the family of carbon nitrides
Research teams from the Humboldt-Universität and the Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (HZB) have investigated a new material from the family of carbon nitrides. Triazine-based graphitic carbon nitride (TGCN) is a semiconductor that is useful in optoelectronic applications. Its structure is two-dimensional and layered, and it resembles that of graphene. Unlike graphene, its conductivity between the layers is 65-times higher than in-plane.
 Some organic materials can be used in optoelectronics just like silicon-based semiconductors. Whether in solar cells, light-emitting diodes, or as transistors – the important property is the bandgap, i.e. the energy-difference of the electrons in the valence band and the conduction band. The basic principle underlying all electronic components is that electrons can be promoted by light or by voltage between the valence and the conduction band. Here, bandgaps between 1 and 2 eV are ideal.
Some organic materials can be used in optoelectronics just like silicon-based semiconductors. Whether in solar cells, light-emitting diodes, or as transistors – the important property is the bandgap, i.e. the energy-difference of the electrons in the valence band and the conduction band. The basic principle underlying all electronic components is that electrons can be promoted by light or by voltage between the valence and the conduction band. Here, bandgaps between 1 and 2 eV are ideal.
A team led by the chemist Dr. Michael J. Bojdys from the chemistry department and IRIS Adlershof of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, has recently synthesized an organic semiconductor from the family of carbon nitrides. This triazine-based graphitic carbon nitride (TGCN) consists exclusively from carbon and nitrogen atoms and can be grown as a brown film on quartz glass substrates. The C- and N-atoms connect in hexagonal, honeycomb patterns like carbon atoms in graphene. Just like in graphene, the crystal structure of TGCN is based on layered, two-dimensional sheets. In graphene, in-plane conductivity is excellent, however, it is much lower through the planes. In the case of TGCN, the opposite is observed: through-plane conductivity is 65-times higher than in-plane. With a bandgap of 1.7 eV TGCN is a good candidate for optoelectronic applications.
The HZB-physicist Dr. Christoph Merschjann has examined the charge carrier transport in samples of TGCN using time-resolved absorption measurements in the femto- to nanosecond regime at the laser lab JULiq – a joint lab between the HZB and the Freie Universität Berlin. Such laser experiments offer a unique way to correlate macroscopic conductivity and microscopic transport models. From his measurements, he was able to deduce how the charge carriers diffuse throughout the material. “Electrons do not exit the hexagonal honeycombs of triazine units horizontally, but they move at a slope to the nearest triazine-unit in the neighboring layer. The crystal structure of the material leads to a preferred movement of charge carriers along tube-like channels.” This mechanism could explain why the conductivity of TGCN is fundamentally higher through-plane than in-plane. “TGCN is the hitherto best candidate to replace silicon semiconductors and the critical, rare-earth dopants used in their manufacture”, says Michael Bojdys. “The production method for TGCN that we developed in my group at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin yields flat layers of semiconducting TGCN on insulating quartz glass. This enables relatively easy upscaling and device production.”
04.06.2019New scientific management at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin
 As of 1 June 2019, Prof. Dr. Bernd Rech and Prof. Dr. Jan Lüning are the new scientific directors of Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie. Bernd Rech is responsible for the “Energy and Information” department and Jan Lüning heads the “Matter” department. Thus the HZB Supervisory Board has appointed two internationally recognised experts at the top of HZB.
As of 1 June 2019, Prof. Dr. Bernd Rech and Prof. Dr. Jan Lüning are the new scientific directors of Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie. Bernd Rech is responsible for the “Energy and Information” department and Jan Lüning heads the “Matter” department. Thus the HZB Supervisory Board has appointed two internationally recognised experts at the top of HZB.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates and looks forward to the continuation of the close scientific collaboration.
more...
31.05.201914th International Symposium on Functional π-Electron Systems in the Berlin-Adlershof Science and Technology park
 The “14th International Symposium on Functional π-Electron Systems” is part of a regular international conference series that began in 1989 in Osaka, Japan. The 14th edition of this series is jointly organized by the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie GmbH (HZB) and IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. It takes place 2nd - 7th June 2019 in the Berlin-Adlershof Science and Technology park, with over 400 participants. The scientific program is co-organized by Prof. Stefan Hecht (Department of Chemistry of HU) and Prof. Norbert Koch (Department of Physics of HU). Both are members of IRIS Adlershof.
The “14th International Symposium on Functional π-Electron Systems” is part of a regular international conference series that began in 1989 in Osaka, Japan. The 14th edition of this series is jointly organized by the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie GmbH (HZB) and IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. It takes place 2nd - 7th June 2019 in the Berlin-Adlershof Science and Technology park, with over 400 participants. The scientific program is co-organized by Prof. Stefan Hecht (Department of Chemistry of HU) and Prof. Norbert Koch (Department of Physics of HU). Both are members of IRIS Adlershof.
The symposium focuses on:
- design and synthesis of new π-conjugated molecules and polymers,
- organic and polymeric semiconducting materials for thin film transistors,
- organic and polymeric photovoltaic and photo-responsive materials and devices,
- organic light-emitting materials for display and lighting application,
- hybrid and perovskite materials and devices,
- conjugated polymers and oligomers in chemo/bio-sensors, and
- bioelectronics.
more...
23.05.2019CRC 951 “Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)” successful to launch third funding period
 The Collaborative Research Centre 951 "Hybrid Inorganic / Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics" (HIOS) will receive funding for another four years. This was decided by the German Research Foundation (DFG) at this years’ spring meeting in Bonn.
The Collaborative Research Centre 951 "Hybrid Inorganic / Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics" (HIOS) will receive funding for another four years. This was decided by the German Research Foundation (DFG) at this years’ spring meeting in Bonn.
Since its establishment in 2011, the development and investigation of innovative hybrid systems has been the scientific focus of the CRC 951. These hybrid systems combine inorganic semiconductors, conjugated organic materials, and metal nanostructures with long-term goal to realize novel and superior opto-electronic functions in the meso- or nanoscopic range not achievable with any of the individual material classes alone. These functionscould be used, for example, in high-frequency and multi-colored light sources and sensors, as well as electronic and optical multifunctional devices of future generations of information technology.
In the past years, the CRC elucidated the fundamental chemical, electronic, photonic, and plasmonic interactions arising from the different nature of the components combined in HIOS. As one of many results, novel hybridized quantum states and coupled excitations at the inorganic/organic interfaces were uncovered. These impressive results laid the foundation for the next four years of exciting HIOS-research.
The German Research Foundation (DFG) has now acknowledged the achievements of the CRC 951 by granting a third funding period for 2019 – 2023. The CRC's spokesperson and deputy spokesperson, Norbert Koch and Oliver Benson (both members of IRIS Adlershof) look forward to the joint work with 21 principal investigators from physics and chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (coordinating university), Technische Universität Berlin, Freie Universität Berlin, Universität Potsdam, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie, and Fritz-Haber-Institut der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft.
18.05.2019Berlin's cluster of excellence MATH+ established
you can find more information about the cluster of excellence MATH+ here.
13.05.2019Qiankun Wang receives 2018 Chinese Government Award

Outstanding Self-financed Students Abroad” of the China Scholarship Council.
Well deserved, Qiankun!
03.05.2019Dr. Valentina Forini was awarded an Einstein Junior Fellowship
.jpg) Valentina Forini is a theoretical physicist who conducts research in the field of mathematical physics with a focus on string and quantum field theory. She specializes in the Anti-de-Sitter/Conformal Field Theory correspondence, hence the study of space-time-matter. Her contributions to string and gauge field theory are internationally recognised. From 2012 to 2017 Valentina Forini was group leader of an Emmy Noether Research Group at the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
Valentina Forini is a theoretical physicist who conducts research in the field of mathematical physics with a focus on string and quantum field theory. She specializes in the Anti-de-Sitter/Conformal Field Theory correspondence, hence the study of space-time-matter. Her contributions to string and gauge field theory are internationally recognised. From 2012 to 2017 Valentina Forini was group leader of an Emmy Noether Research Group at the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
Since then, Forini has been engaged in several research projects at IRIS Adlershof. Meanwhile Valentina Forini has been awarded a 2018/19 Simons Emmy Noether Fellowship at Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics in Canada. At IRIS she is also project leader for the European Marie-Curie ITN network Europlex. Moreover, Forini is a lecturer in Mathematics at City University London.
Now, Ms Forini has been awarded an Einstein Junior Fellowship by the Einstein Foundation Berlin. IRIS Adlershof congratulates Ms. Forini warmly and looks forward to further cooperation.
more...
29.03.2019Prof. Thomas Elsässer receives an ERC Advanced Grant
 Professor Thomas Elsaesser receives a prestigious Advanced Grant from the European Research Council (ERC) which supports, for a period of 5 years, basic research on dynamic electric interactions of DNA and RNA with ions and their water environment. The ERC Advanced Grant is endowed with up to 2.5 million euro and awarded to top researchers in Europe pursuing groundbreaking high-risk projects in science..
Professor Thomas Elsaesser receives a prestigious Advanced Grant from the European Research Council (ERC) which supports, for a period of 5 years, basic research on dynamic electric interactions of DNA and RNA with ions and their water environment. The ERC Advanced Grant is endowed with up to 2.5 million euro and awarded to top researchers in Europe pursuing groundbreaking high-risk projects in science..
Thomas Elsaesser is a director at the Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy, a professor for experimental physics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and a member of IRIS Adlershof. With his research on ultrafast phenomena in condensed matter, including liquids, biomolecular systems, and crystalline materials, he plays a leading role in ultrafast science worldwide. In his experiments, he combines methods of femtosecond spectroscopy and structure research with x-rays. He has received numerous awards for his scientific work, among them a first ERC Advanced Grant in 2009.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates and looks forward to the further close cooperation.
more...
19.03.20198th „Nano and Photonics“ meeting in the Castle of Mauterndorf, Austria
 From 20.3.-22.3.2019 Wolfgang Knoll (Austrian Institute of Technology), Franz Aussenegg (Universität Graz and Erwin-Schrödinger Institute) and Emil J.W. List-Kratochvil (Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Member of IRIS Adlershof) jointly organize the 8th “Nano and Photonics” meeting in the Castle of Mauterndorf, Austria.
From 20.3.-22.3.2019 Wolfgang Knoll (Austrian Institute of Technology), Franz Aussenegg (Universität Graz and Erwin-Schrödinger Institute) and Emil J.W. List-Kratochvil (Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Member of IRIS Adlershof) jointly organize the 8th “Nano and Photonics” meeting in the Castle of Mauterndorf, Austria.
This year’s program was put together with a topical focus on “Sensing applications based on plasmonic nanostructures and on Photovoltaic Technologies“. Invited speakers include S. Kawata from Osaka University, B. Hecht from Universität Würzburg, und T. Dimopoulos from the Austrian Institute of Technology, and many others.
The purpose of this event is to organize an international scientific meeting for those, who are interested in photonic applications of modern nanotechnology. One goal of this event is also to create an informal European wide discussion platform for state of the art work in basic research done at the various universities as well as industrial based research and development. The location, Castle Mauterndorf, provides an ideal environment to discuss the entire range of topics without any pressure of time, in particular between the morning and afternoon sessions as well as in the evening. This year again it is expected to gather 80 participants from 7 different countries.
more...
27.02.2019Cluster of Excellence Matters of Activity ventures on a new culture of the material
 In the Cluster of Excellence "Matters of Activity. Image Space Material", researchers from more than 40 disciplines collaborate in six subprojects to lay the foundations for a new way of thinking of the material. Key to this endeavour is the vision of re-thinking the object world not like commonly done as passive and rigid, but as based on active, changeable and recyclable building materials. Adaptive fiber architectures and complex structured biofilms are among the sources of inspiration for novel designs in the future. The cluster of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is conceptually close to the Bauhaus as well as to the academic movement of New Materialism. The members of IRIS Adlershof Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe and Prof. Matthias Staudacher are involved as principal investigators in the cluster.
In the Cluster of Excellence "Matters of Activity. Image Space Material", researchers from more than 40 disciplines collaborate in six subprojects to lay the foundations for a new way of thinking of the material. Key to this endeavour is the vision of re-thinking the object world not like commonly done as passive and rigid, but as based on active, changeable and recyclable building materials. Adaptive fiber architectures and complex structured biofilms are among the sources of inspiration for novel designs in the future. The cluster of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is conceptually close to the Bauhaus as well as to the academic movement of New Materialism. The members of IRIS Adlershof Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe and Prof. Matthias Staudacher are involved as principal investigators in the cluster.
more..
18.02.2019Enlightening full-color displays
Researchers from the University of Strasbourg & CNRS (France), in collaboration with University College London (United Kingdom), and Humboldt University Berlin (Germany), have shown that a subtle combination of light-emitting semiconducting polymers and small photoswitchable molecules can be used to fabricate light-emitting organic transistors operating under optical remote control, paving the way to the next generation of multifunctional optoelectronic devices. These achievements have now been published in Nature Nanotechnology.
 Organic light-emitting transistors are widely recognized as key components in numerous optoelectronic applications. However, the integration of multiple functionalities into a single electronic device remains a grand challenge in this technological sector. Moreover, the next generation of displays requires to encode high-density visual information into single and ultra-small pixels.
Organic light-emitting transistors are widely recognized as key components in numerous optoelectronic applications. However, the integration of multiple functionalities into a single electronic device remains a grand challenge in this technological sector. Moreover, the next generation of displays requires to encode high-density visual information into single and ultra-small pixels.
Now a team of researchers from Strasbourg, London, and Berlin has taken a big step forward by creating the first organic light-emitting transistor that can be remote-controlled by light itself. They have been blending a custom-designed molecule as a miniaturized optical switch with a light-emitting semiconducting polymer. Upon illumination with ultraviolet and visible light, the molecular switch reversibly changes its electronic properties. As a consequence, the electrical and optical response of the device can be modulated simultaneously by light, which serves as an optical remote control.
However, having a device capable of producing only one color is not sufficient for daily-life applications, such as full-color displays. By choosing appropriate photoswitchable molecules and blending them with suitable light-emitting polymers, the researchers have demonstrated that this new type of organic light-emitting transistors can shine in the range of the three primary colors (red, green, and blue), thereby covering the entire visible spectrum.
The disruptive potential of such approach was demonstrated by writing and erasing spatially defined emitting patterns (a letter for example) within a single device with a beam of laser light, allowing a non-invasive and mask-free process, with a response time on the microsecond scale and a spatial resolution of a few micrometers, thus outperforming the best “retina” displays. Clearly, these findings represent a major breakthrough that offers multiple perspectives for smart displays, active optical memories, and light-controlled logic circuits.
more...
18.01.2019Twelve positions for outstanding researchers and designers
 The Cluster of Excellence "Matters of Activity" is looking for PostDocs on "Molecular Filtering" and "Sensing Knife". Applications until January 22nd!
The Cluster of Excellence "Matters of Activity" is looking for PostDocs on "Molecular Filtering" and "Sensing Knife". Applications until January 22nd!
mehr...
10.12.2018Perspectives on Switchable Systems and Materials for Smart Electronics
 Since 2015 the EU-funded Integrated Training Network "iSwitch" has been bringing together some of the leading European research groups at the interface of chemistry and physics to train the next generation researchers on the the emerging topic of smart electronics. The final symposium of the network organized by Prof. Stefan Hecht and Prof. Norbert Koch, both members of IRIS Adlershof, will highlight key achievements and discuss future perspectives in this burgeoning area of research.
Since 2015 the EU-funded Integrated Training Network "iSwitch" has been bringing together some of the leading European research groups at the interface of chemistry and physics to train the next generation researchers on the the emerging topic of smart electronics. The final symposium of the network organized by Prof. Stefan Hecht and Prof. Norbert Koch, both members of IRIS Adlershof, will highlight key achievements and discuss future perspectives in this burgeoning area of research.
05.11.2018Distinguished Professor Rich Spontak visits IRIS Adlershof
 Distinguished Professor Rich Spontak from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of North Carolina State University visits IRIS Adlershof from November 05th to December 02nd as a guest professor of the Cluster of Excellence Image Knowledge Gestaltung within the project Experimental Systems. Professor Spontak’s focus areas in research are polymer morphology and phase stability, multifunctional and nanostructured polymers, blends and networks, and the application of microscopy techniques to polymer science and engineering. On November 19th, he will speak at an IRIS seminar on "Designing selective membranes from the ground-up: A Polymer Scientists Playground".
Distinguished Professor Rich Spontak from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of North Carolina State University visits IRIS Adlershof from November 05th to December 02nd as a guest professor of the Cluster of Excellence Image Knowledge Gestaltung within the project Experimental Systems. Professor Spontak’s focus areas in research are polymer morphology and phase stability, multifunctional and nanostructured polymers, blends and networks, and the application of microscopy techniques to polymer science and engineering. On November 19th, he will speak at an IRIS seminar on "Designing selective membranes from the ground-up: A Polymer Scientists Playground".
08.10.2018New BMBF junior research group “Diamond Nanophotonics for On-Chip Quantum Technology” as part of the BMBF Quantum Future funding
 Since October Dr. Tim Schröder has been forming a junior research group on “Spin-defect centers in nanophotonic circuits for quantum information processing” at the Physics Department of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. His group will be funded by a five-year BMBF project “Diamond nanophotonics for on-chip quantum technology” within the framework of the program Quantum Futur. Before his return, Dr. Schröder who finished his doctoral studies at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin in 2012 spent the last four years as a researcher at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT, USA) and two years as an assistant professor at the Niels Bohr Institute (NBI, Denmark) where he worked on hybrid integrated photonic systems to control individual spin-based quantum memories in diamonds and gallium arsenide. His research was awarded the Carl Ramsauer Prize and has been funded by a Feodor Lynen scholarship from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation and a Marie Sklodowska Curie fellowship from the European Union. At Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Dr. Schröder will continue to work on these topics while taking advantage of the resources that IRIS Adlershof has to offer. For example, he will collaborate closely with the nano optics research group of Prof. Oliver Benson who is also an IRIS member.
Since October Dr. Tim Schröder has been forming a junior research group on “Spin-defect centers in nanophotonic circuits for quantum information processing” at the Physics Department of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. His group will be funded by a five-year BMBF project “Diamond nanophotonics for on-chip quantum technology” within the framework of the program Quantum Futur. Before his return, Dr. Schröder who finished his doctoral studies at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin in 2012 spent the last four years as a researcher at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT, USA) and two years as an assistant professor at the Niels Bohr Institute (NBI, Denmark) where he worked on hybrid integrated photonic systems to control individual spin-based quantum memories in diamonds and gallium arsenide. His research was awarded the Carl Ramsauer Prize and has been funded by a Feodor Lynen scholarship from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation and a Marie Sklodowska Curie fellowship from the European Union. At Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Dr. Schröder will continue to work on these topics while taking advantage of the resources that IRIS Adlershof has to offer. For example, he will collaborate closely with the nano optics research group of Prof. Oliver Benson who is also an IRIS member.
The overall scientific goal of the project “Diamond Nanophotonics for On-Chip Quantum Technology” is to combine defect centers in diamonds and nanophotonic structures into compact, hybrid on-chip modules and then to demonstrate their operational interconnections, which will be a crucial step towards quantum information processes based on optically active solid state materials. Defect centers that interconnect with high rates form the basis for quantum networks, which can be used for remote quantum communication or complex quantum computing. IRIS Adlershof wishes Dr. Schröder much success in obtaining these goals and is looking forward to a fruitful collaboration.
02.10.2018The President of Universidade de São Paulo visits Adlershof
 The president of the Universidade de São Paulo (USP), Professor Vahan Agopyan, as well as USP’s vice-president for International Relationships, Professor Raul Machado Neto, visited within the framework of a several day Berlin stay to inform themselves as well about the current study conditions and opportunities to do research at the natural science campus of Humboldt-University zu Berlin (HU).
The president of the Universidade de São Paulo (USP), Professor Vahan Agopyan, as well as USP’s vice-president for International Relationships, Professor Raul Machado Neto, visited within the framework of a several day Berlin stay to inform themselves as well about the current study conditions and opportunities to do research at the natural science campus of Humboldt-University zu Berlin (HU).
Prof. Jan Plefka, the vice dean for research at the HU’s mathematics and natural science department and a member of IRIS Adlershof, and Dr. Nikolai Puhlmann, IRIS’s managing director, gave an overview of the HU’s natural science campus and IRIS Adlershof’s concept and development. They also gave details on the IRIS research building still under construction. Prof. Ulf Leser and Prof. Henning Meyerhenke from the Department of Computer Science informed the guests about their department’s current research plans and projects.
 The HU and USP’s jointly run international research training group IGRT 1740 „Dynamical Phenomena in Complex Networks: Fundamentals and Applications“ was introduced to the guests in detail by the research training group’s speaker, Prof. Jürgen Kurths (Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and HU Berlin). At the end of their visit, the guests saw the prototype of a Cherenkov telescope that is being erected in Adlershof within the framework of the international major project „Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA)“ in which the HU and USP are both participating. Prof. Thomas Lohse from the Department of Physics at the HU described how the telescope functioned and the scientific focus of the CTA project.
The HU and USP’s jointly run international research training group IGRT 1740 „Dynamical Phenomena in Complex Networks: Fundamentals and Applications“ was introduced to the guests in detail by the research training group’s speaker, Prof. Jürgen Kurths (Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and HU Berlin). At the end of their visit, the guests saw the prototype of a Cherenkov telescope that is being erected in Adlershof within the framework of the international major project „Cherenkov Telescope Array (CTA)“ in which the HU and USP are both participating. Prof. Thomas Lohse from the Department of Physics at the HU described how the telescope functioned and the scientific focus of the CTA project.
The São Paulo guests were very interested in and impressed by the progress made in the HU’s research results and praised the diverse opportunities that Adlershof science site has to offer for top-ranking natural science research and the education of international young scientists.
The Universidade de São Paulo (USP) is one of three strategic profile partners of the Humboldt University and consistently ranks one of the top universities in the South American subcontinent.
01.10.2018Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) promotes a joint project for fast and secure communication
Digitization permeates our entire society - from Industry 4.0 to healthcare applications. Data security and secure communication are becoming increasingly important. Quantum communication is a promising approach for this: It uses quantum states as information carriers, which can not be copied or unnoticed due to fundamental physical laws. The Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) is supporting this departure into quantum technology by funding the joint project Quantum Link Expansion (Q.Link.X) with a total of 14.8 million euros over the next three years. The working groups of IRIS Adlershof member Prof. Oliver Benson and IRIS Adlershof young research group leader Sven Ramelow are involved.
The goal of the collaborative project is physically tap-proof fiber optic networking. However, this paradigm shift in message encryption away from conventional methods and towards quantum technology encounters a technological challenge: transmission of quantum information with light particles (photons) leads to unavoidable line losses, limiting transmission distances to less than 100 kilometers. With quantum repeaters, this limit should be overcome without security restrictions. Repeaters (repeater stations) are signal amplifiers and conditioners in communication technology. Unlike these repeaters, however, the quantum repeater has to connect signals from different sections using quantum processes in order to bridge larger distances.
The joint project Quantum Link Extension (Q.Link.X) is now intended to promote the development of such quantum repeaters, which use quantum memory and quantum couplers. In the next three years, the Federal Ministry of Education and Research is supporting this move into quantum technology with a total of 14.8 million euros. With quantum dots, diamond color centers and a combination of atomic and ionic systems as three different technical platforms, transmission distances between ten and 100 kilometers are to be realized and the advantages of the respective systems compared to each other. The work should prepare the technology to bridge much longer distances in later phases. For the first time, Q.Link.X not only researches and develops individual components of a quantum repeater, but also entire communication routes.
In the Q.Link.X network, 24 partners from research institutions from universities to industrial laboratories have come together to explore the key technology of quantum repeaters. The close involvement of industrial partners and consultants should facilitate the feasibility from an industrial and engineering perspective from the outset. The exploitation of earnings in Germany is to be secured by patents and spin-offs of the consortium.
24 partners are driving Q.Link.X togetherThe following partners are involved in the project: Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-University Bonn, Technical University Munich, Technical University Dortmund, High Finesse Laser and Electronic Systems GmbH, Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute Berlin, Technical University Berlin, University of Stuttgart, University of Paderborn, University Saarland, Freie Universität Berlin, Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research Dresden, Ruhr University Bochum, Swabian Instruments GmbH, Leibniz University Hannover, Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics (Garching), Julius-Maximilians-University Würzburg, University of Bremen , Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf, University of Ulm, Humboldt University Berlin, University of Kassel, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich.
more...28.09.2018Outstanding Berlin Science: Seven excellence clusters for the Berlin University Alliance
Seven Cluster of Excellence in the Excellence Strategy of the Federal Government and the Länder approved for the Berlin University Alliance. Members of IRIS Adlershof participate in the following clusters as PIs:
Matters of Activity: Image Space Material - A new culture of material (Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe, Prof. Matthias Staudacher)
MATH+ - How Berlin mathematics is shaping the future (Prof. Michael Hintermüller)
Unifying Systems in Catalysis (UniSysCat) - How to Understand and Utilize Networks in Catalysis (Prof. Stefan Hecht, Prof. Christian Limberg)
We congratulate the participating researchers and look forward to a good cooperation!
28.09.2018Falling Walls Lab with two IRIS-Junior Scientists
Great minds, 3 minutes, 1 day:
On September 28, 2018, 18 junior researchers and young professionals will present their research projects, ideas and initiatives in 3 minutes each. The winner of this preliminary decision will receive an invitation to the final in Berlin on 8 November and the opportunity to participate in the Falling Walls Conference.
In addition to 16 other participants, two junior scientists from IRIS Adlershof will also be taking part: Inna Kviatkovsky from the group of Sven Ramelow, who already won the IRIS Roots Day 2017, and Wadim Wormsbecher from the group of Jan Plefka.
The event will take place at BAM (Richard-Willstätter-Straße 15, 12489 Berlin) on Friday, September 28, at 11:00 - 14:00. Admission is free.
We look forward to an exciting event and keep our fingers crossed for our researchers.21.09.2018Elternzeitvertretung für IRIS-Geschäftsstelle gesucht
Die IRIS-Geschäftsstelle sucht eine Elternzeitvertretung, vorauss. befristet bis 30.11.2019.
mehr...
10.09.2018Dr. Olaf Hohm comes to the HU with an ERC-Grant
The Mathematical Physicist Olaf Hohm, who acquired an ERC Consolidator Grant for his research project "Duality Symmetries, Higher Derivatives and their Applications in Cosmology", has moved to the Department of Physics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Previously, he received a "Heisenberg scholarship from the DFG and worked at MIT in Boston and at Stony Brook University in New York. His current research interest is the development of a string-theoretical approach to answer questions about the beginning of the universe purely arithmetically. He will work closely with the IRIS member groups Prof. Jan Plefka and Prof. Matthias Staudacher. Dr. Hohm presents his research at 26.10.2018, 1:15 pm in the IRIS-building, room 2'07.
IRIS Adlershof is looking forward to a fruitful cooperation!
05.09.2018Dr. David Bléger joins CREAVIS, the strategic innovation unit of EVONIK
.jpg) IRIS junior research group leader David Bléger joins CREAVIS, the strategic innovation unit of EVONIK. After studying and working in France, he joined IRIS member Stefan Hecht as a postdoc in 2009 and started his own working group in 2013. He is an expert in the design and manufacture of molecules, polymers and various organic materials that respond to chemical and physical stimuli.
IRIS junior research group leader David Bléger joins CREAVIS, the strategic innovation unit of EVONIK. After studying and working in France, he joined IRIS member Stefan Hecht as a postdoc in 2009 and started his own working group in 2013. He is an expert in the design and manufacture of molecules, polymers and various organic materials that respond to chemical and physical stimuli.
IRIS Adlershof wishes you lots of success!
31.08.2018Egon Steeg successfully defended his dissertation
IRIS Junior Scientist Egon Steeg successfully defended his dissertation "Investigations on growth and structure of silver and silver halide nanostructures formed on amphiphilic dye aggregates". His research was supported by CRC 951 "Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)" and supervised by PD Dr. Stefan Kirstein in the group of IRIS-Director Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates!
22.08.2018Printing solar cells and organic LEDs - HZB & HU cooperate
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin form a joint lab and research group “Generative production processes for hybrid components”.
Solar cells, LEDs and detectors made of organic and hybrid semiconductors can nowadays be simply printed out, even together with teensy nanostructures that make them function better. The development of low-cost printing methods for electronic and optoelectronic components is at the centre of things for the new joint research group and the joint laboratory of the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB) and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU).
 |
|
|
The HySPRINT logo (Helmholtz Innovation Lab) printed on a copper solution symbolizes how the thinnest material layers can be produced simply and cost-effectively. Possible applications are solar cells, organic LEDs or transistors. Photo credit: Humboldt Universität zu Berlin/List-Kratochvil |
Cooperating together in the new research group are the HU workgroup “Hybrid Devices” led by Prof. Dr. Emil List-Kratochvil, the HZB young investigator group of Dr. Eva Unger, the Helmholtz Innovation Lab HySPRINT, and the Competence Centre Photovoltaics Berlin (PVcomB) directed by Prof. Dr. Rutger Schlatmann. The partners are building up a joint lab at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin that will allow the researchers to acquire and use complementary laboratory infrastructures for various coating methods.
Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil is the head of the HU workgroup “Hybrid Devices” at IRIS Adlershof, and has been working for 15 years on developing electronic and optoelectronic hybrid components, resource-efficient deposition techniques (inkjet printing) and in-situ nanostructuring and synthetic methods. This expertise complements the aims of the HZB young investigator group led by Dr. Eva Unger. She will be developing solution-based manufacturing methods for depositing perovskite semiconductor layers onto larger surface areas for solar cells. “The new research group with List-Kratochvil is a real win for us. With his experience in printed electronic components, he is an ideal cooperation partner for us,” Unger says.
In recent months, the researcher and her team have already come much closer to her goal of developing hybrid tandem solar cells with large-surface-areas in the scope of the Helmholtz Innovation Lab HySPRINT. Now, the next step is to upscale the process in order to drive the novel solar cells towards market maturity. The Competence Centre Thin-Film- and Nanotechnology for Photovoltaics Berlin (PVcomB) is the ideal partner for the development of industrially relevant manufacturing processes. The joint research group is now striving towards building a pilot line on which to develop prototypes of hybrid components.
- Helmholtz Innovation Lab HySPRINT
- HU-Group 'Hybride Devices' directed by Prof. Dr. Emil List-Kratochvil
- HZB Young Investigator Group 'Hybrid Materials Formation and Scaling’ directed by Dr. Eva Unger
- Competence Centre Photovoltaics Berlin directed by Prof. Dr. Rutger Schlatmann
21.08.2018Michael N. Borinsky’s dissertation will be released by Springer Theses

The dissertation of Dr. Michael N. Borinsky was selected to be published in Springer Theses, a dedicated book series to recognize outstanding doctoral research and received an reasearch award worth 500 €. Borinsky was IRIS Junior Scientist and supervised by IRIS-Member Prof. Dirk Kreimer.
"This thesis provides an extension of the work of Dirk Kreimer and Alain Connes on the Hopf algebra structure of Feynman graphs and renormalization to general graphs. Additionally, an algebraic structure of the asymptotics of formal power series with factorial growth, which is compatible with the Hopf algebraic structure, will be introduced. [...] [Part of these] structures are motivated by and used to analyze renormalized zero-dimensional quantum field theory at high orders in perturbation theory. As a pure application of the Hopf algebra structure, an Hopf algebraic interpretation of the Legendre transformation in quantum field theory is given."
IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Michael Borinsky and wishes him much success in his future work.1
Dr. Michael Norbert BorinskyGraphs in Perturbation Theory: Algebraic Structure and Asymptotics
Springer Theses, Springer (angekündigt)
PhD thesis "Graphs in perturbation theory: Algebraic structure and asymptotics"
DOI: 10.18452/19201, arXiv: arXiv:1807.02046 [hep-th], 1edoc-HU: 18452/19952
13.08.2018Light-controlled molecules: Scientists develop new recycling strategy
Discovery lays the foundation for recycling of yet non-recyclable plastics.
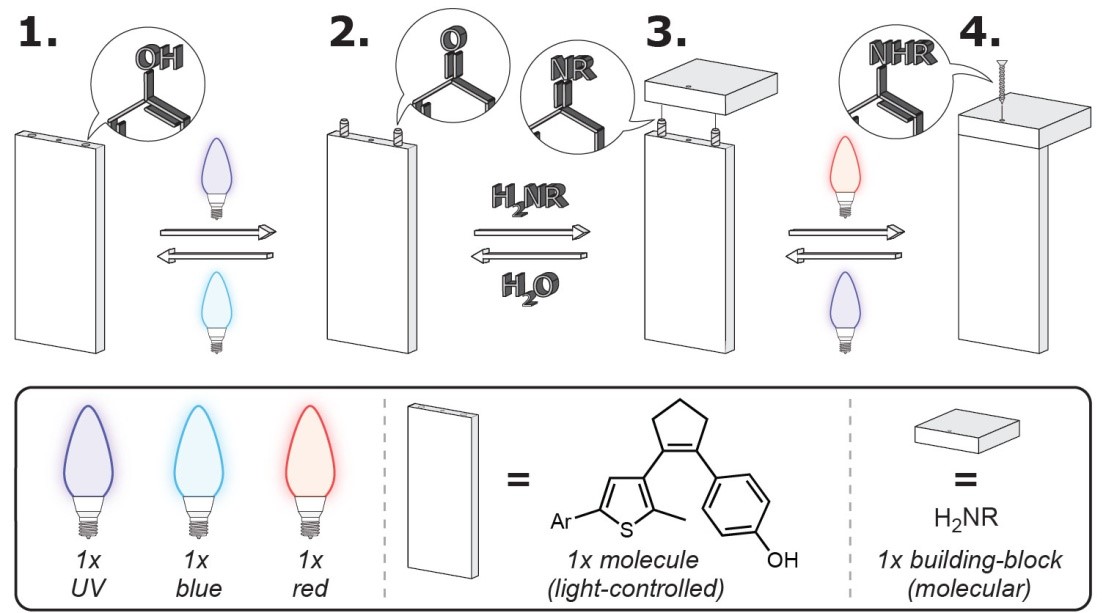
Robust plastics are composed of molecular building-blocks, held together by tough chemical linkages. Their cleavage is extremely difficult to achieve, rendering the recycling of these materials almost impossible. A research team from the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) developed a molecule, which can drive or reverse specific chemical reactions with light of different colors. This enables making and breaking of connections on the molecular scale, even if they are exceptionally strong. The discovery paves the way for the development of novel recycling methods and sustainable materials. Light-driven recovery of individual molecular building-blocks has great potential to enable recycling of yet non-recyclable plastics without compromising on color, quality, or shape.
"The working principle of our system is quite similar to the one of ready-to-assemble furniture” explain Michael Kathan and Fabian Eisenreich, the two first authors of this study. “We are able to repetitively assemble or disassemble molecular architectures, but instead of a hammer and screw-driver, we use red and blue LEDs as tools to control our molecules."
The results of their study have just been published in Nature Chemistry
Further Information
Publication
“Light-driven molecular trap enables bidirectional manipulation of dynamic covalent systems”
by: Michael Kathan, Fabian Eisenreich, Christoph Jurissek, Andre Dallmann, Johannes Gurke, and Stefan Hecht
in: Nature Chemistry (2018), DOI: 10.1038/s41557-018-0106-8
24.07.2018Professor Jan Plefka gets Creating Opportunities funding
 The Humboldt-Universität opens up time for reflection and concentration on new research concepts, as well as the opportunity to exchange ideas, to read and to write without the distraction of everyday responsibilities with its funding line Creating Opportunities. Among the five professors is Prof. Jan Plefka, whi is a member of IRIS Adlershof. His mandatory teaching assignments will be covered by a visiting lecturer for the winter term 2018/19 and Jan Plefka will use the time gained for exploring the Generalized Unitarity for Gravitational Waves:
The Humboldt-Universität opens up time for reflection and concentration on new research concepts, as well as the opportunity to exchange ideas, to read and to write without the distraction of everyday responsibilities with its funding line Creating Opportunities. Among the five professors is Prof. Jan Plefka, whi is a member of IRIS Adlershof. His mandatory teaching assignments will be covered by a visiting lecturer for the winter term 2018/19 and Jan Plefka will use the time gained for exploring the Generalized Unitarity for Gravitational Waves:
"For quantum field theories, such as the Standard Model, revolutionary innovations, the so-called generalized unitarity, have existed in recent years, which can circumvent and greatly simplify this diagrammatic development, thus making it possible to produce highly complicated graviton scattering processes. The central idea of this project is to transfer this innovation in the field of quantum field theory to the problem of gravitational waves in the classical theory of relativity, which results from the collision of massive bodies (black holes or neutron stars).", says Jan Plefka.
We congratulate and wish you much pleasure in this exciting topic!
11.07.2018Professor Jan Plefka elected as new Vice-Dean
At the constituent meeting of the new faculty council after the committee election in early July, Prof. Jan Plefka was elected on 11.07.2018 as the new Vice Dean for Research of the Faculty of Mathematics and Science. He succeeds Prof. Johann-Christoph Freytag, who was also a member of IRIS Adlershof.
We congratulate!
09.07.2018Flipping the switch on supramolecular electronics
For the first time, two-dimensional materials have been decorated with a photoswitchable molecular layer, and electronic components have been fabricated from the resulting hybrid materials that can be controlled by light. The results of this fruitful collaboration of several European research groups have been published in Nature Communications.
 Owing to their outstanding electrical, optical, chemical and thermal properties, two-dimensional (2D) materials, which consist of a single layer of atoms, hold great potential for technological applications such as electronic devices, sensors, catalysts, energy conversion and storage devices, among others. Thanks to their ultra-high surface sensitivity, 2D materials represent an ideal platform to study the interplay between nanoscale molecular assembly on surfaces and macroscopic electrical transport in devices.
Owing to their outstanding electrical, optical, chemical and thermal properties, two-dimensional (2D) materials, which consist of a single layer of atoms, hold great potential for technological applications such as electronic devices, sensors, catalysts, energy conversion and storage devices, among others. Thanks to their ultra-high surface sensitivity, 2D materials represent an ideal platform to study the interplay between nanoscale molecular assembly on surfaces and macroscopic electrical transport in devices.
In order to provide a unique light-responsivity to devices, the researchers have designed and synthesized a photoswitchable spiropyran building block, which is equipped with an anchoring group and which can be reversibly interconverted between two different forms by illumination with ultraviolet and visible light, respectively. On the surface of 2D materials, such as graphene or molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), the molecular photoswitches self-assemble into highly ordered ultrathin layers, thereby generating a hybrid, atomically precise superlattice. Upon illumination the system undergoes a collective structural rearrangement, which could be directly visualized and monitored with sub-nanometer resolution by scanning tunneling microscopy. This light-induced reorganization at the molecular level induces an optical modulation of the energetics of the underlying 2D material, which translates into a change in the electrical characteristics of the fabricated hybrid devices. In this regard, the collective nature of self-assembly allows to convert single-molecule events into a spatially homogeneous switching action, which generates a macroscopic electrical response in graphene and MoS2.
"With our versatile approach of molecularly tailoring 2D materials, we are taking supramolecular electronics to a new level and closer to future applications," says Prof. Stefan Hecht, who is researching hybrid materials at IRIS Adlershof. The work is groundbreaking for the realization of multifunctional hybrid components powered by nature's primary energy source - sunlight.
Further Information
Publication
“Collective molecular switching in hybrid superlattices for light-modulated two-dimensional electronics”
by: Marco Gobbi, Sara Bonacchi, Jian X. Lian, Alexandre Vercouter, Simone Bertolazzi, Björn Zyska, Melanie Timpel, Roberta Tatti, Yoann Olivier, Stefan Hecht, Marco V. Nardi, David Beljonne, Emanuele Orgiu and Paolo Samorì
in: Nature Communications 2018, 9, 2661, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04932-z05.07.2018IRIS Research Building: Exhibition for the Art Competition
In August 2017, the Senate Department for Culture and Europe, together with the Senate Department for Urban Development and Housing, announced an art competition with 10 invited artists for the new research building of IRIS Adlershof. In February 2018, a jury approved the draft by BORGMAN | LENK with the title "Accesss" recommended for implementation (see news from Febr. 05, 2018). This winning design, which features the installation of gold-colored components and elements that are inconsistent with the functional processes and entrances of the house, will be on display at the IRIS-House from 09 to 20 July 2018, along with the other designs submitted to the art competition be visited.
02.07.2018Light-controlled production of biodegradable polymers
A research team from Berlin, leaded by Prof. Stefan Hecht, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, has developed a novel catalyst system, which enables the regulation of multiple polymerization processes to produce biodegradable plastics solely by illumination with light of different colors. The results of this work have now been published in Nature Catalysis.
The properties of a polymeric material are highly dependent on factors, such as the connected monomer building blocks as well as the length and composition of the formed polymer chains. Typically, these factors are predetermined by the choice of the employed reaction conditions. In order to overcome this limitation and generate materials with new and unprecedented properties, regulation of polymerizations by means of external stimuli represents an attractive goal. Similarly to dental repair, light serves to precisely control the location and duration of the chemical reaction during polymer formation.
Fabian Eisenreich and Michael Kathan, the first authors of the study, are excited: “With our remote-controlled catalyst we are in principle able to program the formation of a desired polymer strand by employing a specific order and duration of light pulses.” Their promising development is an important step toward smart production processes of (biodegradable) polymers with the aim to meet the growing demands of future applications, including light-guided 3D printing and photolithography.
Weitere Informationen
Publication
“A photoswitchable catalyst system for remote-controlled (co)polymerization in situ”
by: Fabian Eisenreich, Michael Kathan, Andre Dallmann, Svante P. Ihrig, Timm Schwaar, Bernd M. Schmidt and Stefan Hecht
in: Nature Catalysis (2018), DOI: 10.1038/s41929-018-0091-8
29.06.2018Francesco Bianchi successfully defended his dissertation
 IRIS Junior Scientist Francesco Bianchi successfully defended his dissertation "Energy Transfer in Organic-Inorganic Semiconductor Structures" at IRIS Adlershof. His research was supported by CRC 951 "Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)" and supervised by IRIS-members Prof. Fritz Henneberger and Prof. Oliver Benson.
IRIS Junior Scientist Francesco Bianchi successfully defended his dissertation "Energy Transfer in Organic-Inorganic Semiconductor Structures" at IRIS Adlershof. His research was supported by CRC 951 "Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)" and supervised by IRIS-members Prof. Fritz Henneberger and Prof. Oliver Benson.
We congratulate very much!
28.06.2018Chain reaction switches molecules in depth
A new method developed by a team of chemists in Berlin open the door for using optically switchable molecules. The results of the study have been published in Chem.
 Smart materials become increasingly common in our daily life as they adapt their properties to their surroundings, such as temperature and light. Think about light-adaptive lenses in sunglasses that change their color in response to brightness or darkness. In these materials, photoswitchable molecules able to change their properties, such as color or the ability to conduct electricity, upon illumination serve as key components. However, photoswitches typically require the use of high-energy UV light and in addition do neither switch quantitatively nor efficiently since many more quanta than molecules are needed. These drawbacks limit the applicability of photoswitches, in particular since the more energy-rich light is, the less it can penetrate into materials.
Smart materials become increasingly common in our daily life as they adapt their properties to their surroundings, such as temperature and light. Think about light-adaptive lenses in sunglasses that change their color in response to brightness or darkness. In these materials, photoswitchable molecules able to change their properties, such as color or the ability to conduct electricity, upon illumination serve as key components. However, photoswitches typically require the use of high-energy UV light and in addition do neither switch quantitatively nor efficiently since many more quanta than molecules are needed. These drawbacks limit the applicability of photoswitches, in particular since the more energy-rich light is, the less it can penetrate into materials.
Now, chemists of Berlin’s Humboldt University and the University of Potsdam have developed a method, which allows one to efficiently and quantitatively operate photoswitches with the smallest amounts of low-energy red photons, thus solving both issues described above. By coincidence they came across the phenomenon that the oxidation of only a few switch molecules was sufficient to switch the entire sample. Subsequently, they investigated the underlying chain reaction in great detail and optimized it by introducing dyes to allow for the use of red light. The latter allowed them to boost the quantum yield – typically way below 100% – to a record-setting value of almost 200%.
The impact of their discovery is tremendous according to Dr. Alexis Goulet-Hanssens and Prof. Stefan Hecht, who works at the Department of Chemistry and IRIS Adlershof: „With our method, for the first time we can address molecular switches deep in a material. Thus, we can operate optical devices efficiently but also penetrate deep into the skin through the biological window“ they explain and are excited about possible applications in optoelectronics as well as medicine.
Further Informationen
Publication
“Hole Catalysis as a General Mechanism for Efficient and Wavelength-Independent Z/E Azobenzene Isomerization”
by: Alexis Goulet-Hanssens, Clemens Rietze, Evgenii Titov, Leonora Abdullahu, Lutz Grubert, Peter Saalfrank und Stefan Hecht
in: Chem (2018), DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2018.06.002
21.06.2018Best-Poster-Award for Laura Orphal at Symposium IRIS 2018
 |
|
| Director Jürgen P. Rabe, Awardee Laura Orphal, Jury member Emil List-Kratochvil |
The IRIS Symposium has firmly established itself as an annual highlight in the scientific life of IRIS Adlershof, and it has a growing interest beyond the Adlershof location, as the annually increasing number of participants impressively demonstrates. This year, ideas for the further development of IRIS in the areas of Advanced Microscopies, Hybrid Materials for Optics and Electronics, Mathematical Physics of Complex Systems, and Quantum Technologies were in the focus of interest. These topics were introduced to an extremely open-minded audience of internationally renowned researchers and representatives of business enterprises.
In order to give young scientists the opportunity to present their own research results to the invited speakers and the symposium participants, this year's symposium has been expanded to include a poster competition. The jury, consisting of the representative of the young researchers Julian Miczajka, as well as the IRIS members Prof. Yan Lu and Prof. Emil List-Kratovchvil, was visibly struggling to make the choice for the best poster. Finally, Laura Orphal was able to prevail with a total of 30 competitors with her poster. Laura Orphal, master student in the group 'Photonics', which is currently led by IRIS member Prof. Oliver Benson, received the Best Poster Award and a book voucher at the end of the symposium by IRIS Director Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe before the event ended with grilled and drinks.
18.06.2018Lise-Meitner Prize 2018 for Anne Spiering
 |
|
| Anne Spiering, M.Sc. |
Anne Spiering, former Master in the group "Quantum Field and String Theory", led by IRIS Adlershof member Jan Plefka, has been awarded with this year's Lise-Meitner Prize of the "Vereinigung der Freunde und Förderer des Instituts für Physik" in the category Mono-Master for her thesis "From Yangian symmetry to factored scattering". The jury said: "in her Master thesis she showed her ability to further develop advanced and highly complex concepts in particle physics. In addition to being of high scientific value, her thesis is also written in a pedagogically highly valuable manner." Ms. Spiering is currently continuing her research with at the Trinity College Dublin with a doctorate in mathematical physics.
We congratulate very much!
10.06.2018IRIS Adlershof at the Long Night of the Sciences
 |
| The Cube of Physics in action; photographed by Stephan Röhl |
Members from IRIS Adlershof were able to present some of their projects to the broader public in this year’s "Long Night of the Sciences", too.
IRIS member Alexander Reinefeld offered lectures and tours at the Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik ranging from the origin of computers and autostereoscopic displays to the computer-supported molecule development. In the Max Born Institute for Nonlinear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy, IRIS member Thomas Elsässer could inform visitors about extremely short light impulses and lasers with lab tours, exhibits, and experiments. In the Institute for Physics, IRIS’s young researchers gave some interesting insights into molecular physics; IRIS member Jan Plekfa could present some of his current research findings in the lecture, "The world as a hologram: some news about string theory", in a chock-full Gehrtsen lecture hall.
A highlight was a presentation of "The cube of physics" (#cubeofphysics) from the Excellence Cluster on "Image Knowledge Gestaltung" in the foyer of the Lise-Meitner-Haus. IRIS members, Jürgen P. Rabe and Mathias Staudacher, presented there together with Professor Christian Kassung from the Social Sciences, as well as the scenographer Franziska Paul and several other colleagues some ways to approach a world formula from Newtonian mechanics with an interactive media station and a meter-high installation.
07.06.2018Professor Claudia Draxl accepted into the Austrian Academy of Sciences
 |
| Prof. Claudia Draxl and Prof. Oliver Jens Schmitt, President at ÖAW |
The Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW) welcomes 29 new members in its ranks. At the annual election meeting 16 male and 9 female researchers from a wide range of disciplines in the humanities, social and cultural sciences as well as mathematics, natural and engineering sciences were admitted to the academy due to their outstanding scientific achievements and their professional reputation. Among them is Prof. Claudia Draxl, who has been conducting research at the IRIS Adlershof since 2012 with her research group "Theoretical Solid State Physics".
We congratulate!
07.06.2018Study Prize of the Physical Society of Berlin for Julian Miczajka
 The Physical Society of Berlin has awarded the Physics Study Award 2018, sponsored by Siemens AG, to outstanding graduates of the diploma or master's degree in physics. Among the winners is also the elected representative of the junior researchers of IRIS Adlershof, Julian Miczajka. Mr. Miczajka is currently a doctoral student in the group of IRIS-member Professor Jan Plefka and is focusing on an exceptional class of higher spin theories in flat spaces, especially on their relationship with hidden symmetries, integrability, and duality.
The Physical Society of Berlin has awarded the Physics Study Award 2018, sponsored by Siemens AG, to outstanding graduates of the diploma or master's degree in physics. Among the winners is also the elected representative of the junior researchers of IRIS Adlershof, Julian Miczajka. Mr. Miczajka is currently a doctoral student in the group of IRIS-member Professor Jan Plefka and is focusing on an exceptional class of higher spin theories in flat spaces, especially on their relationship with hidden symmetries, integrability, and duality.
The award will be presented on July 12, 2018 as part of a public celebration in the Magnus House.
We congratulate Julian Miczajka very much!
more...
05.06.2018Emmy Noether Junior Research Group for Dr. Stijn van Tongeren
 Dr. Stijn van Tongeren, a member of the group Mathematical Physics of Space, Time and Matter, has been selected to lead an Emmy Noether Junior Research Group. This will allow him to run his own independent research group here at Humboldt University and IRIS Adlershof for up to 5 years in collaboration with the group Mathematical Physics of Space, Time and Matter. He and his group will be working on deformations of AdS/CFT and related integrable structures, beginning in september 2018.
Dr. Stijn van Tongeren, a member of the group Mathematical Physics of Space, Time and Matter, has been selected to lead an Emmy Noether Junior Research Group. This will allow him to run his own independent research group here at Humboldt University and IRIS Adlershof for up to 5 years in collaboration with the group Mathematical Physics of Space, Time and Matter. He and his group will be working on deformations of AdS/CFT and related integrable structures, beginning in september 2018.
We congratulate Mr. van Tongeren very much and are looking forward to an exciting and fruitful continued cooperation!
04.06.2018Humboldt research prize for Professor Seth Marder
 Seth Marder, Professor of Chemistry and Materials Science and Engineering (courtesy) at the Georgia Institute of Technology, was awarded the renowned research prize from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Seth Marder is internationally recognized for his leadership in developing structure-property relationships for organic and metallo-organic materials for optical and electronic applications. Among his accomplishments he created a new class of extremely efficient two-photon absorbing materials that helped to enable the field of two-photon 3D microfabrication, which is now a commerical technology used around the world. He has also contributed to the development of organic electronic materials, in particular dopants that can be used to convert semiconducting materials to materials with substantial conductivities. While in Germany he will continue his collaborative studies of the effects of dopants on the properties of both organic and inorganic materials. Professor Seth Marder is hosted by Professor Nobert Koch at IRIS Adlershof and the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
Seth Marder, Professor of Chemistry and Materials Science and Engineering (courtesy) at the Georgia Institute of Technology, was awarded the renowned research prize from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Seth Marder is internationally recognized for his leadership in developing structure-property relationships for organic and metallo-organic materials for optical and electronic applications. Among his accomplishments he created a new class of extremely efficient two-photon absorbing materials that helped to enable the field of two-photon 3D microfabrication, which is now a commerical technology used around the world. He has also contributed to the development of organic electronic materials, in particular dopants that can be used to convert semiconducting materials to materials with substantial conductivities. While in Germany he will continue his collaborative studies of the effects of dopants on the properties of both organic and inorganic materials. Professor Seth Marder is hosted by Professor Nobert Koch at IRIS Adlershof and the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
We heartily congratulate Prof. Marder and are looking forward to an exciting and productive collaboration!
30.05.2018International students visit IRIS Adlershof
 A group of students and professors from Morehouse and Spelman Colleges, two so-called “historically black colleges and universities” or colleges from the “Black Ivy League” from Atlanta, Georgia (USA), visited the natural science campus of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin in the framework of several day Berlin stay to inform themselves about the local study conditions and research opportunities. IRIS administrative head Dr. Nikolai Puhlmann and IRIS member Prof. Christoph Koch as well as Mohammad Fardin Gholami, a doctoral student in the group from IRIS director Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe gave some insight into IRIS Adlershof’s research and graduate education. The guests were quite interested in and impressed about the nascent IRIS research building as well as the diverse opportunities for international young scientists at the Adlershof location.
A group of students and professors from Morehouse and Spelman Colleges, two so-called “historically black colleges and universities” or colleges from the “Black Ivy League” from Atlanta, Georgia (USA), visited the natural science campus of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin in the framework of several day Berlin stay to inform themselves about the local study conditions and research opportunities. IRIS administrative head Dr. Nikolai Puhlmann and IRIS member Prof. Christoph Koch as well as Mohammad Fardin Gholami, a doctoral student in the group from IRIS director Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe gave some insight into IRIS Adlershof’s research and graduate education. The guests were quite interested in and impressed about the nascent IRIS research building as well as the diverse opportunities for international young scientists at the Adlershof location.
30.05.2018Humboldt research prize for Professor Niklas Beisert
 Niklas Beisert, professor for mathematical physics at the ETH Zürich, Switzerland, was awarded the renowned research prize from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Prof. Beisert is an internationally known leading researcher in the area of the quantum field theory and integrable models. His work was important for the creation of research area integrability of the string-gauge theory duality that led for the first time to exact results in four-dimension quantum field theories. He also concerns himself with extremely complex questions into quantum gravitation and has produced a program to prove integrability in super symmetrical models.
Niklas Beisert, professor for mathematical physics at the ETH Zürich, Switzerland, was awarded the renowned research prize from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Prof. Beisert is an internationally known leading researcher in the area of the quantum field theory and integrable models. His work was important for the creation of research area integrability of the string-gauge theory duality that led for the first time to exact results in four-dimension quantum field theories. He also concerns himself with extremely complex questions into quantum gravitation and has produced a program to prove integrability in super symmetrical models.
The research prize gives Prof. Beisert the opportunity to discover with his colleagues, Jan Plefka, Matthias Staudacher, and Dirk Kreimer from IRIS Adlershof as well from the Institutes for Physics and Mathematics of the Humboldt University Berlin, some exact nonperturbative solutions in quantum field theory and to investigate the hidden symmetries in quantum field theories in depth. He will stay seven months as guest of IRIS Adlershof and strengthen with his expertise the IRIS research field “Space-Time-Material” in the academic year of 2018/2019.
We heartily congratulate Prof. Beisert and are looking forward to an exciting and productive collaboration!
28.05.2018José David Cojal González successfully defended his dissertation
 IRIS Junior Scientist José David Cojal González successfully defended his dissertation "Self-Assembly and Electronic Properties of π-expanded Macrocycles". His research was supported by CRC 658 "Elementary Processes in Molecular Switches at Surfaces", CRC 951 "Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)" and IRIS Adlershof and supervised by Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe.
IRIS Junior Scientist José David Cojal González successfully defended his dissertation "Self-Assembly and Electronic Properties of π-expanded Macrocycles". His research was supported by CRC 658 "Elementary Processes in Molecular Switches at Surfaces", CRC 951 "Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)" and IRIS Adlershof and supervised by Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates!
17.05.2018Michael J. Bojdys joined the Humboldt-Universität
 |
| Dr. Michael J. Bojdys |
He will present his current research at Symposium IRIS 2018 with the talk: "2D or not 2D? Metal-free nanomaterials beyond graphene".
IRIS Adlershof is looking forward to a fruitful collaboration!
08.05.2018Alexander von Humboldt Professorship for Arno Rauschenbeutel
 |
| Photo: Jacqueline Godany |
Rauschenbeutel, who had previously worked at the Vienna University of Technology, sees as a big vote of confidence that Prof. Dr. Oliver Benson, member of IRIS Adlershof, and the Humboldt Universität have proposed him and given him completely new freedom for his research at the Department of Physics and at the IRIS Adlershof of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
more...
At IRIS Adlershof he will present his current research as part of a special colloquium of the CRC 951 HIOS, and also at Symposium IRIS 2018:
IRIS Adlershof congratulates cordially!.
17.04.2018Humboldt-Innovation GmbH der HU für "Beste Innovationsförderung" ausgezeichnet
Die Humboldt-Innovation GmbH (HI) ist vom Deutschen Institut für Erfindungswesen (DIE e.V.) in der Kategorie „Beste Innovationsförderung“ mit der Dieselmedaille 2018 ausgezeichnet worden.Die 2005 gegründete Humboldt-Innovation GmbH ist ein 100-prozentiges Tochterunternehmen der HU und engagiert sich an der Schnittstelle von Wissenschaft und Wirtschaft.
mehr...
06.04.2018Innovative Training Network SAGEX "Scattering Amplitudes: from Geometry to Experiment" will be funded
The Innovative Training Network of the European Commission SAGEX "Scattering Amplitudes: from Geometry to Experiment" was accepted for funding and will start on Sep. 1st 2018. Two Early-Stage Researcher (PhD) positions will be funded at Humboldt University, one in the Research Group "Mathematical Physics of Space, Time and Matter" (Prof. Dr. Matthias Staudacher) and one in the Research Group "Quantum Field and String Theory" (Prof. Dr. Jan Plefka). Both are members of IRIS Adlershof.
Applications will open in April.
more...
03.04.2018Humboldt-Universität is a project partner in the national development association, "The Future of STEM Learning"
 Together with the universities of Kiel, Koblenz-Landau, Würzburg, and Kaiserslautern, the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin will be developing,
Together with the universities of Kiel, Koblenz-Landau, Würzburg, and Kaiserslautern, the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin will be developing,
testing, and integrating concepts for good STEM lessons in the digital world for the education and further training of STEM teachers from
autumn 2018 onwards. The Telekom Foundation is supporting the project with € 1.6 million.
more...
22.03.2018IRIS's young scientist Anne Fuhrmann was awarded the Carl Roth Prize by the Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker (GDCh).
 At the 20th Younger Chemists' Forum in Konstanz, Anne Fuhrmann, a doctoral student at the Department of Chemistry and IRIS Adlershof of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, was awarded the Carl Roth Prize by the Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker (GDCh) "in recognition of her innovative contributions developing polymer networks with optically switchable healing properties for smart and sustainable materials." The Carl Roth Prize is annually rewarded to the young scientists in Germany in the area of a sustainable chemistry for "an efficient use of chemical resources for synthesis or an innovative application of chemicals."
At the 20th Younger Chemists' Forum in Konstanz, Anne Fuhrmann, a doctoral student at the Department of Chemistry and IRIS Adlershof of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, was awarded the Carl Roth Prize by the Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker (GDCh) "in recognition of her innovative contributions developing polymer networks with optically switchable healing properties for smart and sustainable materials." The Carl Roth Prize is annually rewarded to the young scientists in Germany in the area of a sustainable chemistry for "an efficient use of chemical resources for synthesis or an innovative application of chemicals."
Anne Fuhrmann developed her plastic coatings, which can target and heal damage with the help of light, for her doctoral work in the research group of Prof. Stefan Hecht who is an IRIS member. The damaged site repairs itself only where it has previously been heated up and then lit with a special color of light. These promising results were published, for example, in Nature Communications.
IRIS Adlershof cordially congratulates the prize winner.
15.03.2018Professor E. List-Kratochvil inspires the Humboldt Children's University
 Everything should be like a real university at the Humboldt-Kinder-Uni, which means real lectures on interesting topics, smart professors, and a large auditorium. Our member, Prof. Dr. Ing. Emil J. W. List-Kratochvil, gave a lecture entitled “Bendable screens - fluorescent fish - red beets” in front of the elementary students on March 15, 2018.
Everything should be like a real university at the Humboldt-Kinder-Uni, which means real lectures on interesting topics, smart professors, and a large auditorium. Our member, Prof. Dr. Ing. Emil J. W. List-Kratochvil, gave a lecture entitled “Bendable screens - fluorescent fish - red beets” in front of the elementary students on March 15, 2018.
 Im Rahmen der ausgebuchten Vorlesung wurt.At the fully booked lecture, it was found that the glow of fish in the deep sea, the color of leaves, and flexible screens are based on very
Im Rahmen der ausgebuchten Vorlesung wurt.At the fully booked lecture, it was found that the glow of fish in the deep sea, the color of leaves, and flexible screens are based on very
similar material concepts. At the end of the lecture, a solar cell was made from beet juice.
28.02.2018An honorary professorship for Ingolf V. Hertel
 The Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has awarded Prof. Dr. Ingolf V. Hertel an honorary professorship because of his excellent scientific work, his service to the science and technology park in Berlin-Adlershof, as well as his many years of dedication to the MINT teachers’ training.
The Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has awarded Prof. Dr. Ingolf V. Hertel an honorary professorship because of his excellent scientific work, his service to the science and technology park in Berlin-Adlershof, as well as his many years of dedication to the MINT teachers’ training.
Professor Hertel is one of Germany’s leading and internationally outstanding representatives in the field of experimental physics for atomic, molecular, and laser physics. In 2009 he was appointed to the Humboldt University’s “Wilhelm and Else Heraeus” senior professorship for further development of teacher education in the physics field. His particular focus is on didactics on the university level for teachers’ education and didactics regarding physics. Prof. Hertel is linked with IRIS Adlershof through the interdisciplinary Humboldt-ProMINT-Kolleg, where he is actively involved and supervises didactic research and development work.
We congratulate Prof. Hertel very much.
more...
27.02.2018Professor Michael Hintermüller, a new member at IRIS Adlershof
 Michael Hintermüller is a new member at IRIS Adlershof. The Professor for Applied Mathematics at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Director of the Weierstraß-Institute for Applied Analysis and Stochastics, and Chair of the Einstein Center for Mathematics Berlin is a new member at IRIS Adlershof. His current research interests lie in the area of mathematical modeling, the analysis of the resulting variational problems or operator equations as well as in the development, analysis and numerical implementation of associated solution methods.
Michael Hintermüller is a new member at IRIS Adlershof. The Professor for Applied Mathematics at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Director of the Weierstraß-Institute for Applied Analysis and Stochastics, and Chair of the Einstein Center for Mathematics Berlin is a new member at IRIS Adlershof. His current research interests lie in the area of mathematical modeling, the analysis of the resulting variational problems or operator equations as well as in the development, analysis and numerical implementation of associated solution methods.
IRIS Adlershof is looking very much forward to a fruitful collaboration.
19.02.2018Jürgen P. Rabe re-elected Chairman of the Berlin-Brandenburgischen Verband für Polymerforschung (BVP)
 The General Assembly of the Berlin-Brandenburgischen Verband für Polymerforschung (BVP) has re-elected its Executive Board for further two years. Chairman is Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe (Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin), Deputies are Prof. Rainer Haag (Freie Universität Berlin) and Prof. Dieter Neher (Universität Potsdam), treasurer is Prof. Michael Gradzielski (Technische Universität Berlin), and Managing Director is Prof. Andreas Lendlein (Universität Potsdam).
The General Assembly of the Berlin-Brandenburgischen Verband für Polymerforschung (BVP) has re-elected its Executive Board for further two years. Chairman is Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe (Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin), Deputies are Prof. Rainer Haag (Freie Universität Berlin) and Prof. Dieter Neher (Universität Potsdam), treasurer is Prof. Michael Gradzielski (Technische Universität Berlin), and Managing Director is Prof. Andreas Lendlein (Universität Potsdam).
19.02.2018IRIS Junior Scientist Christian Seifert successfully defended his dissertation "Control of the electrical transport through single molecules and graphene"
IRIS Junior Scientist Christian Seifert successfully defended his dissertation Control of the electrical transport through single molecules and graphene. His work was supervised by IRIS director Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe.
Congratulations!
15.02.2018Humboldt Research Award for Lance J. Dixon
 Lance J. Dixon Professor at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University, USA, has been awarded an Research Award of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Lance Dixon is a leading researcher in theoretical high-energy physics. His contributions range from seminal and mathematically profound papers in the early phase of string theory to very practical high precision calculations in Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) relevant to collider physics, and to an ever deeper understanding of scattering amplitudes for quantum field theory. He has even tackled the daunting subject of understanding the perturbative structure of field theory approaches to quantum gravity.
Lance J. Dixon Professor at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, Stanford University, USA, has been awarded an Research Award of the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. Lance Dixon is a leading researcher in theoretical high-energy physics. His contributions range from seminal and mathematically profound papers in the early phase of string theory to very practical high precision calculations in Quantum Chromodynamics (QCD) relevant to collider physics, and to an ever deeper understanding of scattering amplitudes for quantum field theory. He has even tackled the daunting subject of understanding the perturbative structure of field theory approaches to quantum gravity.
The price will allow him to work for a total of one year with scientists at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin to develop new ways to solve quantum field theory nonperturbatively, and to investigate further the elusive theory of quantum gravity. He will be hosted by IRIS Adlershof within the research area "Space-Time-Matter“ (AG Staudacher) and the fields of competence "Mathematical Physics“ (AGs Kreimer, Plefka, Staudacher).
IRIS Adlershof congratulates Mr. Dixon very much and is looking forward to an exciting and fruitful cooperation.
13.02.2018Professor Jürgen P. Rabe re-elected as director of IRIS Adlershof
 The IRIS General Assembly re-elected Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe as the director and Prof. Norbert Koch as his deputy for the second IRIS funding phase (Nov. 01, .2017 - Oct. 31, .2021). Matthias Staudacher, Bridge Professor for Mathematics and Physics, and Emil List-Kratochvil, Bridge Professor for Chemistry and Physics, have been elected as members of the IRIS Council. All elections were unanimous. The elected representative of the IRIS junior scientist Julian Miczajka is also a member of the council.
The IRIS General Assembly re-elected Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe as the director and Prof. Norbert Koch as his deputy for the second IRIS funding phase (Nov. 01, .2017 - Oct. 31, .2021). Matthias Staudacher, Bridge Professor for Mathematics and Physics, and Emil List-Kratochvil, Bridge Professor for Chemistry and Physics, have been elected as members of the IRIS Council. All elections were unanimous. The elected representative of the IRIS junior scientist Julian Miczajka is also a member of the council.
05.02.2018Art competition for the IRIS research building has been judged
Following an earlier than planned Berlin wide application process, the Senate Department for Culture and Europe together with the Senate Department for Urban Development and Housing held an art competition in August 2017 with 10 invited artists for the newly built research building of the IRIS Adlershof (Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences) at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
The goal of the art competition was to develop independent artistic designs that also corresponded with the scope of the institute’s cutting-edge research work. The artwork was supposed to reflect and contribute to the ongoing discussion with the architecture, urban environment of the Adlershof campus, and the use of the building as a lively place of research and exchange.
The jury, which was chaired by the artist Veronike Hinsberg, unanimously awarded on February 1st, 2018, first prize to the artist group BORGMAN | LENK (Anna Borgman and Candy Lenk). Second prize was awarded to Gunda Förster and Barbara Trautmann and an honorable mention went to Thomas Henninger.
.png)
The winning proposal designed by BORGMAN | LENK with the title “Accesses” is an installation of inoperative golden building blocks and elements thus contrasting the working processes and approaches of the institute. The jury therefore honors the artistic idea of contradicting architecture’s functionality. Gold-colored elements like an air lock door, entrance hatch, and elevator display give a new momentum to a “free and searching movement of thoughts.” The proposed design has a dry humor and great sensitivity for the used materials.
We plan to exhibit all the submitted entries of art competition in IRIS Adlershof in due time.
29.01.2018Dr. Agostino Patella accepted a new position at Humboldt-Universität
 Dr. Agostino Patella (Theoretical Physics Department, CERN) has accepted the W2-Professorship "Theoretical Particle Physics - Lattice Field Theory" at the Department of Physics of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
Dr. Agostino Patella (Theoretical Physics Department, CERN) has accepted the W2-Professorship "Theoretical Particle Physics - Lattice Field Theory" at the Department of Physics of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
26.01.2018IRIS Junior Scientist David Meidinger successfully defended his dissertation "Integrability in weakly coupled super Yang‐Mills theory: form factors, on‐shell methods and Q‐operators"
IRIS Junior Scientist David Meidinger successfully defended his dissertation Integrability in weakly coupled super Yang‐Mills theory: form factors, on‐shell methods and Q‐operators. His work was supervised by IRIS council member Prof. Matthias Staudacher.
Congratulations!
19.12.2017The first IRIS Roots-Day
 At an IRIS Roots-Day, which was being held for the first time this year, numerous participants followed with much interest and pleasure the contributions from nine IRIS young scientists who took up the challenge to give a synopsis of their current research work in just five minutes. The jury, who was made up of IRIS members and representatives from IRIS’s young scientists, found it difficult to choose the best ones. In the end, they decided to increase the award money so they could give a second third place.
At an IRIS Roots-Day, which was being held for the first time this year, numerous participants followed with much interest and pleasure the contributions from nine IRIS young scientists who took up the challenge to give a synopsis of their current research work in just five minutes. The jury, who was made up of IRIS members and representatives from IRIS’s young scientists, found it difficult to choose the best ones. In the end, they decided to increase the award money so they could give a second third place.
The first prize, which was coupled with a travel grant so that the awardee could take an active part at a national or international scientific conference, went to Ms. Inna Kviatkovska who came to Dr. Ramelow’s IRIS young scientists a few months ago to do research on infra-red quantum imaging. The second prize was awarded to Yuhang Zhao who is doing a doctorate in Prof. Yan Lu’s group at the HZB. Wadim Wormsbecher, a doctoral student in Prof. Plefka’s group, and Matthias Runge, a master student in Prof. List-Kratochvil’s group, each received third place.
Afterwards, the young and senior scientists as well as the guests could continue discussing their research with bagels, fruitcake, and mulled wine.
Inna Kviatkovsky Yuhang Zhao Wadim Wormsbecher Matthias Runge
IRIS Adlershof cordially congratulates the awardees and already announces that the successful format of the IRIS Roots-Day will be continued.
15.12.2017Leibniz-Preis für Prof. A. Buonanno (MPI-G,UP,HU)
|
The gravitational physicist Alessandra Buonanno, director at the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics in Potsdam-Golm and honorary professor at the Humboldt-Universität and the University of Potsdam, is awarded the Leibniz Prize, the most important German research prize. She is among those who have demonstrated in 2014 the gravitational waves postulated by Einstein. She and 10 other scientists will receive the award on March 19, 2018 in Berlin. On the occasion of the awarding of the honorary professorship on December 19, 2017 she will give a lecture at the Department of Physics. IRIS Adlershof congratulates.
more... |
 |
| © A. Buonanno |
14.12.2017Longer lifetimes for perovskite absorbers
|
An international team of scientists has improved greatly the stability of organic-inorganic lead halide perovskites. These materials have enormous potential for photovoltaic applications but still suffer from comparably moderate device lifetime. The scientists, led by researchers from the EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland, incorporated a large organic cation – guanidinium - into the perovskite crystal structure, in part replacing the traditionally used methylammonium and formamidinium cations. Overall, the new material delivered average power conversion efficiencies over 19%, and stabilized performance for 1,000 h under continuous light illumination. This is a fundamental step within the perovskite field. These groundbreaking research results were recently published in Nature Energy. Among the authors is the member of IRIS Adlershof, Prof. Norbert Koch.
more... |
13.12.2017Julian Miczajka and Dr. Sven Ramelow were elected young scientist representatives
 |
|
Julian Miczajka Dr. Sven Ramelow ©: Albert-Einstein-Institut |
IRIS Adlershof’s young scientists have elected Julian Miczajka to be their representative and Dr. Sven Ramelow as their substitute representative in IRIS’s committees. The young scientists are therefore being represented in IRIS general meetings as well on IRIS’s board with rights to speak, submit applications, and vote. Julian Miczajka who is a doctoral student in Prof. Jan Plefka’s group is focusing on an exceptional class of higher spin theories in flat spaces, especially on their relationship with hidden symmetries, integrability, and duality. Dr. Sven Ramelow is the head of an independent Emmy-Noether young scientist group “Nonlinear Quantum Optics.” As their first official act, both young scientist representatives will sit in the jury of the IRIS Roots Day and evaluate the pitches of in total nine IRIS young scientists.
IRIS Adlershof cordially congratulates Mr. Miczajka und Dr. Ramelow and loooks forward to a good cooperation.
16.11.201715 years Matheon
The research center MATHEON, in which IRIS Adlershof-member Prof. Jürg Kramer is participating, celebrated its 15th anniversary on 15.11.2017 with a festival of Berlin Mathematics.
IRIS Adlershof congratulates warmly!
more...
13.11.2017Beating the thermodynamic limit with photo-activation of n-doping in organic semiconductors using “hyper-reductants”
|
In an article that just appeared in Nature Materials, a team of researchers from the Georgia Institute of Technology, the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, and Princeton University demonstrates a new approach towards n-doping of organic semiconductors, which allows bypassing the dopant sensitivity to the ambient and simultaneously enables doping organic electron transport materials that have been out of reach for n-doping so far.
“We believe that our work enables simple processing of n-doped organic semiconductors in numerous device architectures, where the critical step - doping activation - can take place after standard device encapsulation. This will contribute substantially to improved device lifetime and in some case simplify device fabrication.” notes Prof. Norbert Koch from Humboldt-Universität, member of IRIS Adlershof. more... |
 |
|
| Image by Jing Wang and Xin Lin | ||
04.11.2017Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe appointed to Advisory Committee of the Executive Board of the Einstein Foundation Berlin
 Jürgen P. Rabe, Professor at the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Director of IRIS Adlershof, has been appointed as new member of the Advisory Committee of the Executive Board of the Einstein Foundation Berlin. We congratulate warmly and wish him success in his new additional function.
Jürgen P. Rabe, Professor at the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Director of IRIS Adlershof, has been appointed as new member of the Advisory Committee of the Executive Board of the Einstein Foundation Berlin. We congratulate warmly and wish him success in his new additional function.
27.10.2017Dr. Christian Bogner was awarded a Einstein Junior Fellowship
 |
|
Dr. Christian Bogner, Foto: Anne Kathrin Doerr |
Christian Bogner was working as a postdoc and principal investigator of a DFG project in the group of Prof. Dirk Kreimer, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, at the Department of Physics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Since May 2013 Christian Bogner is a candidate for postdoctoral lecture qualification (Habilitand). He is involved in the field of elementary particle physics at the interface between mathematics and physics. His interest is in new function classes that play an role in the calculation of Feynman integrals. From January 2018, Christian Bogner will be supported by a Einstein Junior Fellowship.
We are delighted that the talented young scientist will remain in Berlin and cordially congratulate!
20.10.2017“Distinguished Award 2017 for Novel Materials and their Synthesis” for Prof. Norbert Koch
 At the IUPAC NMS-XIII conference in Nanjing, Norbert Koch, Professor at the Department of Physics, member of IRIS Adlershof and head of a joint research group at the Helmholtz-Centre Berlin for materials and energy, has been awarded the "Distinguished Award 2017 for Novel Materials and their Synthesis "of IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) and of the Conference Committee. Norbert Koch received the award for his research on hybrid electronic materials and their interfaces in electronic and optoelectronic components. IRIS Adlershof congratulates warmly.
At the IUPAC NMS-XIII conference in Nanjing, Norbert Koch, Professor at the Department of Physics, member of IRIS Adlershof and head of a joint research group at the Helmholtz-Centre Berlin for materials and energy, has been awarded the "Distinguished Award 2017 for Novel Materials and their Synthesis "of IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) and of the Conference Committee. Norbert Koch received the award for his research on hybrid electronic materials and their interfaces in electronic and optoelectronic components. IRIS Adlershof congratulates warmly. 06.10.2017Prof. Dr. Arno Rauschenbeutel accepted professorship
|
Prof. Dr. Arno Rauschenbeutel (Technische Universität Wien) has accepted the W3-professorship "Fundamentals of Optics and Photonics" at the Department of Physics of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. The laureate of the renowned Alexander von Humboldt-Professorship is going to research in the field of experimental quantum optics and quantum information. IRIS Adlershof gratulates and is looking forward to a fruitful cooperation. |
 Foto: Jacqueline Godan |
02.10.2017Berlin Science successfully clears first hurdle within the framework of the Excellence Strategy
 |
A total of nine research projects from Berlin are invited for the full application within the framework of the Excellence Strategy. IRIS Adlershof and its members participate in the Cluster of Excellence projects
Matters of Activity: Image Space Material
A new Culture of Matter
The Power of Mathematics
Unifying Systems in Catalysis (UniSysCat)
Sustainability needs Catalysis Research.
29.08.2017Dr. Edoardo Vescovi receives Springer Thesis Award 2016
 The Springer Thesis Award 2016 has been awarded to Edoardo Vescovi for his PhD Thesis “Perturbative and non-perturbative approaches to string sigma-models in AdS/CFT”. Edoardo’s dissertation, nominated by the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, was published in Springer Theses, a book series to recognize outstanding doctoral research. The thesis introduces readers to the type II superstring theories in the AdS5×S5 and AdS4×CP3 backgrounds, fokussing on fundamental aspects. The Springer Thesis Award 2016 has been awarded to Edoardo Vescovi for his PhD Thesis “Perturbative and non-perturbative approaches to string sigma-models in AdS/CFT”. Edoardo’s dissertation, nominated by the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, was published in Springer Theses, a book series to recognize outstanding doctoral research. The thesis introduces readers to the type II superstring theories in the AdS5×S5 and AdS4×CP3 backgrounds, fokussing on fundamental aspects.Eduardos’s work, conceived and performed at IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, was supervised by Dr. Valentina Forini, one of our associated research group leaders. IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Edoardo Vescovi and wishes him much success in his future work. |
Dr. E. Vescovi
Perturbative and Non-perturbative Approaches to String Sigma-Models in AdS/CFT
ISBN 978-3-319-63420-3
16.08.2017Prof. K. Balasubramanian, Prof. C. Cocchi and Prof. I.M. Sokolov new members at IRIS Adlershof


 Kannan Balasubramanian (left image), and Caterina Cocchi (center), both new professors at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin since the beginning of the year, and Igor M. Sokolov (right) are new members of IRIS Adlershof.
Kannan Balasubramanian (left image), and Caterina Cocchi (center), both new professors at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin since the beginning of the year, and Igor M. Sokolov (right) are new members of IRIS Adlershof.
Kannan Balasubramanians research focuses on nanostructured materials, systems and devices for the development of novel analytical tools in a microscopic environment. In the focus of Catherina Cocchi's research interests is Light-matter interaction with advanced first principles methods, based on density-functional theory (DFT) and its time-dependent extension (TDDFT) as well as of many-body perturbation theory (MBPT). The main interest of Igor Sokolov's research is on statistical physics and the physical chemistry of condensed and soft matter, especially problems in which the discrete, disordered structure and fluctuations play the leading role.
IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate all new members and is looking very much forward to a fruitful collaboration.
18.07.2017Water makes the proton shake
A team led by Prof. Thomas Elsässer, who is a meber of IRIS Adlershof, reported on the mapping of fluctuating proton transfer motions and provides direct evidence that protons in liquid water are predominantly shared by two water molecules, applying ultrafast vibrational spectroscopy. They could identify the Zundel cation as the predominant species in liquid water. This new picture of proton dynamics is highly relevant for proton transport by the infamous von Grotthuss mechanism, and for proton translocation mechanisms in biological systems.
more...
17.07.2017Prize for good teaching in 2016 to Professor Jürg Kramer
 The Prize for Good Teaching 2016 of the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences at the Humboldt- Universität zu Berlin was awraded to Professor Jürg Kramer, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof. The prize has been awarded annually since 2009 for special achievements in teaching.-Mitglied.
The Prize for Good Teaching 2016 of the Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences at the Humboldt- Universität zu Berlin was awraded to Professor Jürg Kramer, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof. The prize has been awarded annually since 2009 for special achievements in teaching.-Mitglied.
We congratulate warmly!!
more...
13.07.2017Topping ceremony of the new research building of IRIS Adlershof
 At the invitation of the Senator for Urban Development, Katrin Lompscher, and in the presence of the Governing Mayor of Berlin, Michael Müller, and the President of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dr. Sabine Kunst, and the architect Prof. Hans Nickl of Nickl & Partner, this Thursday, the 13th of July, the topping ceremony of the new research building of. IRIS Adlershof was celebrated.
At the invitation of the Senator for Urban Development, Katrin Lompscher, and in the presence of the Governing Mayor of Berlin, Michael Müller, and the President of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dr. Sabine Kunst, and the architect Prof. Hans Nickl of Nickl & Partner, this Thursday, the 13th of July, the topping ceremony of the new research building of. IRIS Adlershof was celebrated.
more..
07.07.2017"Image Knowledge Gestaltung. An Interdisciplinary Laboratory" celebrates its five-year anniversary
 The Cluster of Excellence "Image Knowlegde Gestaltung. An Interdisciplinary Laboratory", celebrated its five-year anniversary on 7 July 2017. The Interdisciplinary Laboratory brings together the humanities, the natural sciences and engineering sciences, medicine and – for the first time in basic research – design and architecture, with the objective to strengthen and enrich each discipline through interdisciplinary collaboration. IRIS Adlershof, which is actively involved with four of its members in the interdisciplinary research of the cluster, warmly congratulates.
The Cluster of Excellence "Image Knowlegde Gestaltung. An Interdisciplinary Laboratory", celebrated its five-year anniversary on 7 July 2017. The Interdisciplinary Laboratory brings together the humanities, the natural sciences and engineering sciences, medicine and – for the first time in basic research – design and architecture, with the objective to strengthen and enrich each discipline through interdisciplinary collaboration. IRIS Adlershof, which is actively involved with four of its members in the interdisciplinary research of the cluster, warmly congratulates.
mehr...
26.06.2017Distinguished Professor Rich Spontak at IRIS Adlershof
 Distinguished Professor Rich Spontak from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of North Carolina State University visits IRIS Adlershof from June 26th through July 27th as a guest professor of the Cluster of Excellence Image Knowledge Gestaltung within the project Experimental Systems. Professor Spontak’s focus areas in research are polymer morphology and phase stability, multifunctional and nanostructured polymers, blends and networks, and the application of microscopy techniques to polymer science and engineering.
Distinguished Professor Rich Spontak from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of North Carolina State University visits IRIS Adlershof from June 26th through July 27th as a guest professor of the Cluster of Excellence Image Knowledge Gestaltung within the project Experimental Systems. Professor Spontak’s focus areas in research are polymer morphology and phase stability, multifunctional and nanostructured polymers, blends and networks, and the application of microscopy techniques to polymer science and engineering.
15.06.2017Humboldt-Universität continues to improve in the physical sciences of THE Ranking.
 The Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin reached the rank of 51-60 in the current Times Higher Education (THE) World Reputation Ranking. On a national level, this is the second place behind the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, together with the University of Heidelberg. The strategic international partner of IRIS Adlershof and Profile Partner of HU, Princeton University and the National University of Singapore are ranked number 7 and 24 (# 1 in Asia). In the physical sciences, the Humboldt-Universität has improved to 46th place in the World University Ranking, and in Germany it was ranked 4th.
The Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin reached the rank of 51-60 in the current Times Higher Education (THE) World Reputation Ranking. On a national level, this is the second place behind the Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, together with the University of Heidelberg. The strategic international partner of IRIS Adlershof and Profile Partner of HU, Princeton University and the National University of Singapore are ranked number 7 and 24 (# 1 in Asia). In the physical sciences, the Humboldt-Universität has improved to 46th place in the World University Ranking, and in Germany it was ranked 4th.
12.06.2017Advanced Material Competition 2017
 The Innovation Network for Advanced Materials (INAM) announces the Advanced Materials Competition (AdMaCom), a two week workshop from September 25 to October 06, 2017 to be held in Berlin. The AdMaCom addresses scientific driven startups with outstanding technologies and business models in the area of advanced materials and related digital services. Startups with applications ranging from lighting and displays to sensors and wearables can apply for participation until July 26, 2017.
The Innovation Network for Advanced Materials (INAM) announces the Advanced Materials Competition (AdMaCom), a two week workshop from September 25 to October 06, 2017 to be held in Berlin. The AdMaCom addresses scientific driven startups with outstanding technologies and business models in the area of advanced materials and related digital services. Startups with applications ranging from lighting and displays to sensors and wearables can apply for participation until July 26, 2017.
more...
30.05.2017Alexander von Humboldt professorship for Arno Rauschenbeutel
|
Prof. Dr. Arno Rauschenbeutel does research in the area of experimental quantum optics. One of his most important research topics is the coupling of individual atoms and photons with optic fibers that are now being used to transfer information. This successful approach is a milestone in optic quantum technology and fundamental quantum physics that will lead to concrete new applications in the future. The “Fundamentals in Optics and Photonics” professorship for Arno Rauschenbeutel is a starting signal for the “Berlin Joint Lab for Photonic Quantum Technologies.” |
 Foto: Jacqueline Godany Foto: Jacqueline Godany |
||
|
This lab will bring together the unique expertise in photonics, optics, microsystem technology, and fundamentals of quantum physics at the Technology and Science Campus of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU). In close cooperation with the department of Physics, IRIS Adlershof, and research institutions at other universities, especially the Ferdinand-Braun Institute, the goal is to integrate research and advance viable quantum systems in the immediate area, which then can picked up by local high tech companies. The HU is therefore in the good position to be a driving force in new photonic quantum technologies for the new EU billion-Euro quantum technology program. more... |
|||
27.04.2017Prof. Yan Lu, a new member at IRIS Adlershof
 Yan Lu is a new member at IRIS Adlershof. She was previously associated with IRIS as an HZB junior research group leader, and in April 2017 she started a W2-S professorship for "Polymer-based Hybrid Materials" at the Universität Potsdam. Her new position is linked to the management of a working group at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie GmbH. There she is researching in the field of colloid chemistry, focusing on the synthesis and characterization of hybrid functional materials.
Yan Lu is a new member at IRIS Adlershof. She was previously associated with IRIS as an HZB junior research group leader, and in April 2017 she started a W2-S professorship for "Polymer-based Hybrid Materials" at the Universität Potsdam. Her new position is linked to the management of a working group at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie GmbH. There she is researching in the field of colloid chemistry, focusing on the synthesis and characterization of hybrid functional materials.
27.04.2017Call for applications: Postdoc fellowships in Analytical Sciences
 The School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof (SALSA) at Humboldt-Universität Berlin is announcing a call for postdoc fellowships in selected areas of Analytical Sciences. Research areas of interest include nanoanalytics, x-ray structure analysis, inorganic mass spectrometry, ambient mass spectrometry, plasmon enhanced nanospectroscopy and in situ optical spectroscopies. Candidates should apply with their own project in the research areas named above and take into account the research of the hosting groups. Please apply via email only. Detailed information on the application process and requirements, on project areas defined by the hosting groups and on the conditions of the fellowship can be found here.
The School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof (SALSA) at Humboldt-Universität Berlin is announcing a call for postdoc fellowships in selected areas of Analytical Sciences. Research areas of interest include nanoanalytics, x-ray structure analysis, inorganic mass spectrometry, ambient mass spectrometry, plasmon enhanced nanospectroscopy and in situ optical spectroscopies. Candidates should apply with their own project in the research areas named above and take into account the research of the hosting groups. Please apply via email only. Detailed information on the application process and requirements, on project areas defined by the hosting groups and on the conditions of the fellowship can be found here.
25.04.2017IRIS founding chairman Prof. J.P. Rabe elected as chairman of the Academic Council (HU)
|
Professor Jürgen P. Rabe, physicist, material- and nanoscientist at the Department of Physics and founding chairman of IRIS Adlershof, has been elected as the new chairman of the Academic Council of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU). His deputies are Heidi Neugebauer, Maren Huberty and Christine Ilgert. IRIS Adlershof congratulates warmly and wishes him success in his new additional function. more... |
 Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe Image: Ralph Bergel |
22.04.201722. Berlin Day of Mathematics on the Campus Adlershof of HU Berlin
 Team Die Hankinators 2.0: John Huynh, Julius Paul Russmann, Hanke Guo, Paul Barth und Arman Pour Tak Dost (v.l.n.r.) Foto: Nora Butter, IRIS Adlershof |
About 1,000 pupils took part in the annual Berlin Day of Mathematics at the Campus Adlershof of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) on 22 April 2017. The winning team is Die Hankinators 2.0 from the Herder-Gymnasium in Berlin-Charlottenburg. Like the winning teams from the years before, they travel to Oslo to receive the Abel Prize 2017, one of the world's most important awards in mathematics. The student competition was organized with great help this year by theIRIS Adlershof. more... |
18.04.2017Berlin's governing mayor Michael Müller visited the Technologypark Adlershof
 On April 18, 2017 Berlin's governing mayor Michael Müller visited the Technologypark Adlershof. The visit was under the motto: "Growth Accelerator Adlershof - How to come from science to business". Among the participants was the founding chairman of IRIS Adlershof, Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe.
On April 18, 2017 Berlin's governing mayor Michael Müller visited the Technologypark Adlershof. The visit was under the motto: "Growth Accelerator Adlershof - How to come from science to business". Among the participants was the founding chairman of IRIS Adlershof, Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe.
more...
03.04.2017Einstein Center Digital Future has opened up
 On April 3rd 2017 the Einstein Center Digital Future (ECDF) opened up at the Robert Koch Forum on Wilhelmstrasse in the Berlin district Mitte. Fifty new professorships will be filled in core areas of digital infrastructure, methods, and algorithms as well as in the innovative areas of digital health, digital society, and social sciences and in digital industry and services. Altogether 38.5 million euros will flow into the project. The speaker of ECDF is Prof. Dr. Odej Kao from the Technische Universität Berlin. Johann-Christoph Freytag, professor for computer sciences at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and a member of IRIS Adlershof, is speaker for the area of digital infrastructure, methods, and algorithms.
On April 3rd 2017 the Einstein Center Digital Future (ECDF) opened up at the Robert Koch Forum on Wilhelmstrasse in the Berlin district Mitte. Fifty new professorships will be filled in core areas of digital infrastructure, methods, and algorithms as well as in the innovative areas of digital health, digital society, and social sciences and in digital industry and services. Altogether 38.5 million euros will flow into the project. The speaker of ECDF is Prof. Dr. Odej Kao from the Technische Universität Berlin. Johann-Christoph Freytag, professor for computer sciences at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and a member of IRIS Adlershof, is speaker for the area of digital infrastructure, methods, and algorithms.
more...
01.04.2017IRIS’s head of an independent junior research group Yan Lu has been appointed a university professor at Potsdam
 Dr. Yan Lu, head of an independent junior research group at the Helmholtz Center Berlin for Materials and Energy (HZB) and at IRIS Adlershof, has been appointed a W2-S professor by the Universität Potsdam. She also leads a research group at the Institute for Soft Matter and Functional Materials at the HZB. Yan Lu is involved with the design and synthesis of colloid particles for tailor-made mesoscopic structures as well as organic/inorganic hybrid particles and their application as energy storage devices, sensors, and solar cells. IRIS Adlershof cordially congratulates Professor Lu and anticipates with pleasure a further fruitful cooperation.
Dr. Yan Lu, head of an independent junior research group at the Helmholtz Center Berlin for Materials and Energy (HZB) and at IRIS Adlershof, has been appointed a W2-S professor by the Universität Potsdam. She also leads a research group at the Institute for Soft Matter and Functional Materials at the HZB. Yan Lu is involved with the design and synthesis of colloid particles for tailor-made mesoscopic structures as well as organic/inorganic hybrid particles and their application as energy storage devices, sensors, and solar cells. IRIS Adlershof cordially congratulates Professor Lu and anticipates with pleasure a further fruitful cooperation.28.03.2017IRIS Junior Scientist Wan-Ing Lin successfully defended her dissertation "Enhanced Raman Scattering of Molecular Monolayers"
 IRIS Junior Scientist Wan-Ing Lin successfully defended her dissertation Enhanced Raman Scattering of Molecular Monolayers. Her work was supervised by IRIS founding spokesman Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe and Prof. Renato Zenobi (ETH Zürich) in the
IRIS Junior Scientist Wan-Ing Lin successfully defended her dissertation Enhanced Raman Scattering of Molecular Monolayers. Her work was supervised by IRIS founding spokesman Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe and Prof. Renato Zenobi (ETH Zürich) in the
SALSA School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof.
Congratulations!
03.03.2017IRIS Junior Scientist Manuel Gensler successfully defended his dissertation "Binding forces in metallo-supramolecular coordination compounds"
 IRIS Junior Scientist Manuel Gensler successfully defended his dissertation Binding forces in metallo-supramolecular coordination compounds. His work was supervised by IRIS founding spokesman Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe in the
IRIS Junior Scientist Manuel Gensler successfully defended his dissertation Binding forces in metallo-supramolecular coordination compounds. His work was supervised by IRIS founding spokesman Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe in the
Integriertes Graduiertenkolleg of the CRC 765
Self-Assembled Soft Matter Nano-Structures at Interfaces:
New architectures, functions and applications.
Congratulations!
24.02.2017IRIS Junior Scientist Tobias Liebig successfully defended his dissertation "Optomechanical properties of macromolecules on solid surfaces"
 IRIS Junior Scientist Tobias Liebig successfully defended his dissertation Optomechanical properties of macromolecules on solid surfaces. His work was supervised by IRIS founding spokesman Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe in the
IRIS Junior Scientist Tobias Liebig successfully defended his dissertation Optomechanical properties of macromolecules on solid surfaces. His work was supervised by IRIS founding spokesman Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe in the
International Research Training Group 1524
Self-Assembled Soft Matter Nano-Structures at Interfaces.
Congratulations!
22.02.2017Dr. Raphael Schlesinger’s dissertation released by Springer Theses
 The dissertation of Dr. Raphael Schlesinger was selected to be published in Springer Theses, a dedicated book series to recognize outstanding doctoralresearch. Raphael’s work, conceived and performed within the CRC 951 at the physics department and IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, was supervised by Prof. Norbert Koch, who is the deputy chairman of IRIS Adlershof. The thesis unravels fundamental mechanisms governing hybrid inorganic organic energy-level alignment and its purposeful manipulation.These insights pave the way towards new technological control and enable usage of hybrid materials and interfaces in future devices and applications. The dissertation of Dr. Raphael Schlesinger was selected to be published in Springer Theses, a dedicated book series to recognize outstanding doctoralresearch. Raphael’s work, conceived and performed within the CRC 951 at the physics department and IRIS Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, was supervised by Prof. Norbert Koch, who is the deputy chairman of IRIS Adlershof. The thesis unravels fundamental mechanisms governing hybrid inorganic organic energy-level alignment and its purposeful manipulation.These insights pave the way towards new technological control and enable usage of hybrid materials and interfaces in future devices and applications.IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Raphael Schlesinger and wishes him much success in his future work. |
Dr. R. Schlesinger
Energy-Level Control at Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Semiconductor Interfaces
ISBN 978-3-319-46623-1 (Print)
ISBN 978-3-319-46624-8 (Online)
17.02.20177th „Nano and Photonics“ meeting in the Castle of Mauterndorf, Austria
From 22.3.-25.3.2017 Wolfgang Knoll (Austrian Institute of Technology), Franz Aussenegg (Universität Graz and Erwin-Schrödinger Institute) and Emil J.W. List-Kratochvil (Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Member of IRIS Adlershof) jointly organize the 7th “Nano and Photonics” meeting in the Castle of Mauterndorf, Austria.
This year’s program was put together with a topical focus on “Sensing applications based on plasmonic nanostructures “. Invited speakers include N. Halas from Rice University, E. Maillart from HORIBA Jobin-Yvon, Paris/FRA), G. Strasser from TU Wien, and many others.
The purpose of this event is to organize an international scientific meeting for those, who are interested in photonic applications of modern nanotechnology. One goal of this event is also to create an informal European wide discussion platform for state of the art work in basic research done at the various universities as well as industrial based research and development. The location, Castle Mauterndorf, provides an ideal environment to discuss the entire range of topics without any pressure of time, in particular between the morning and afternoon sessions as well as in the evening. This year again it is expected to gather 70 participants from 8 different countries.
more...
30.01.2017GLAD makes new organic memory devices possible
In the last news, nanotechweb.org (IOP Publishing) features an Nano Letters article by Giovanni Ligorio, Marco Vittorio Nardi, and Norbert Koch, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof:
"Researchers in Germany have used a technique called glancing angle deposition (GLAD) to fabricate non-volatile memory devices that are smaller than 100nm2. When integrated into the appropriate architectures, these devices have a memory density of more than 1 GB/cm2. They could be used in high-density, high-speed and low-power memories of the future."
more...
Lithography-Free Miniaturization of Resistive Nonvolatile Memory Devices to the 100 nm Scale by Glancing Angle Deposition
G. Ligorio, M.V. Nardi, N. Koch
Nano Lett., Article published online
23.12.2016Color Duality in Photons - an APS Highlight of the Year 2016
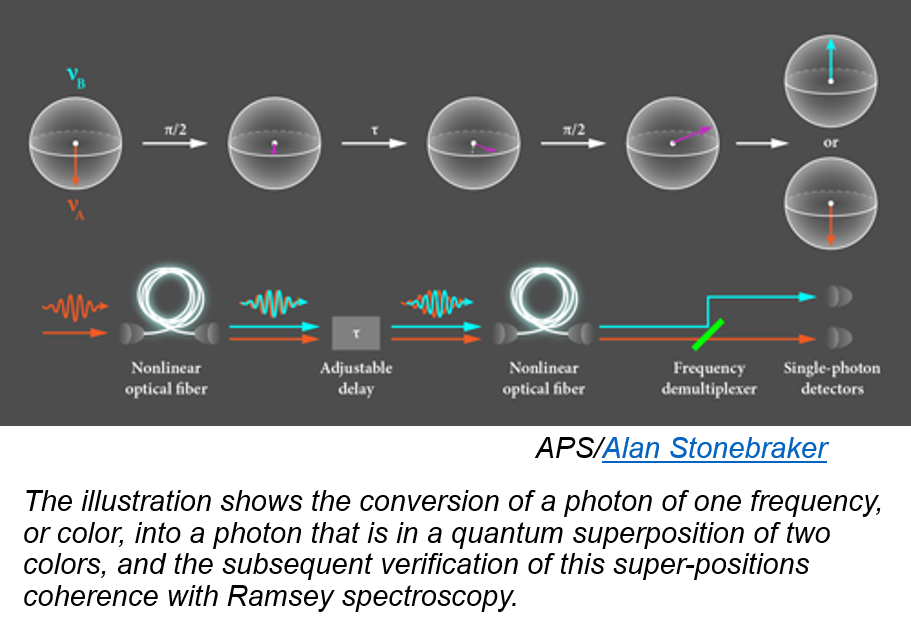 The paper “Ramsey Interference with Single Photons”[1] and accompanying Viewpoint “Photon Qubit is Made of Two Colors”[2] have been selected as one of the Highlights of the Year 2016 by APS Physics. It was co-authored by Dr. Sven Ramelow, who recently started his Emmy-Noether-Group at the Institute for Physics, Humboldt-University Berlin, and is associated with IRIS Adlershof. While there have numerous highly interesting papers in Physical Review Letters in 2016, APS Physics explains their selection, writing: “It’s no surprise that LIGO’s discovery of gravitational waves tops our list of favorite Physics stories in 2016. The other slots went to research that marked a change in perspective, demonstrated an impressive experimental feat, or simply made us think.”
The paper “Ramsey Interference with Single Photons”[1] and accompanying Viewpoint “Photon Qubit is Made of Two Colors”[2] have been selected as one of the Highlights of the Year 2016 by APS Physics. It was co-authored by Dr. Sven Ramelow, who recently started his Emmy-Noether-Group at the Institute for Physics, Humboldt-University Berlin, and is associated with IRIS Adlershof. While there have numerous highly interesting papers in Physical Review Letters in 2016, APS Physics explains their selection, writing: “It’s no surprise that LIGO’s discovery of gravitational waves tops our list of favorite Physics stories in 2016. The other slots went to research that marked a change in perspective, demonstrated an impressive experimental feat, or simply made us think.”
Incidentally, Dr. Sven Ramelow is working on follow-up ideas and experiments of this paper, which he looks forward to soon being implemented at the HU Physics Department and at IRIS Adlershof and yielding new intriguing results.
[1] “Ramsey Interference with Single Photons”, Stéphane Clemmen, Alessandro Farsi, Sven Ramelow, Alexander L. Gaeta, Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 223601 (2016)
[2] Viewpoint: Photon Qubit is Made of Two Colors, Philipp Treutlein, Physics 9, 135 (2016)
12.12.2016Light controls repair of materials
 A team of German researchers led by chemists of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has developed a new type of plastic coating, which can heal damages selectively by illumination with light. A heat-induced repair of the material occurs where the damaged area has previously been illuminated with light of a specific color.
A team of German researchers led by chemists of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has developed a new type of plastic coating, which can heal damages selectively by illumination with light. A heat-induced repair of the material occurs where the damaged area has previously been illuminated with light of a specific color.
more....
07.12.2016Prof. Christoph T. Koch and Prof. Nicola Pinna new members at IRIS Adlershof
 Christoph T. Koch (photo left), professor for structural research and electron microscopy at Humboldt-Universität's physics department and Nicola Pinna, professor for functional materials at the department of chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin are new members at IRIS Adlershof. Christop Koch's research focuses on the development of new methods in quantitative transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and their application to materials science problems. Nanostructured materials are in the focus of Nicola Pinna's research interests. Special emphasis is laid on the synthesis of novel multifunctional materials, their characterization and the study of their physical properties. IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate both new members and is looking very much forward to a fruitful collaboration.
Christoph T. Koch (photo left), professor for structural research and electron microscopy at Humboldt-Universität's physics department and Nicola Pinna, professor for functional materials at the department of chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin are new members at IRIS Adlershof. Christop Koch's research focuses on the development of new methods in quantitative transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and their application to materials science problems. Nanostructured materials are in the focus of Nicola Pinna's research interests. Special emphasis is laid on the synthesis of novel multifunctional materials, their characterization and the study of their physical properties. IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate both new members and is looking very much forward to a fruitful collaboration.
23.11.2016Dr. Lorenzo Bianchi awarded with Carl-Ramsauer-Prize 2016
 Dr. Lorenzo Bianchi, former member of the Emmy-Noether Junior Research group of Dr. Valentina Forini in the working group of Prof. Jan Plefka, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, has been awarded the Carl-Ramsauer-Prize 2016 of the Physikalische Gesellschaft zu Berlin for his outstanding PhD thesis on perturbation theory for string sigma models. This is an active research field to which Bianchi contributed by developing new powerful techniques, allowing for substantial simplifications in perturbative computations. Using these innovative methods several new results in the strong coupling regime of the AdS/CFT correspondence have been obtained. IRIS Adlershof congratulates the laureate.
Dr. Lorenzo Bianchi, former member of the Emmy-Noether Junior Research group of Dr. Valentina Forini in the working group of Prof. Jan Plefka, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, has been awarded the Carl-Ramsauer-Prize 2016 of the Physikalische Gesellschaft zu Berlin for his outstanding PhD thesis on perturbation theory for string sigma models. This is an active research field to which Bianchi contributed by developing new powerful techniques, allowing for substantial simplifications in perturbative computations. Using these innovative methods several new results in the strong coupling regime of the AdS/CFT correspondence have been obtained. IRIS Adlershof congratulates the laureate.
more...
17.11.2016Claire Glanois awarded with a Humboldt Research Fellowship
 Dr Claire Glanois has been awrded an Alexander von Humboldt Research Fellowship for Postdocs. Starting April 2017 she will join the group of Prof. Kreimer who is a meber of IRIS Adlershof, at Humboldt University. She received her PhD in mathematics in January 2016 from the Université Pierre et Marie Curie (Paris) and is currently a postdoc at the MPI Mathematics in Bonn. The number theorist concentrates on periods as they appear in computations in quantum field theory, a central topic in Prof. Kreimer's group.
Dr Claire Glanois has been awrded an Alexander von Humboldt Research Fellowship for Postdocs. Starting April 2017 she will join the group of Prof. Kreimer who is a meber of IRIS Adlershof, at Humboldt University. She received her PhD in mathematics in January 2016 from the Université Pierre et Marie Curie (Paris) and is currently a postdoc at the MPI Mathematics in Bonn. The number theorist concentrates on periods as they appear in computations in quantum field theory, a central topic in Prof. Kreimer's group.
15.11.2016Dr. Ludwig Kronthaler elected as new Vice President for Finance, Personnel and Technical Matters

Image: Matthias Heyde
IRIS Adlershof congratulates very warmly and looks forward to a successful cooperation.
mehr...
10.11.2016“Lucrative quantum technology is already here” Interview with IRIS member, Prof. Thomas Elsässer
 Within the framework of Science Week, the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is holding the Next Frontier Debate on November 10th. Prof. Dr. Birgitta Whaley (University of California, Berkeley) and the IRIS Adlershof members, Prof. Dr. Oliver Benson and Prof. Dr. Thomas Elsässer, will be speaking in a podium discussion in the Tieranatomisches Theater on state-of-the-art quantum research and different approaches and perspectives for future developments. Prof. Elsässer has also given a few insights into the research area as a whole in the interview.
Within the framework of Science Week, the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is holding the Next Frontier Debate on November 10th. Prof. Dr. Birgitta Whaley (University of California, Berkeley) and the IRIS Adlershof members, Prof. Dr. Oliver Benson and Prof. Dr. Thomas Elsässer, will be speaking in a podium discussion in the Tieranatomisches Theater on state-of-the-art quantum research and different approaches and perspectives for future developments. Prof. Elsässer has also given a few insights into the research area as a whole in the interview.
more...
18.10.2016Getting Light into Shape for New Applications - A new collaborative research project for photonic nanofilms
 The BMBF is funding the collaborative research project „Nanofilm – Photonic Nanofilms with Comprehensive Optical Functionality,” which is being coordinated by the Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, with just under two million Euros for the next three years. Oliver Benson, a member of IRIS Adlershof, and Prof. Kurt Busch are taking part in the project from the HU Berlin’s side.
The BMBF is funding the collaborative research project „Nanofilm – Photonic Nanofilms with Comprehensive Optical Functionality,” which is being coordinated by the Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, with just under two million Euros for the next three years. Oliver Benson, a member of IRIS Adlershof, and Prof. Kurt Busch are taking part in the project from the HU Berlin’s side.
more...
09.10.2016Humboldt Research Fellowship for Prof. Karen Yeats
 Professor Karen Yeats has been awarded a Humboldt Research Fellowship for Experienced Researchers. The fellowship provides funding for highly-qualified scientists and scholars to make extended research visits to Germany. Karen will be spending 3 months in the summer of 2017, and then 12 months in 2018-2019, at the Humboldt University of Berlin, where she will work with Professor Dirk Kreimer, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, and his research group.
Professor Karen Yeats has been awarded a Humboldt Research Fellowship for Experienced Researchers. The fellowship provides funding for highly-qualified scientists and scholars to make extended research visits to Germany. Karen will be spending 3 months in the summer of 2017, and then 12 months in 2018-2019, at the Humboldt University of Berlin, where she will work with Professor Dirk Kreimer, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, and his research group.
Karen joined the Department of Combinatorics and Optimization of tne University of Waterloo as an Associate Professor August 1st 2016. She received a B.Math. in Pure Mathematics from the University of Waterloo in 2003, and was the recipient of a Governor General Silver Medal. She completed her Ph.D. in mathematics from Boston University in 2008; her thesis was on Growth Estimates for Dyson-Schwinger Equations. In 2009, she began a professorship in the Department of Mathematics at Simon Fraser University. Karen's research interests are in combinatorics and quantum field theory. The primary objectives of her research are a mathematical understanding of the Dyson-Schwinger quantum equations of motion, and of Feynman integrals. Her work draws upon the interplay between algebraic combinatorics, graph theory, algebraic geometry, and mathematical physics.
30.09.2016New Emmy-Noether Junior Research Group on "Mid-Infrared Quantum Imaging and Spektroscopy“ for Dr. Sven Ramelow
 Dr. Sven Ramelow will start this fall to establish an Emmy Noether Junior Research Group on the topic of "Mid-Infrared Quantum Imaging and Spectroscopy" at Humboldt-Universität's Physics Department. He will closely cooperate with the Nano-Optics-Group led by Prof. Oliver Benson, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof.
Dr. Sven Ramelow will start this fall to establish an Emmy Noether Junior Research Group on the topic of "Mid-Infrared Quantum Imaging and Spectroscopy" at Humboldt-Universität's Physics Department. He will closely cooperate with the Nano-Optics-Group led by Prof. Oliver Benson, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof.In the past Dr. Ramelow has carryied out research at the University of Vienna (Austria) and Cornell University (Ithaca, NY, USA) on experimental topics of nonlinear quantum optics with single photons. A main goal of his group will be to pioneer and establish quantum imaging and spectroscopy in the technologically highly relevant mid-infrared wavelength regime. A special focus will be on opening up specific real-world applications in bio-medical imaging and sensing as well as on doing basic research with experimental demonstrations on how to overcome fundamental limits of classical optics by using quantum optical methods. IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Sven Ramelow and wishes him much success in his future work.
13.09.2016Discovering paths from research to potential applications
 The Adlershofer special 46 applies to "INAM - An alliance for new materials". In the editorial founding chairman Professor Jürgen P. Rabe explains how IRIS Adlershof strengthens its cooperation to support the transition of basic research findings to final applications.
The Adlershofer special 46 applies to "INAM - An alliance for new materials". In the editorial founding chairman Professor Jürgen P. Rabe explains how IRIS Adlershof strengthens its cooperation to support the transition of basic research findings to final applications.
06.09.2016The Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is currently the 5th best German university in the QS world university ranking.
 In the current QS World University Ranking, the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is among the best German universities and has advanced to fifth place. In the worldwide ranking list, the HU Berlin has improved itself from 126th to 121th place. The HU ranks in the top 100 in each of these subjects: computer science, mathematics, and physics.
In the current QS World University Ranking, the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is among the best German universities and has advanced to fifth place. In the worldwide ranking list, the HU Berlin has improved itself from 126th to 121th place. The HU ranks in the top 100 in each of these subjects: computer science, mathematics, and physics.
18.08.2016AdMaCom Kick-Off: Advanced Material Startups meet in Berlin
 As their first big internationally visible activity, the Innovation Network for Advanced Materials (INAM) will hold the Advanced Materials Competition (AdMaCom), which is a six-week workshop from August 28th to October 10th, 2016, for developing innovative product concepts with international start-ups. Established (large) companies like OSRAM, LG, Ledvance, and Henkel will provide the technological infrastructure and know-how and/or sponsor money. The 15 participating Berlin and international start-ups will take advantage of this to improve their existing products and create new product concepts.
As their first big internationally visible activity, the Innovation Network for Advanced Materials (INAM) will hold the Advanced Materials Competition (AdMaCom), which is a six-week workshop from August 28th to October 10th, 2016, for developing innovative product concepts with international start-ups. Established (large) companies like OSRAM, LG, Ledvance, and Henkel will provide the technological infrastructure and know-how and/or sponsor money. The 15 participating Berlin and international start-ups will take advantage of this to improve their existing products and create new product concepts.
The participants will be able to draw upon the expertise of mentors from renowned international research facilities and industrial companies like LG Technology Center Europe, BASF Ventures, the London School of Economics, the Imperial College London as well as from Berlin like OSRAM, Direct Photonics Industries, Specs Nano Surface Analytics, Fab Lab Berlin, the Humboldt University’s IRIS Adlershof, Humboldt Innovation, ESMT, WISTA and Berlin Partner. Berlin should be visualized as an international high tech location not only for start-ups but also for innovative departments from large companies.
AdMaCom is being held under the patronage of the governing Mayor of Berlin.
more...
04.07.2016Tapping the sun
 A team of researchers from IRIS Adlershof of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Technische Universiteit Eindhoven in the Netherlands have developed thin plastic films, which continuously move upon exposure to sunlight. These materials are able to convert the sunlight’s energy directly into motion and have great promise for the development of sun-driven active coatings and surfaces, for example self-cleaning windows. These results have been published in Nature Communications.
A team of researchers from IRIS Adlershof of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Technische Universiteit Eindhoven in the Netherlands have developed thin plastic films, which continuously move upon exposure to sunlight. These materials are able to convert the sunlight’s energy directly into motion and have great promise for the development of sun-driven active coatings and surfaces, for example self-cleaning windows. These results have been published in Nature Communications.
more...
20.06.2016Enlightening and flexing memories
 Researchers from Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, led by Professor Stefan Hecht, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, in collaboration with the University of Strasbourg & CNRS (France) and the University of Nova Gorica (Slovenia), have shown that a carefully chosen blend of a small photoswitchable molecule and a semiconducting polymer can be used to fabricate high-performance memory devices that can be written and erased by light. Such multilevel (8-bit) optical memories have also been implemented on flexible substrates, paving the way to applications in wearable electronics, E-papers, and smart devices. These results have been published in Nature Nanotechnology.
Researchers from Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, led by Professor Stefan Hecht, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, in collaboration with the University of Strasbourg & CNRS (France) and the University of Nova Gorica (Slovenia), have shown that a carefully chosen blend of a small photoswitchable molecule and a semiconducting polymer can be used to fabricate high-performance memory devices that can be written and erased by light. Such multilevel (8-bit) optical memories have also been implemented on flexible substrates, paving the way to applications in wearable electronics, E-papers, and smart devices. These results have been published in Nature Nanotechnology.
more...
18.06.2016Advanced Materials Competition Application open!
 The Innovation Network for Advanced Materials based in Berlin opens the application period for ambitious hardware startups, which are focused on the development of innovative and marketable high-tech products! These products can be based on organic and molecular electronics,surface engineering, polymer science,compounds, battery technology, photovoltaics, hybrid materials, fibers, sensors, lighting as well as printedelectronics for all sorts of game changing applications! During a period of 6 weeks, start-ups discuss intensively their unique needs and challenges with professionals and industry experts to establish new business opportunities. Corporate teams, start-ups, researchers and internationally selected mentors work together, receive weekly trainings as well as business and technology guidance to develop innovative products and solutions. The 20 selected start-ups will receive gratis access to a co-working space, labs and materials in order to bring their product and business to the next level. Additionally, we will invite all our international start-ups to stay in sponsored apartments. Confirmed *Partners* so far: Osram, Tesla, Henkel, Embraer *Mentors*: BASF, LG, Direct Photonics, Pilotfish, Columbia University, London School of Economics, Humboldt University, Weitnauer, Embraer, Henkel, Osram, and many more.
The Innovation Network for Advanced Materials based in Berlin opens the application period for ambitious hardware startups, which are focused on the development of innovative and marketable high-tech products! These products can be based on organic and molecular electronics,surface engineering, polymer science,compounds, battery technology, photovoltaics, hybrid materials, fibers, sensors, lighting as well as printedelectronics for all sorts of game changing applications! During a period of 6 weeks, start-ups discuss intensively their unique needs and challenges with professionals and industry experts to establish new business opportunities. Corporate teams, start-ups, researchers and internationally selected mentors work together, receive weekly trainings as well as business and technology guidance to develop innovative products and solutions. The 20 selected start-ups will receive gratis access to a co-working space, labs and materials in order to bring their product and business to the next level. Additionally, we will invite all our international start-ups to stay in sponsored apartments. Confirmed *Partners* so far: Osram, Tesla, Henkel, Embraer *Mentors*: BASF, LG, Direct Photonics, Pilotfish, Columbia University, London School of Economics, Humboldt University, Weitnauer, Embraer, Henkel, Osram, and many more.
Apply at: www.inam.berlin
07.06.2016Forging new products in electronics, optics and photonics
INAM Innovation Network for Advanced Materials founded in Berlin Adlershof

Scientists and business representatives of the Science and Technology Park have come together to form a new network. The INAM Innovation Network for Advanced Materials spans the whole value chain from basic research to product design.
Next to industrial partners such as Osram GmbH, INAM’s partners include the Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences (IRIS Adlershof), Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU Berlin), the economic development company Berlin Partner, and WISTA-MANAGEMENT GMBH. Initially planned for three years, the network’s aim is to develop and implement concepts for the use of new materials and technology in electronics, optics, and photonics, which in-clude, for example, new printing technology for cheaper production pro-cesses, transparent and conductive coatings for thin-film solar cells, or new organic light-emitting diodes (OLED) for the car industry.
INAM e.V. was established following an initiative of the Science and Technology Park Berlin Adlershof, where non-university research institutions and innovative companies have created a competence centre for optical analyt-ics and materials science in the vicinity of IRIS Adlershof of HU Berlin. The INAM network does more than to connect science and business and research and development. It also consists of partners who help to make products ready for the market. They range from the Agentur Pilotfish GmbH, a specialist for product design, to Fab Lab Berlin, an open workshop for development, or Humboldt Innovation GmbH and the attorneys of Weitnauer Rechtsanwälte Partnerschaftsgesellschaft, who offer advisory services on patents and technology transfer.
“Interdisciplinary cooperation will create new applications and, lastly, finished products which will increase the competitiveness of the companies in the region,” says Peter A. Frensch, vice-president for research at Humboldt-Universität. This will be facilitated by the existing infrastructure of Berlin Adlershof, which can be used for joint research and development, and com-plemented by entrepreneurship, start-up, and accelerator programmes, joint events, and showcases at conferences and trade fairs. The INAM network has already successfully attracted a new company to the Technology Park Adlershof this year: “The Inuru GmbH start-up has an inno-vative idea: it offers companies unprecedented marketing opportunities by using flat OLEDs to bring light and animation to paper,” Jonas Pauly ex-plains, who is the designated head of INAM. The Certi Foundation from Brazil, which is specialized on high technology, is the network’s first strategic partner from overseas.
24.05.2016Call for 20 SALSA doctoral fellowships open
SALSA, the Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is announcing 20 doctoral fellowships to begin between August 1st and November 1st, 2016. The program offers a structured, three-year period of multidisciplinary research combined with an integrated curriculum in Analytical Sciences. Deadline ends June 8th, 2016.
more…
22.04.2016The DZLM goes into the second round
 The Deutsche Zentrum für Lehrerbildung Mathematik (DZLM), which was initiated by the Deutsche Telekom Stiftung, has been very successful as the first federal interstate contact point to go for further education in mathematics since October 2011. The German Telekom Foundation will be supporting the DZLM for another three years with 4.5 million euros by the end of 2019. The director of DZLM, Professor Jürg Kramer (a member of IRIS Adlershof) is very pleased about the further funding and associated recognition of the previous work of the DZLM, in which the Humboldt University played a large part as the coordinating university for the program.
The Deutsche Zentrum für Lehrerbildung Mathematik (DZLM), which was initiated by the Deutsche Telekom Stiftung, has been very successful as the first federal interstate contact point to go for further education in mathematics since October 2011. The German Telekom Foundation will be supporting the DZLM for another three years with 4.5 million euros by the end of 2019. The director of DZLM, Professor Jürg Kramer (a member of IRIS Adlershof) is very pleased about the further funding and associated recognition of the previous work of the DZLM, in which the Humboldt University played a large part as the coordinating university for the program.
The DZLM has been developing research-based and applied further education programs that are continually being researched and constantly improved in cooperation with the federal states and academic institutions. Kramer projects that they will be more strongly focused on long-term further education programs for teachers who in turn will educate and accompany others as multiplicators. The existing net works and cooperation will be built up with the educational administration. IRIS Adlershof congratulates the successful project applicants and, of course, its member Jürg Kramer heartily.
19.04.2016Bessel Preis für Professor Gabriele Travaglini
 Prof. Dr. Gabriele Travaglini from Queen Mary University London receives the Friedrich-Wilhelm Bessel Prize from the Alexander-von-Humboldt Foundation. The prize will enable him to spend one year of research at the institute of physics and IRIS Adlershof. The award is 45.000 Euro.
Prof. Dr. Gabriele Travaglini from Queen Mary University London receives the Friedrich-Wilhelm Bessel Prize from the Alexander-von-Humboldt Foundation. The prize will enable him to spend one year of research at the institute of physics and IRIS Adlershof. The award is 45.000 Euro.
Prof. Travaglini is a renowned theoretical physicist exploring the connection between quantum field theory and string theory. He has made substantial contributions to our understanding of scattering amplitudes in quantum field theory and gravity, which quantify the fundamental interactions of elementary particles at the microscopic scale. This core research area of high-energy theory was revolutionized in the past ten years through the development of novel so-called on-shell techniques surpassing the traditional approach due to Feynman. Travaglini has been at the forefront of these developments. During his stay in Berlin, he intends to focus on the study of and search for hidden symmetries in scattering amplitudes and form factors.
Professor Travaglini is hosted by Professor Jan Plefka at the Institute of Physics and IRIS Adlershof of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
18.03.2016Professor Thomas Elsaesser is the 2016 recipient of the Ellis R. Lippincott Award
 Thomas Elsaesser, Director at the Max-Born-Institute and Member of IRIS Adlershof, receives the Ellis R. Lippincott Award for his “seminal contributions to the understanding of the ultrafast coherent and incoherent vibrational dynamics of hydrogen bonds in liquids and biomolecules”. The prize recognizes his pioneering work elucidating molecular processes and interactions in water, hydrogen bonded dimers, nucleobase pairs, and biomolecules in an aqueous environment such as hydrated DNA and phospholipids. This research is based on methods of nonlinear infrared spectroscopy in the pico- and femtosecond time domain. IRIS Adlershof congratulates the laureate.
Thomas Elsaesser, Director at the Max-Born-Institute and Member of IRIS Adlershof, receives the Ellis R. Lippincott Award for his “seminal contributions to the understanding of the ultrafast coherent and incoherent vibrational dynamics of hydrogen bonds in liquids and biomolecules”. The prize recognizes his pioneering work elucidating molecular processes and interactions in water, hydrogen bonded dimers, nucleobase pairs, and biomolecules in an aqueous environment such as hydrated DNA and phospholipids. This research is based on methods of nonlinear infrared spectroscopy in the pico- and femtosecond time domain. IRIS Adlershof congratulates the laureate.
more...
05.03.2016Construction work on IRIS Research Building started
 After the federal and state Gemeinsame Wissenschaftskonference (GWK) (Joint Science Conference) decided in June 2013 to finance a research building for IRIS Adlershof’s project, “Hybrid systems for electronics, optoelectronics, and phototonics,” and after completion of comprehensive planning and work and a subsequent call for proposals, construction has now begun on the building site of “Zum Großen Windkanal 6.”
After the federal and state Gemeinsame Wissenschaftskonference (GWK) (Joint Science Conference) decided in June 2013 to finance a research building for IRIS Adlershof’s project, “Hybrid systems for electronics, optoelectronics, and phototonics,” and after completion of comprehensive planning and work and a subsequent call for proposals, construction has now begun on the building site of “Zum Großen Windkanal 6.”
more...
25.02.2016Professorship offered to Stefan Fredenhagen
 IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Professor Stefan Fredenhagen, who is at the MPI for Gravitational Physics and currently doing a guest professorship in Professor Staudachers research group "Space-Time-Matter", for receiving an offer for a professorship in mathematical physics in the Physics Department at the University of Vienna.
IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Professor Stefan Fredenhagen, who is at the MPI for Gravitational Physics and currently doing a guest professorship in Professor Staudachers research group "Space-Time-Matter", for receiving an offer for a professorship in mathematical physics in the Physics Department at the University of Vienna.
19.02.2016Gravitational waves detected 100 years after Einstein's prediction - IRIS congratulates
 Gravitational waves, which were predicted on the basis of Einstein’s Theory of Gravity exactly 100 years ago in the form of ripples in space and time, have been proven for the first time by a LIGO detector in the USA. IRIS Adlershof would like to especially heartily congratulate its cooperation partners in the research field of Space-Time-Matter at MPI for Gravitational Physics (Albert Einstein Institute), who were significantly involved in this once-in-a-century event.
Gravitational waves, which were predicted on the basis of Einstein’s Theory of Gravity exactly 100 years ago in the form of ripples in space and time, have been proven for the first time by a LIGO detector in the USA. IRIS Adlershof would like to especially heartily congratulate its cooperation partners in the research field of Space-Time-Matter at MPI for Gravitational Physics (Albert Einstein Institute), who were significantly involved in this once-in-a-century event.
more...
12.02.2016The Academic Council of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) reappoints Peter A. Frensch
 The current Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) Vice President for Research, Prof. Dr. Peter A. Frensch, was re-elected on 9 February 2016, winning 34 votes. The Academic Council thereby confirmed his reappointment, and he will be one of the four President's office executive staff who report directly to the President, Dr.-Ing. Dr. Sabine Kunst.
The current Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) Vice President for Research, Prof. Dr. Peter A. Frensch, was re-elected on 9 February 2016, winning 34 votes. The Academic Council thereby confirmed his reappointment, and he will be one of the four President's office executive staff who report directly to the President, Dr.-Ing. Dr. Sabine Kunst.
more...
12.02.2016Humboldt-Universitäts-Medaille und Dissertationspreis Adlershof verliehen
Gleich zwei Überraschungen gab es anlässlich der Verleihung des Dissertationspreises Adlershof 2015 am 9. Februar 2016 auf dem Campus Adlershof. Der Preis ging erstmalig in der 14-jährigen Geschichte der Auszeichnung an zwei Preisträger: Neysha Lobo-Ploch und Jan-Ferenc Kischkat.
Nach der Preisvergabe betrat Jan-Hendrik Olbertz, Präsident der HU, als Überraschungsgast die Bühne, um Hardy R. Schmitz für seine Verdienste für die HU zu ehren. Schmitz war zum Jahreswechsel nach 14 Jahren als Geschäftsführer der Wista in den Ruhestand gegangen.
mehr...
11.02.2016Second Joint Call for Proposals: TAU-HU Project "Biological and Soft Matter Physics" - Deadline extended

After three years of successful cooperation between Tel Aviv University and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin IRIS Adlershof and the IRI for the Life Sciences announce a second joint call for proposals either to start or to continue the research in the field of biological and soft matter physics. Funding is available for bilateral collaborative research projects comprising researchers or research teams from the two participating universities. The main goal of the program is to support the ongoing and stimulate new collaborations between the research groups of the two universities.
Joint project proposals by scientists from TAU and HU may be submitted until January 31st, 2016. Deadline extended: March 31st, 2016
more...
27.01.2016Einstein on the Test Bench
 Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity provides a theory on space and time that has held up for over a hundred years of experimental testing. It nonetheless contradicts quantum mechanics, which describes small-scale matter and is almost as old and is heavily examined as well. Experiments that bring both theories closer together are particularly interesting for IRIS Adlershof’s intensively studied research area “Space-Time-Matter.” Some current examples are the recent tests that were successfully performed in the KALEXUS and FOKUS projects, which were developed by Adlershof’s researchers in Prof. Achim Peters’ group in the Physics Department at the Humboldt-Universität and at the Ferdinand-Braun-Institut.
Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity provides a theory on space and time that has held up for over a hundred years of experimental testing. It nonetheless contradicts quantum mechanics, which describes small-scale matter and is almost as old and is heavily examined as well. Experiments that bring both theories closer together are particularly interesting for IRIS Adlershof’s intensively studied research area “Space-Time-Matter.” Some current examples are the recent tests that were successfully performed in the KALEXUS and FOKUS projects, which were developed by Adlershof’s researchers in Prof. Achim Peters’ group in the Physics Department at the Humboldt-Universität and at the Ferdinand-Braun-Institut.
more…
19.01.2016Prof. Sabine Kunst appointed as the new president of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
 |
|
| Sabine Kunst; Foto: Mark Wagner | |
The Board of Trustees of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) has appointed Prof. Dr.-Ing. Dr. Sabine Kunst on Jan 19, 2016 as the new president. She is likely to take up her post at the start of the summer semester. Sabine Kunst is currently the Minister of Science, Research and Culture of the state of Brandenburg, and also chairs the Administrative Commission of the German Council of Science and Humanities, Germany's most important science policy advisory body, where she is also the coordinator of the federal state representatives on the Council. The internationally renowned university professor and politician has extensive experience in the fields of science and research and also in the development of academic institutions and structures.
more...
05.01.2016Prof. J.-C. Freytag, Ph.D. was elected into the executive committee of the Gesellschaft für Informatik e.V.
 Professor Johann-Christoph Freytag, Ph.D., a member of IRIS Adlershof, was elected into the executive committee of the Gesellschaft für Informatik (GI) e.V. All GI members were called upon to vote so that three of the five candidates could be elected to the committee. Prof. Freytag will therefore be able to put to good use his many years of experience, including his past 6 years as the Speaker for GI’s Department of Databases and Information Systems (DBIS).
Professor Johann-Christoph Freytag, Ph.D., a member of IRIS Adlershof, was elected into the executive committee of the Gesellschaft für Informatik (GI) e.V. All GI members were called upon to vote so that three of the five candidates could be elected to the committee. Prof. Freytag will therefore be able to put to good use his many years of experience, including his past 6 years as the Speaker for GI’s Department of Databases and Information Systems (DBIS).
mehr...
15.12.2015Second Joint Call for Proposals: TAU-HU Project "Biological and Soft Matter Physics"

After three years of successful cooperation between Tel Aviv University and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin IRIS Adlershof and the IRI for the Life Sciences announce a second joint call for proposals either to start or to continue the research in the field of biological and soft matter physics. Funding is available for bilateral collaborative research projects comprising researchers or research teams from the two participating universities. The main goal of the program is to support the ongoing and stimulate new collaborations between the research groups of the two universities.
Joint project proposals by scientists from TAU and HU may be submitted until January 31st, 2016.
more...
10.12.2015HU Wissenschaftler/innen im Dialog mit Unternehmen – Synergien in der modernen Materialforschung
 Am 8. Dezember fand zum vierten Mal das jährliche Wissens- und Technologietransfer-Forum „Wissenschaft trifft Wirtschaft“ der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin statt. Die Veranstaltungsreihe dient der Vernetzung zwischen Wissenschaft und Wirtschaft, fördert den Austausch untereinander und ermöglicht die Initiierung gemeinsamer Projekte.
Am 8. Dezember fand zum vierten Mal das jährliche Wissens- und Technologietransfer-Forum „Wissenschaft trifft Wirtschaft“ der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin statt. Die Veranstaltungsreihe dient der Vernetzung zwischen Wissenschaft und Wirtschaft, fördert den Austausch untereinander und ermöglicht die Initiierung gemeinsamer Projekte.
Der stellvertretende Sprecher von IRIS Adlershof und Impulsgeber des neuen Formates der Veranstaltung, Prof. Norbert Koch, sagte: „Um gemeinsame Ansätze in der modernen Materialforschung zu finden, müssen sich die Partner kennenlernen. Dies ist das Ziel am 8. Dezember. Die Wissenschaftler/innen der HU werden ihr Expertisen-Portfolio darstellen und – noch wichtiger – die Unternehmen ihre aktuellen Fragestellungen. Genaues Zuhören, mitunter auch Zwischentöne zu erhaschen, und Aufeinanderzugehen sind hier gefragt.“
20.11.2015Berlin Science Prize for Prof. Peter Hegemann
Peter Hegemann, professor for experimental biophysics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and member of UniCat, has been granted, the Berlin Sciencs Prize (Berliner Wissenschaftspreis) 2015. Prof. Hegemann is one of the founders of the research field of optogenetics – a new and innovative method, with which a wide variety of cell types can be "switched" using light once they are equipped with a specific light receptor protein. IRIS Adlershof congratulates the laureate and is sharing his delight about this outstanding award..
mehr...
19.11.2015Prof. Emil List-Kratochvil, a new member at IRIS Adlershof
 Emil List-Kratochvil, Professor for Hybrid Devices at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is a new member at IRIS Adlershof. His position is a brigde-professorship of IRIS Adlershof and it is embedded in both the departments of physics and chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Prof. List-Kratochvil is an leading expert on organic and printed electronics. He is internationally well known for his work on organic devices, as for instance light emitting diodes and hybrid storage elements. IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Emil List-Kratochvil and is looking very much forward to his collaboration.
Emil List-Kratochvil, Professor for Hybrid Devices at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is a new member at IRIS Adlershof. His position is a brigde-professorship of IRIS Adlershof and it is embedded in both the departments of physics and chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Prof. List-Kratochvil is an leading expert on organic and printed electronics. He is internationally well known for his work on organic devices, as for instance light emitting diodes and hybrid storage elements. IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Emil List-Kratochvil and is looking very much forward to his collaboration.
12.10.2015Preis für gute Lehre 2015 der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin an PD Dr. Thomas Klose
Klassische Theoretische Physik und Quantenmechanik ausgezeichnet gelehrt
 Thomas Klose, Gewinner des Humboldt-Preis für gute Lehre 2015 Abbildung: Florian Loebbert |
„Das Ziel guter Lehre ist für mich, die Studierenden zu motivieren”, sagt Thomas Klose. Dazu sei es wichtig, stets konkrete Anwendungsbeispiele für abstrakte Fragestellungen zu geben. „Lichtstreuung klingt beispielsweise erstmal nicht so spannend. Warum sich jedoch abends der Himmel rot färbt, ist schon interessanter zu wissen.“ Auch die eigene Begeisterung für ein Thema spiele eine große Rolle. „Obwohl ich das Ergebnis schon kenne, muss ich es schaffen, das Interesse meines Publikums zu wecken. Da gehört auch ein bisschen Schauspielerei dazu“, so der Wissenschaftler.
21 Dozenten haben eine Nominierung erhalten. PD Dr. Thomas Klose aus der AG Quantenfeld- und Stringtheorie von IRIS Adlershof-Mitglied Jan Plefka hat die Wahl einstimmig gewonnen. „Damit habe ich überhaupt nicht gerechnet. Das hat mich ehrlich gesagt sehr überrascht. Ich freue mich natürlich über die Auszeichnung!“ 10.000 Euro Preisgeld stehen dem Physiker nun zur Verfügung.
mehr...15.09.2015Im aktuellen QS World University Ranking Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin auf Platz 6 der besten deutschen Universitäten
 Im aktuellen QS World University Ranking gehört die Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin zu den besten deutschen Hochschulen. Sie verteidigte ihren sechsten Platz im Vergleich zum Vorjahr. In der weltweiten Rangliste verbesserte sich die HU von Platz 134 auf 126. Im Bereich der Naturwissenschaften liegt die HU weltweit auf Platz 121 und in der Informatik, der Mathematik und der Physik jeweils unter den Top 100.
Im aktuellen QS World University Ranking gehört die Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin zu den besten deutschen Hochschulen. Sie verteidigte ihren sechsten Platz im Vergleich zum Vorjahr. In der weltweiten Rangliste verbesserte sich die HU von Platz 134 auf 126. Im Bereich der Naturwissenschaften liegt die HU weltweit auf Platz 121 und in der Informatik, der Mathematik und der Physik jeweils unter den Top 100.
01.09.2015Professor Emil J. W. List-Kratochvil accepted a new position at Humboldt-Universität
 Prof. Dr. Emil J. W. List-Kratochvil (TU Graz) has accepted the offer of a W3-Professorship "Hybrid Devices" at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, beginning on October 1, 2015. This professorship is located as a bridging professorship of IRIS Adlershof both at the Institute of Physics and the Institute of Chemistry.
Prof. Dr. Emil J. W. List-Kratochvil (TU Graz) has accepted the offer of a W3-Professorship "Hybrid Devices" at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, beginning on October 1, 2015. This professorship is located as a bridging professorship of IRIS Adlershof both at the Institute of Physics and the Institute of Chemistry.
01.09.2015Dr. Simone Raoux accepted a new position at Humboldt-Universität
 Dr. Simone Raoux (HZB) has accepted the offer of a W3-S-Professorship "Nano Spectroscopy for Design and Optimization of energy-related Materials" at the Department of Physics of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
Dr. Simone Raoux (HZB) has accepted the offer of a W3-S-Professorship "Nano Spectroscopy for Design and Optimization of energy-related Materials" at the Department of Physics of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
The professorship is linked to the position of a director of the Institute for Nanospectroscopy at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin GmbH.
28.07.2015Personaler sehen Absolventen der Naturwissenschaften der Humboldt-Universität bundesweit auf Platz 3
 Welche Hochschule bildet die Studenten für Ihre Bedürfnisse am besten aus? Diese Frage wurden 540 Personalern aus ganz Deutschland gestellt. In den Naturwissenschaften sehen 15,4 % die Humboldt-Universität auf Platz 1. Genau so viele nennen die LMU München. Nur die RWTH Aachen (19,6%) und die TU München (15,9%) werden noch etwas häufiger genannt.
Welche Hochschule bildet die Studenten für Ihre Bedürfnisse am besten aus? Diese Frage wurden 540 Personalern aus ganz Deutschland gestellt. In den Naturwissenschaften sehen 15,4 % die Humboldt-Universität auf Platz 1. Genau so viele nennen die LMU München. Nur die RWTH Aachen (19,6%) und die TU München (15,9%) werden noch etwas häufiger genannt.
Link zum bundesweiten Hochschulranking 2015 der Wirtschaftswoche
07.07.2015Flexible nanowires: A Berlin-Graz research team develops molecular wires with higher conductivity and bendability
 An international team under the direction of Stefan Hecht, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, and Leonhard Grill from Karl-Franzens-University Graz could develop for the first time molecular chains that have unexpectedly high conductivity in spite of their flexibility. The researchers’ new approach will allow the design of flexible nanowires and therefore enable a detailed insight into the relationship between a chemical structure and its electronic and mechanistic properties. This type of conductible and flexible nanowires will be a key component for future logical circuitry in “molecular electronics” and for flexible electronic everyday objects like “wearable plastic electronics.” This study has appeared in the current issue of the Nature Communications.
An international team under the direction of Stefan Hecht, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof, and Leonhard Grill from Karl-Franzens-University Graz could develop for the first time molecular chains that have unexpectedly high conductivity in spite of their flexibility. The researchers’ new approach will allow the design of flexible nanowires and therefore enable a detailed insight into the relationship between a chemical structure and its electronic and mechanistic properties. This type of conductible and flexible nanowires will be a key component for future logical circuitry in “molecular electronics” and for flexible electronic everyday objects like “wearable plastic electronics.” This study has appeared in the current issue of the Nature Communications.
more...
26.05.2015CRC 951 “Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)” successful to launch second funding period
 CRC 951 scientists perform cutting-edge research on hybrid systems that unite inorganic semiconductors, metal nanostructures, and conjugated organic materials, with the aim to realize and tailor novel opto-electronic functions. The achievements made during the first funding period (2011-2015) laid the foundations for the next four years of exciting HIOS-research. In the long term, the CRC aims for solid-state opto-electronic devices that exhibit superior performance compared to those based on any of the individual material classes alone. The CRC's coordinator and vice-coordinator, Norbert Koch and Oliver Benson (both members of IRIS Adlershof), are delighted with the success in obtaining continued funding from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), and they look forward to the joint work of 25 principal investigators from physics and chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (coordinating university), Technische Universität Berlin, Universität Potsdam, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie, and Fritz-Haber-Institut der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft.
CRC 951 scientists perform cutting-edge research on hybrid systems that unite inorganic semiconductors, metal nanostructures, and conjugated organic materials, with the aim to realize and tailor novel opto-electronic functions. The achievements made during the first funding period (2011-2015) laid the foundations for the next four years of exciting HIOS-research. In the long term, the CRC aims for solid-state opto-electronic devices that exhibit superior performance compared to those based on any of the individual material classes alone. The CRC's coordinator and vice-coordinator, Norbert Koch and Oliver Benson (both members of IRIS Adlershof), are delighted with the success in obtaining continued funding from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), and they look forward to the joint work of 25 principal investigators from physics and chemistry of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (coordinating university), Technische Universität Berlin, Universität Potsdam, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie, and Fritz-Haber-Institut der Max-Planck-Gesellschaft.
more...
20.05.2015Studentische/n Mitarbeiter/in gesucht
Die IRIS-Geschäftsstelle sucht zum frühestmöglichen Zeitpunkt für die Dauer von 24 Monaten eine/n studentische/n Mitarbeiter/in
mehr...
07.05.2015Mehr Photonen durch optische Nanofaser
Einem von Professor Oliver Benson, Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof, geleitetem internationalen Team aus Forschern der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) und der Universität Kyoto in Japan ist es gelungen, durch Einsatz einer neuartigen strukturierten Nanofaser die Emission von einzelnen Photonen zu verstärken. Bei dem Experiment konnte nicht nur eine außerordentlich große Anzahl an Photonen erzeugt werden, sondern es gelang auch, deren Wellenlänge genau einzustellen. Über die Faser können diese maßgeschneiderten Lichtteilchen für Anwendungen in den neuen Quantentechnologien direkt verfügbar gemacht werden. Die Forschungsergebnisse sind in der aktuellen Onlineausgabe der Open-Access-Zeitschrift „Scientific Reports“ der Nature Publishing Group erschienen.
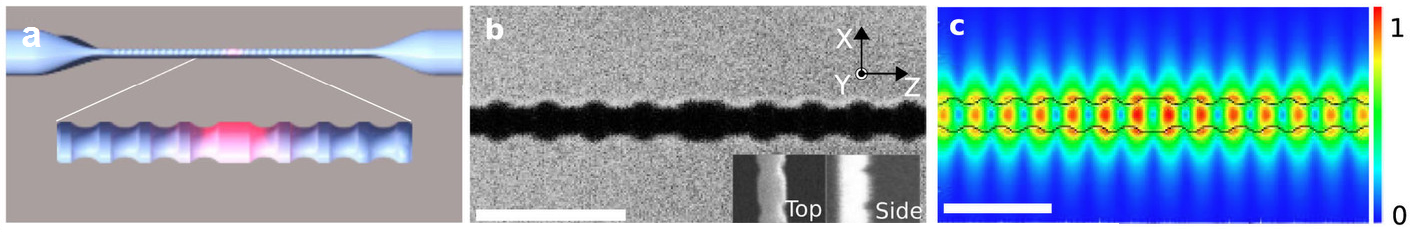
mehr...
17.04.2015Christian Kassung vertritt Professur für Experimentalsysteme
 Christian Kassung, Professor für Kulturtechniken und Wissensgeschichte im Institut für Kulturwissenschaft der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin vertritt im Sommersemester 2015 die Professur Theorie und Geschichte der Experimentalsysteme des Exzellenzclusters „Bild Wissen Gestaltung. Ein interdisziplinäres Labor" und wird dazu auch am IRIS Adlershof lehren und forschen.
Christian Kassung, Professor für Kulturtechniken und Wissensgeschichte im Institut für Kulturwissenschaft der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin vertritt im Sommersemester 2015 die Professur Theorie und Geschichte der Experimentalsysteme des Exzellenzclusters „Bild Wissen Gestaltung. Ein interdisziplinäres Labor" und wird dazu auch am IRIS Adlershof lehren und forschen.
mehr…
15.04.2015Chinese Ambassador Shi Mingde visited IRIS Adlershof
 The Ambassador of the People's Republic of China, Shi Mingde, visited the Science and Technology Park Adlershof, on April 8th, in the “Year of innovation cooperation between Germany and China”.
The Ambassador of the People's Republic of China, Shi Mingde, visited the Science and Technology Park Adlershof, on April 8th, in the “Year of innovation cooperation between Germany and China”.
At IRIS Adlershof, Founding Chairman Jürgen P. Rabe informed him on the research and development at IRIS on site in Adlershof as well as on cooperations with Chinese partners such as Peking University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Shi Mingde was particular interested in the education of young scientists such as within the Berlin-wide Master Program on "Polymer Science", which has produced many, now internationally succesfull Chinese alumnae.
The dialogue with Ambassador Shi Mingde, as begun here, shall be carried on.
more…
15.04.2015KOSMOS Summer University 2016 at IRIS Adlershof
 IRIS Adlershof will host a three-week KOSMOS program from August 15th to September 2nd 2016 on the topic of Integrability for the Holographic Universe. The program will bring together young and experienced researchers with an interest in theoretical physics, mathematics and symbolic programming. It is organised by Prof. Matthias Staudacher, Dr. Alessandro Sfondrini and Prof. Jan Plefka, and funded by Humboldt-Universität though the KOSMOS program and by the Marie Curie Network "Gauge theory as an Integrable system" (GATIS).
IRIS Adlershof will host a three-week KOSMOS program from August 15th to September 2nd 2016 on the topic of Integrability for the Holographic Universe. The program will bring together young and experienced researchers with an interest in theoretical physics, mathematics and symbolic programming. It is organised by Prof. Matthias Staudacher, Dr. Alessandro Sfondrini and Prof. Jan Plefka, and funded by Humboldt-Universität though the KOSMOS program and by the Marie Curie Network "Gauge theory as an Integrable system" (GATIS).
14.04.2015Call for 10 SALSA doctoral fellowships open
 SALSA, the Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is announcing 10 doctoral fellowships to begin on October 10st, 2015. The program offers a structured, three-year period of multidisciplinary research combined with an integrated curriculum in Analytical Sciences.
SALSA, the Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is announcing 10 doctoral fellowships to begin on October 10st, 2015. The program offers a structured, three-year period of multidisciplinary research combined with an integrated curriculum in Analytical Sciences.
Applications will be accepted upon submission via our online application tool only (www.analytical-sciences.de), which will be accessible from April 15th until May 11th, 2015. Graduate students (master’s degree or equivalent) in chemistry, biology, physics and related disciplines with an interest in Analytical Sciences as well as graduates with a background in natural sciences education are invited to apply. For further information please visit http://www.analytical-sciences.de.
12.03.2015Humboldt-Universität among the Top 50 Universities in the World
 The current "Times Higher Education World Reputation Ranking" ranks Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) at position 41 of the worldwide most prestigious universities. Thereby HU advanced significantly with respect to the past year, when it was ranked in the group 71-80. HU’s Physical Sciences advanced by 31 places to rank 69th.
The current "Times Higher Education World Reputation Ranking" ranks Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) at position 41 of the worldwide most prestigious universities. Thereby HU advanced significantly with respect to the past year, when it was ranked in the group 71-80. HU’s Physical Sciences advanced by 31 places to rank 69th.
05.03.2015Optically switchable organic field effect transistors created
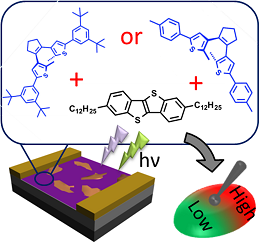 An international team of researchers led by Stefan Hecht, member of IRIS Adlershof, and Paolo Samori from the Université de Strasbourg (France), in collaboration with scientists from Stanford University (USA) and the Université libre de Bruxelles (Belgium), demonstrated that high-performance optically switchable field-effect transistors can be developed by blending photochromic molecules with small organic semiconductor molecules. Such optically addressable molecular devices are considered as key elements in future logic circuits. Their study just appeared in the journal Nature Communications.
An international team of researchers led by Stefan Hecht, member of IRIS Adlershof, and Paolo Samori from the Université de Strasbourg (France), in collaboration with scientists from Stanford University (USA) and the Université libre de Bruxelles (Belgium), demonstrated that high-performance optically switchable field-effect transistors can be developed by blending photochromic molecules with small organic semiconductor molecules. Such optically addressable molecular devices are considered as key elements in future logic circuits. Their study just appeared in the journal Nature Communications.
more...
01.03.2015Professor Christoph T. Koch accepted a new position at Humboldt-Universität
|
Prof. Dr. Christoph T. Koch (University of Ulm) has accepted the offer of a W3-Professorship "Structural research/Electronmicroscoy" at the Physics Department of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. He will start his new position in Berlin on August 1, 2015 |
 |
23.02.2015Professor Norbert Koch was elected to be spokesman of the CRC 951
|
Prof. Dr. Norbert Koch, vice-chairman of IRIS Adlershof, was elected to be spokesman at the plenary meeting of the CRC 951: "Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics" on February 20, 2015. Prof. Dr. Oliver Benson, also a member of IRIS Adlershof, was chosen as deputy spokesman. more... |
 |
12.02.2015Professor Steven L. Bernasek (Princeton University) appointed KOSMOS Fellow at IRIS Adlershof
|
Professor Steven L. Bernasek from the Department of Chemistry of Princeton University has been appointed Fellow of the KOSMOS Summer University on Chemistry and Physics of Novel Materials for (Opto-)Electronics at IRIS Adlershof. Professor Bernasek's research interest focusses on organic molecule self-assembly at graphite, graphene, and interfaces with other inorganic materials. During the next two months he will work together with scientists of IRIS-chairman Professor Jürgen P. Rabe's group, using scanning probe microscopy and optical spectroscopy methods. |
 |
01.02.2015We deeply mourn the loss of Professor Fritz Henneberger
|
We were very sorry and shocked to hear about the sudden, completely unexpected death of our colleague, Professor Dr. Fritz Henneberger. Professor Henneberger was a founding member of IRIS Adlershof and spokesman for the Collaborative Research Center 951. We are losing an excellent researcher, whose great commitment to research and teaching as well as to academic self-government considerably contributed to the successful development of our institution. We would like to offer Professor Henneberger’s family our deepest sympathy. more... |
 |
20.12.2014Merry Christmas and a happy New Year 2015!

IRIS Adlershof wishes you
Happy Holidays
and a
Happy New Year 2015!
19.12.2014Watching Single Macromolecules Move in Response to Light
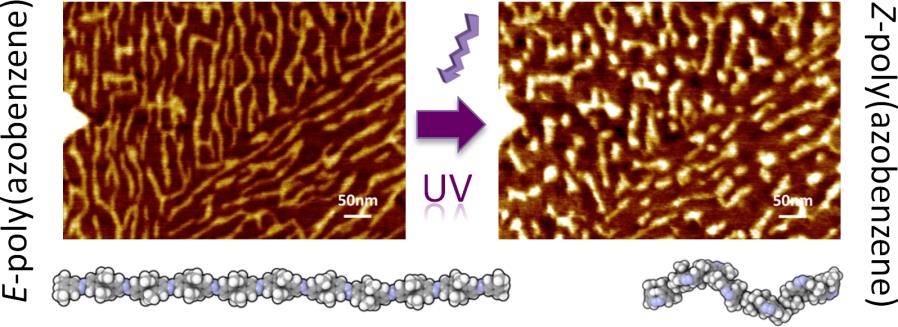 Nature has long inspired scientists with its seemingly unlimited ability to harness solar energy and to utilize it to drive various physiological processes. With the help of man-made molecular photoswitches, we now have the potential to outperform natural systems in many ways, with the ultimate goal of fabricating multifunctional materials that operate at different light wavelengths. An important challenge in developing light-controlled artificial molecular machines lies in attaining a detailed understanding of the photoisomerization-coupled conformational changes that occur in macromolecules and molecular assemblies. A team of chemists and physicists at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, led by David Bléger and Jürgen P. Rabe, member of IRIS Adlershof, have now used force microscopy to provide interesting insights into the behavior of individual photoresponsive molecules and to identify contraction, extension, and crawling events accompanying light-induced isomerization. In particular they have realized a system, in which single macromolecules can “work”, i.e. they were reversibly contracted and stretched on a modified graphite surface by using UV- and blue light, respectively. The paper by C.-L. Lee, T. Liebig, S. Hecht, D. Bléger, and J.P. Rabe was published in the current issue of ACS Nano (DOI: 10.1021/nn505325w), and has been highlighted with a “Perspective” by ACS & ACS Nano (DOI: 10.1021/nn506656r.
Nature has long inspired scientists with its seemingly unlimited ability to harness solar energy and to utilize it to drive various physiological processes. With the help of man-made molecular photoswitches, we now have the potential to outperform natural systems in many ways, with the ultimate goal of fabricating multifunctional materials that operate at different light wavelengths. An important challenge in developing light-controlled artificial molecular machines lies in attaining a detailed understanding of the photoisomerization-coupled conformational changes that occur in macromolecules and molecular assemblies. A team of chemists and physicists at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, led by David Bléger and Jürgen P. Rabe, member of IRIS Adlershof, have now used force microscopy to provide interesting insights into the behavior of individual photoresponsive molecules and to identify contraction, extension, and crawling events accompanying light-induced isomerization. In particular they have realized a system, in which single macromolecules can “work”, i.e. they were reversibly contracted and stretched on a modified graphite surface by using UV- and blue light, respectively. The paper by C.-L. Lee, T. Liebig, S. Hecht, D. Bléger, and J.P. Rabe was published in the current issue of ACS Nano (DOI: 10.1021/nn505325w), and has been highlighted with a “Perspective” by ACS & ACS Nano (DOI: 10.1021/nn506656r.
more...
19.12.2014Humboldt-Universität schließt Profilpartnerschaft mit der National University of Singapore
 Die Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin und die National University of Singapore (NUS) sind nun Profilpartner: Beide Universitäten werden künftig in Forschung und Lehre eng kooperieren und ihren Angehörigen vielfältige Gelegenheiten zum gemeinsamen Forschen, Lehren und Lernen geben sowie den Austausch auf Verwaltungsebene stärken. Die NUS ist eine der besten Universitäten Asiens und mit der HU durch langjährige und erfolgreiche Forschungskooperationen verbunden. Auch IRIS Adlershof hat enge Beziehungen zur NUS aufgebaut. Sichtbarstes Zeichen hierfür sind zwei gemeinsam ausgerichetete KOSMOS Summer Universities in den Jahren 2011 und 2014, sowie Internships für NUS-Studenten und der Austausch von Masterstudenten, Doktoranden und Postdocs.
Die Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin und die National University of Singapore (NUS) sind nun Profilpartner: Beide Universitäten werden künftig in Forschung und Lehre eng kooperieren und ihren Angehörigen vielfältige Gelegenheiten zum gemeinsamen Forschen, Lehren und Lernen geben sowie den Austausch auf Verwaltungsebene stärken. Die NUS ist eine der besten Universitäten Asiens und mit der HU durch langjährige und erfolgreiche Forschungskooperationen verbunden. Auch IRIS Adlershof hat enge Beziehungen zur NUS aufgebaut. Sichtbarstes Zeichen hierfür sind zwei gemeinsam ausgerichetete KOSMOS Summer Universities in den Jahren 2011 und 2014, sowie Internships für NUS-Studenten und der Austausch von Masterstudenten, Doktoranden und Postdocs.
mehr...
17.12.2014Professor Jürg Kramer has been elected a member of the National Academy of Science and Engineering - acatech - gewählt
 The General Assembly of acatech – the National Academy of Science and Engineering has asked Jürg Kramer, who is a professor for the Department of Mathematics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and a member of IRIS Adlershof, to join their ranks. Herr Kramer’s research is concerned with arithmetic geometry and the theory of automorphic forms, as well as mathematic didactics. Furthermore, he is heavily involved with popularizing mathematics. He is the president of the German Mathematical Society, a member of Academia Europaea, speaker of the Berlin Mathematical School, the international research training group “Moduli and Automorphic Forms,” as well as the director of the German Center for Mathematics Teacher Education(DZLM). With his appointment as an acatech member, Herr Kramer will be able to draw upon his considerable expertise as a political and social advisor and help acatech’s thematic networks evaluate recommendations. IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Herr Kramer and wishes him much success in his future work.
The General Assembly of acatech – the National Academy of Science and Engineering has asked Jürg Kramer, who is a professor for the Department of Mathematics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and a member of IRIS Adlershof, to join their ranks. Herr Kramer’s research is concerned with arithmetic geometry and the theory of automorphic forms, as well as mathematic didactics. Furthermore, he is heavily involved with popularizing mathematics. He is the president of the German Mathematical Society, a member of Academia Europaea, speaker of the Berlin Mathematical School, the international research training group “Moduli and Automorphic Forms,” as well as the director of the German Center for Mathematics Teacher Education(DZLM). With his appointment as an acatech member, Herr Kramer will be able to draw upon his considerable expertise as a political and social advisor and help acatech’s thematic networks evaluate recommendations. IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Herr Kramer and wishes him much success in his future work.
more...
03.12.2014Forum Junge Spitzenforscher – Humboldt-Universität successful in this year’s competition
 |
 |
| Dr. Joachim Paier | Andreas Schell |
In the annual competition „Forum Junge Spitzenforscher“ launched by the foundation Stiftung Industrieforschung in cooperation with the Humboldt-Innovation GmbH, young HU researchers proved very successful: Five out of six well-endowed prizes were awarded to HU scientists. IRIS is particularly pleased to announce that Andreas Schell was awarded the second prize for his contribution “Novel hybrid materials for quantum optical applications”. Mr. Schell is a PhD student in the group of Prof. Oliver Benson and was financially supported by IRIS Adlershof. Another awardee is Dr. Joachim Paier, a postdoctoral fellow in the laboratory of IRIS member Prof. Joachim Sauer. We heartily congratulate all winners.
more...
02.12.2014Prof. Matthias Staudacher was elected to be spokesman of the CRC 647
|
Prof. Dr. Matthias Staudacher, member of the board of IRIS Adlershof, was elected to be spokesman at the Plenary Meeting of the "CRC 647: Space - Time - Matter. Analytic and Geometric Structures." on December 2nd, 2014. The previous speaker, Prof. Dr. Jochen Brüning, also a member of IRIS Adlershof, was chosen as Deputy Chairman. more... |
 |
12.11.2014Bita Rezania was awarded the 2014 Adlershof Research Forum Poster Prize
|
The Best Poster Prize of 500 Euros went to Bita Rezania at the November 11th Adlershof Research Forum Poster Show for her contribution “Hydration of Bilayered Graphene Oxide.” Miss Rezania is a doctoral student of Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe, the Spokesperson of IRIS Adlershof. We heartily congratulate Bita for winning the prize. more... |
 |
15.10.2014An der Grenze des Denkbaren - ein Schlaglicht auf IRIS Adlershof
|
Artikel in der HU-Beilage 2014 des Tagesspiegel zum Forschungsfeld Hybridsysteme von IRIS Adlershof und zur kürzlichen Entdeckung des graphitischen Halbleiters TGCN. mehr... |
 |
14.10.2014Call for 10 SALSA doctoral fellowships open - deadline extended
 SALSA, the Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is announcing 10 doctoral fellowships to begin on April 1st, 2015. The program offers a structured, three-year period of multidisciplinary research combined with an integrated curriculum in Analytical Sciences.
SALSA, the Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is announcing 10 doctoral fellowships to begin on April 1st, 2015. The program offers a structured, three-year period of multidisciplinary research combined with an integrated curriculum in Analytical Sciences.
Applications will be accepted upon submission via our online application tool only (www.analytical-sciences.de), which will be accessible from October 14th until November 16th, 2014. Graduate students (master’s degree or equivalent) in chemistry, biology, physics and related disciplines with an interest in Analytical Sciences as well as graduates with a background in natural sciences education are invited to apply. For further information please visit http://www.analytical-sciences.de.
02.10.2014Humboldt-Universität im THE World University Ranking weiter verbessert
 In den Physical Sciences hat sich die Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin im Times Higher Education World University Ranking weltweit auf Platz 69 und in Deutschland auf Platz 6 hinter den Universitäten aus München, Göttingen und Heidelberg, der TU München und der Universität Bonn verbessert. Auch die Arts & Humanities und die Social Sciences zählen zu den Top 100. Die Humboldt-Universität als Ganze wird weltweit auf Platz 80 und in Deutschland auf Platz 4 geführt.
In den Physical Sciences hat sich die Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin im Times Higher Education World University Ranking weltweit auf Platz 69 und in Deutschland auf Platz 6 hinter den Universitäten aus München, Göttingen und Heidelberg, der TU München und der Universität Bonn verbessert. Auch die Arts & Humanities und die Social Sciences zählen zu den Top 100. Die Humboldt-Universität als Ganze wird weltweit auf Platz 80 und in Deutschland auf Platz 4 geführt.
01.10.2014Janik Wolters awarded with the Carl-Ramsauer and the Humboldt-Prize
 Dr. Janik Wolters received the Carl-Ramsauer Prize from the Physical Society of Berlin for his doctoral thesis, “Integrated Quantum Hybrid Systems,” which he did with Prof. Oliver Benson, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof. Dr. Wolter’s was able to present outstanding results from his optical studies of individual quantum systems in his thesis. The results will be, on the one hand, highly relevant for application in a future integrated quantum technology. On the other, the quantum zeno effect, which he was the first to observe on a single spin, illustrates special features in measurements of individually isolated quantum systems.
Dr. Janik Wolters received the Carl-Ramsauer Prize from the Physical Society of Berlin for his doctoral thesis, “Integrated Quantum Hybrid Systems,” which he did with Prof. Oliver Benson, who is a member of IRIS Adlershof. Dr. Wolter’s was able to present outstanding results from his optical studies of individual quantum systems in his thesis. The results will be, on the one hand, highly relevant for application in a future integrated quantum technology. On the other, the quantum zeno effect, which he was the first to observe on a single spin, illustrates special features in measurements of individually isolated quantum systems.
Moreover, the Humboldt-Universität has awarded janik Wolters the Humboldt-Prize for his outstanding doctoral thesis.
IRIS Adlershof would like to take this opportunity to heartily congratulate this young researcher..
more...
08.09.2014Movie - KOSMOS Summer University 2014
 The participants of the KOSMOS Summer University 2014 on "Chemistry and Physics of Novel Materials for (Opto-)Electronics" - Film have been followed by a filmteam. It can be watched here. There you can also find some pictures.
The participants of the KOSMOS Summer University 2014 on "Chemistry and Physics of Novel Materials for (Opto-)Electronics" - Film have been followed by a filmteam. It can be watched here. There you can also find some pictures.
17.07.2014Philipp Lange awarded the Lise-Meitner Prize
 The 2014 Lise-Meitner Prize for the best dissertation went to Dr. Phillip Lange from the Physics Department at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. This prize has been annually granted from the Vereinigung der Freunde und Förderer des Instituts für Physik e.V (Friends and Supporters of the Institute of Physics) since 1998. Dr. Lange did his summa cum laude doctoral degree in macromolecular physics on the topic of optical and structural properties of systems of conjugated molecules and graphenes with IRIS’s chairman, Prof. Dr. Jürgen P. Rabe. Dr. Lange was also supported by IRIS Adlershof. Kathrin Höfner and Johann Förster were additionally awarded for their master theses. We heartly congratulate these young researchers for their fine work.
The 2014 Lise-Meitner Prize for the best dissertation went to Dr. Phillip Lange from the Physics Department at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. This prize has been annually granted from the Vereinigung der Freunde und Förderer des Instituts für Physik e.V (Friends and Supporters of the Institute of Physics) since 1998. Dr. Lange did his summa cum laude doctoral degree in macromolecular physics on the topic of optical and structural properties of systems of conjugated molecules and graphenes with IRIS’s chairman, Prof. Dr. Jürgen P. Rabe. Dr. Lange was also supported by IRIS Adlershof. Kathrin Höfner and Johann Förster were additionally awarded for their master theses. We heartly congratulate these young researchers for their fine work.
more...
02.07.2014Prof. Christian Limberg, a new member at IRIS Adlershof
 Christian Limberg, Professor for Inorganic and General Chemistry at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is a new member at IRIS Adlershof. He is internationally well known for his work on molecular metal-oxygen systems and their application for catalytic oxidation of hydrocarbons. He is a member of the Excellence Cluster “Unifying Concepts in Catalysis” (UniCat) and Spokesman for the new SFB 1109 “Understanding of Metal Oxide/Water Systems at the Molecular Scale: Structural Evolution, Interfaces, and Dissolution” which began in April 2014. IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Christian Limberg and is looking forward to his collaboration.
Christian Limberg, Professor for Inorganic and General Chemistry at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is a new member at IRIS Adlershof. He is internationally well known for his work on molecular metal-oxygen systems and their application for catalytic oxidation of hydrocarbons. He is a member of the Excellence Cluster “Unifying Concepts in Catalysis” (UniCat) and Spokesman for the new SFB 1109 “Understanding of Metal Oxide/Water Systems at the Molecular Scale: Structural Evolution, Interfaces, and Dissolution” which began in April 2014. IRIS Adlershof would like to congratulate Christian Limberg and is looking forward to his collaboration.
more..
30.06.2014Einstein Professor: Claudia Draxl has become a Max Planck fellow at the Fritz-Haber-Institut Berlin

Professor Claudia Draxl, who is a member at IRIS-Adlershof, has been appointed by the President of the Max-Planck Society a Max Planck fellow at the Fritz-Haber Institute of the MPG in Berlin. The Max Planck fellow program will not only be responsible for documenting and strengthening the cooperation between the universities and the Max-Planck Institutes but will also set up a research group of its own at the Fritz-Haber Institut.
more...17.06.2014"HoW exciting! 2014" - Workshop July 31 - August 8
 Computational materials science from an ab-initio point of view is mostly based on density-functional theory, which is also the first rung on the multi-scale modeling ladder to quantitatively describe processes and phenomena seen in real materials. It is an excellent technique for the calculation of structures and molecular dynamics, being used by a swiftly growing number of researchers around the world. There is, however, also rapidly increasing demand for understanding and predicting various kinds of excitations.
Computational materials science from an ab-initio point of view is mostly based on density-functional theory, which is also the first rung on the multi-scale modeling ladder to quantitatively describe processes and phenomena seen in real materials. It is an excellent technique for the calculation of structures and molecular dynamics, being used by a swiftly growing number of researchers around the world. There is, however, also rapidly increasing demand for understanding and predicting various kinds of excitations.
The workshop, organized by Prof. Claudia Draxl, member of IRIS Adlershof, and coworkers, aims to introduce young scientists to the theoretical foundations of state-of-the-art ab-initio techniques through keynote lectures given by world-leading experts. They will focus on the treatment of various excitations, crucial to understand and predict electronic, optical, and thermodynamic properties of materials. This knowledge will pe put into practice by hands-on excercises with the program package "exciting" that is developed in her group.
For more information see how-exciting-2014.physik.hu-berlin.de
05.06.2014Matteo Guzzo awarded with a Humboldt Research Fellowship
 Matteo Guzzo was awarded with a Humboldt Research Fellowship for Postdoctoral Researchers by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. This is going to support the work in his new research area Electron-phonon Coupling in Photoemission Spectra within Advanced Greens Function Methods. Guzzo did a doctorate at the Ecole Polytechnique, where his thesis on Dynamical Correlations in Solids was awarded as the best in 2012. Since 2013 he is working as a postdoc in the group Solid State Theory of Prof. Claudia Draxl and was also funded by IRIS Adlershof.
Matteo Guzzo was awarded with a Humboldt Research Fellowship for Postdoctoral Researchers by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. This is going to support the work in his new research area Electron-phonon Coupling in Photoemission Spectra within Advanced Greens Function Methods. Guzzo did a doctorate at the Ecole Polytechnique, where his thesis on Dynamical Correlations in Solids was awarded as the best in 2012. Since 2013 he is working as a postdoc in the group Solid State Theory of Prof. Claudia Draxl and was also funded by IRIS Adlershof.
02.06.2014Funding of cooperation projects between Tel Aviv University and Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
Biological Physics and Soft Matter Physics are emerging fields for the understanding of biological structures and processes. They allow to develop materials which mimic biological structures that can be used in nano-bio-technology or for medical purposes, e.g. for regenerative therapies. The universities involved have complementing expertise in these fields, providing an attractive basis for joint highly innovative projects. The aim of the proposed program is to create an interdisciplinary platform for both senior scientists and junior researchers of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Tel Aviv University to collaborate on the physical principles governing the interdependent functioning of single biological molecules, their ensembles and aggregates, both in vitro and in living cells.


more...
23.05.2014Long Sought Two-Dimensional Graphitic Semiconductor Discovered
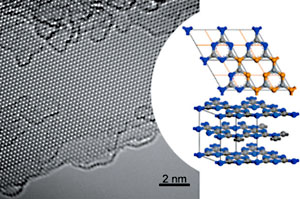 A European team of chemists and physicists, including Dr. Nikolai Severin and Professor Jürgen P. Rabe of the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität and the Joint Laboratory of Structural Research at IRIS Adlershof, have discovered a new quasi two-dimensional semiconductor related to graphene (see comment in ars technica). The novel material, ‘triazine-based graphitic carbon nitride’ (TGCN) was predicted theoretically in 1996, but this is the first time that it has been presented. TGCN is a member of the graphene family, of which only five non-metallic 2D materials were known up to date: graphene itself, hexagonal boron nitride, boron carbon nitride, fluorographene and graphene oxide. TGCN is structurally similar to graphite but a semiconductor, which is of high interest for opto-electronic applications. Cooperation partners in this project are Dr. Michael J. Bojdys and Professor Arne Thomas (TU Berlin), Professor Markus Antonietti (MPI of Colloids and Interfaces) and five further groups from the UK, Germany and Finland. Within IRIS Adlershof 2D atomic crystals play an important role in the Research Area “Hybrid Systems for Optic and Electronics”.
A European team of chemists and physicists, including Dr. Nikolai Severin and Professor Jürgen P. Rabe of the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität and the Joint Laboratory of Structural Research at IRIS Adlershof, have discovered a new quasi two-dimensional semiconductor related to graphene (see comment in ars technica). The novel material, ‘triazine-based graphitic carbon nitride’ (TGCN) was predicted theoretically in 1996, but this is the first time that it has been presented. TGCN is a member of the graphene family, of which only five non-metallic 2D materials were known up to date: graphene itself, hexagonal boron nitride, boron carbon nitride, fluorographene and graphene oxide. TGCN is structurally similar to graphite but a semiconductor, which is of high interest for opto-electronic applications. Cooperation partners in this project are Dr. Michael J. Bojdys and Professor Arne Thomas (TU Berlin), Professor Markus Antonietti (MPI of Colloids and Interfaces) and five further groups from the UK, Germany and Finland. Within IRIS Adlershof 2D atomic crystals play an important role in the Research Area “Hybrid Systems for Optic and Electronics”.
16.05.2014Architekten und Planer für Forschungsbau von IRIS Adlershof beauftragt
Nachdem im Juni 2013 die Gemeinsame Wissenschaftskonferenz (GWK) des Bundes und der Länder beschlossen hatte, einen Forschungsbau für das am IRIS Adlershof bearbeitete Vorhaben "Hybridsysteme für Elektronik, Optoelektronik und Photonik" zu finanzieren, hat jetzt der Bauherr, die Senatsverwaltung für Stadtentwicklung und Umwelt Berlin, im Rahmen eines VOF-Vergabeverfahrens ein Vorentwurfskonzept ausgewählt, das nun umgesetzt wird.
Das von den Architekten Nickl & Partner und dem Planungsbüro IDK Kleinjohann entwickelte Vorentwurfskonzept sieht auf dem Grundstück Zum Großen Windkanal 6 einen eigenständigen markanten Baukörper vor, der sich wie selbstverständlich in die Bestandsstruktur zweier ehemaliger Kasernen integriert und dabei IRIS Adlershof als zusammenhängende Forschungseinrichtung präsentiert. Der Neubau wird als Verbinder zwischen beide Bestandsbauten gesetzt. So bleibt zur Straße Zum Großen Windkanal ein repräsentativer hofartiger Außenraum erhalten, der zusammen mit dem Foyer als gemeinsamer Eingangsbereich und verbindendes Element der verschiedenen Arbeitsgruppen von IRIS Adlershof fungiert.
IRIS-Sprecher Professor Jürgen P. Rabe ist von diesem Konzept begeistert: „Wir freuen uns sehr, dass es den Architekten und Planern gelungen ist, die vom Forschungsthema vorgegebenen funktionalen Erfordernisse mit einer anspruchsvollen und modernen Architektur zu verbinden. Wenn das Gebäude 2018 fertiggestellt ist, wird dies eine echte Bereicherung nicht nur für die Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler sowie die Studierenden der Humboldt-Universität, sondern auch für unsere strategischen Partner hier an unserem Standort in Berlin-Adlershof und darüber hinaus.“
15.05.2014DFG verlängert Graduiertenkolleg SOAMED
 Die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) wird die zweite Phase des Graduiertenkollegs „Service-orientierter Architekturen zur Integration Software-gestützter Prozesse am Beispiel des Gesundheitswesens und der Medizintechnik“ (SOAMED) mit insgesamt ungefähr 3.5 Millionen Euro fördern. Das Graduiertenkolleg nahm im Jahr 2010 seine Arbeit auf und kann diese nun bis 2019 fortsetzen.SOAMED erforscht die Frage, wie man rechnerbasierte Systeme zur Unterstützung komplexer medizinischer Prozesse durch das Zusammenfügen verteilter Softwarekomponenten (auch Services genannt) konstruieren kann. Seitens IRIS Adlershof ist Professor Johann-Christoph Freytag am Graduiertenkolleg beteiligt.
Die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) wird die zweite Phase des Graduiertenkollegs „Service-orientierter Architekturen zur Integration Software-gestützter Prozesse am Beispiel des Gesundheitswesens und der Medizintechnik“ (SOAMED) mit insgesamt ungefähr 3.5 Millionen Euro fördern. Das Graduiertenkolleg nahm im Jahr 2010 seine Arbeit auf und kann diese nun bis 2019 fortsetzen.SOAMED erforscht die Frage, wie man rechnerbasierte Systeme zur Unterstützung komplexer medizinischer Prozesse durch das Zusammenfügen verteilter Softwarekomponenten (auch Services genannt) konstruieren kann. Seitens IRIS Adlershof ist Professor Johann-Christoph Freytag am Graduiertenkolleg beteiligt.
more...
10.05.2014Science at Work @ IRIS Adlershof
In time for the Langen Nacht der Wissenschaften, IRIS Adlershof joind the WISTA-Kampagne "Adlershof. Science at Work.". There are posters at the campus with four respective motives.

14.04.2014Jürgen P. Rabe Visiting Professor at Princeton University in Spring Term 2014
 Jürgen P. Rabe, Professor at the Department of Physics and Chairman of IRIS Adlershof, has been appointed Visiting Professor at the Department of Chemistry at Princeton University during Spring Term 2014. He works together with Professor Steven L. Bernasek on organic-inorganic hybrid systems, and he teaches a Graduate Course for graduate students in physics, chemistry and at the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. On the other hand, Professor Bernasek and Professor Roberto Car from Princeton will contribute to the upcoming KOSMOS Summer University 2014 on Chemistry and Physics of Novel Materials for (Opto-)Electronics hosted by IRIS Adlershof. Humboldt-Universität and Princeton University are cooperating in the framework of a strategic profile partnership. Physical Sciences at Princeton University is ranked worldwide number 2 in the current „Times Higher Education“ World Reputation Ranking (after the California Institute of Technology).
Jürgen P. Rabe, Professor at the Department of Physics and Chairman of IRIS Adlershof, has been appointed Visiting Professor at the Department of Chemistry at Princeton University during Spring Term 2014. He works together with Professor Steven L. Bernasek on organic-inorganic hybrid systems, and he teaches a Graduate Course for graduate students in physics, chemistry and at the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences. On the other hand, Professor Bernasek and Professor Roberto Car from Princeton will contribute to the upcoming KOSMOS Summer University 2014 on Chemistry and Physics of Novel Materials for (Opto-)Electronics hosted by IRIS Adlershof. Humboldt-Universität and Princeton University are cooperating in the framework of a strategic profile partnership. Physical Sciences at Princeton University is ranked worldwide number 2 in the current „Times Higher Education“ World Reputation Ranking (after the California Institute of Technology).
08.04.2014KOSMOS Summer University 2014 on Chemistry and Physics of Novel Materials for (Opto-)Electronics

The KOSMOS Summer University 2014 on "Chemistry and Physics of Novel Materials for (Opto-) Electronics" hosted by IRIS Adlershof will take place at the Campus Adlershof from July 8-19, 2014. Organized in cooperation with the National University of Singapore and Princeton University, this summer university will focus on an integrative approach combining the key expertise from outstanding scientists.
In a creative and interactive learning environment young researchers from different backgrounds will be trained in the following topics:· Electronic structure theory
· Synthesis of molecular materials
· Spectroscopic techniques
· Materials classes and properties
· Interfacial design and analysis
· Device fabrication and characterization
Scientific Chairs
Claudia Draxl, IRIS Adlershof & Department of Physics, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany
Stefan Hecht, IRIS Adlershof & Department of Chemistry, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Germany
For more information see kosmos2014.iris-adlershof.de and the flyer (PDF, 876 kb), or contact our organisation team:
Ms Nora Butter
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, IRIS Adlershof
Zum Großen Windkanal 6, 12489 Berlin, Germany
Phone: +49 30 2093 66350
Fax: +49 30 2093 66351
Email: kosmos2014iris-adlershof.de
The participants of the KOSMOS Summer University 2014 on "Chemistry and Physics of Novel Materials for (Opto-)Electronics" - Film have been followed by a filmteam. It can be watched here. There you can also find some pictures.
07.04.2014Jan Plefka im Sommersemester 2014 Gastprofessor an der ETH Zürich
 Professor Jan Plefka verbringt sein Forschungsfreisemester 2014 am renommierten Institut für theoretische Physik an der ETH Zürich. Er forscht dort gemeinsam mit den Mitgliedern der Arbeitsgruppen Quantenfeldtheorie und Stringtheorie von Prof. M. Gaberdiel und Prof. N. Beisert zu Themen der Mathematischen Physik. Der Austausch stärkt die Kooperation von IRIS Adlershof mit der ETH. Darüberhinaus hält er eine Spezialvorlesung an der ETH zum Thema "Streuamplituden in Eichtheorien", einem aktuellen Forschungsthema am Schnittpunkt von mathematischer Physik und der Phänomenologie der Elementarteilchen. Diesem Thema ist auch sein kürzlich erschienenes Lehrbuch in der Lecture Notes in Physics Reihe des Springer Verlags gewidmet, das mit Dr. J. Henn (IAS Princeton) verfasst wurde.
Professor Jan Plefka verbringt sein Forschungsfreisemester 2014 am renommierten Institut für theoretische Physik an der ETH Zürich. Er forscht dort gemeinsam mit den Mitgliedern der Arbeitsgruppen Quantenfeldtheorie und Stringtheorie von Prof. M. Gaberdiel und Prof. N. Beisert zu Themen der Mathematischen Physik. Der Austausch stärkt die Kooperation von IRIS Adlershof mit der ETH. Darüberhinaus hält er eine Spezialvorlesung an der ETH zum Thema "Streuamplituden in Eichtheorien", einem aktuellen Forschungsthema am Schnittpunkt von mathematischer Physik und der Phänomenologie der Elementarteilchen. Diesem Thema ist auch sein kürzlich erschienenes Lehrbuch in der Lecture Notes in Physics Reihe des Springer Verlags gewidmet, das mit Dr. J. Henn (IAS Princeton) verfasst wurde.
02.04.2014Call for 12 SALSA doctoral fellowships open
 SALSA, the Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is announcing 12 doctoral fellowships to begin on October 1st, 2014. The program offers a structured, three-year period of multidisciplinary research combined with an integrated curriculum in Analytical Sciences.
SALSA, the Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is announcing 12 doctoral fellowships to begin on October 1st, 2014. The program offers a structured, three-year period of multidisciplinary research combined with an integrated curriculum in Analytical Sciences.
Applications will be accepted upon submission via our online application tool only (www.analytical-sciences.de), which will be accessible from April 7th until May 4th, 2014. Graduate students (master’s degree or equivalent) in chemistry, biology, physics and related disciplines with an interest in Analytical Sciences as well as graduates with a background in natural sciences education are invited to apply.
more...
17.03.201478th Annual Meeting of the DPG and DPG Spring Meeting SAMOP at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
 From March 17th - 21st, 2014 the 78th Annual Meeting of the DPG and DPG Spring Meeting of the SAMOP (Department of atoms, molecules, quantum optics and plasmas) took place at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. The meeting was headed and organized by the member of IRIS Adlershof, Prof. Oliver Benson.
From March 17th - 21st, 2014 the 78th Annual Meeting of the DPG and DPG Spring Meeting of the SAMOP (Department of atoms, molecules, quantum optics and plasmas) took place at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. The meeting was headed and organized by the member of IRIS Adlershof, Prof. Oliver Benson.
more....
12.03.2014Humboldt University in the field of Physical Sciences among the top 100 Universities in the world
 The "Times Higher Education World Reputation Ranking" ranks Humboldt University in Berlin among the 100 worldwide most prestigious universities. The departments "Arts & Humanities" and "Social Sciences" as well as the entire Humboldt University are counted among the top 100. In Germany in the "Physical Sciences", both universities in Munich as well as universities in Göttingen, Heidelberg, Aachen and Bonn have been added to this category.
The "Times Higher Education World Reputation Ranking" ranks Humboldt University in Berlin among the 100 worldwide most prestigious universities. The departments "Arts & Humanities" and "Social Sciences" as well as the entire Humboldt University are counted among the top 100. In Germany in the "Physical Sciences", both universities in Munich as well as universities in Göttingen, Heidelberg, Aachen and Bonn have been added to this category.
more...
21.02.2014Norbert Koch new Chair Professor at FUNSOM, Soochow University, VR China
 On 19 February 2014, Professor Norbert Koch, a member of IRIS Adlershof, was appointed as Chair Professor of the Functional Nano & Soft Materials Laboratory (FUNSOM), a key institute of Soochow University in Suzhou, China (PRC).
On 19 February 2014, Professor Norbert Koch, a member of IRIS Adlershof, was appointed as Chair Professor of the Functional Nano & Soft Materials Laboratory (FUNSOM), a key institute of Soochow University in Suzhou, China (PRC).
"With this appointment I can contribute to the internationalization strategy of FUNSOM, which promotes interdisciplinary research (physics, chemistry, electrical engineering, biology, medicine) in the field of nanostructured and soft materials for electronics and optoelectronics in China. The faculty pays particular attention to an excellent education of students in an open-minded environment, and I am looking forward to contributing with topical block-seminars and coaching in small groups. The mutual exchange of students between IRIS Adlershof and FUNSOM is another focus of this enticing cooperation.", says Norbert Koch.
14.02.2014Dissertationspreis Adlershof an Dr. Martin Hempel
Bei der diesjährigen Verleihung des Dissertationspreises konnte sich Herr Dr. Martin Hempel erfolgreich gegen seine beiden Mitnominierten durchsetzen. Seit 2002 wird der Dissertationspreis Adlershof jährlich von der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, der Initiativgemeinschaft Außeruniversitärer Forschungseinrichtungen in Adlershof e.V. (IGAFA) und der WISTA-MANAGEMENT GMBH verliehen. Drei Nominierte treten mit Kurzvorträgen zum Thema ihrer Dissertation aus dem gerade zu Ende gegangenen Jahr gegeneinander an. Die Jury entscheidet im Anschluss, wer nicht nur sehr gut forschen, sondern auch mitreißend und überzeugend vortragen kann.
Dr. Martin Hempel promovierte in der Arbeitsgruppe von IRIS-Mitglied Prof. Dr. Thomas Elsässer, Max-Born-Institut für Nichtlineare Optik und Kurzzeitspektroskopie (MBI) und Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Er hat als Doktorand am MBI Defektmechanismen in Hochleistungs-Diodenlasern untersucht. Dabei erfasste und interpretierte er den zeitlichen Ablauf der Degradation für unterschiedliche Klassen kommerzieller Diodenlaser. Hochleistungs-Diodenlaser sind derzeit die effizienteste menschengemachte Struktur zur Umwandlung von elektrischer Energie in Licht. Die Forschungsergebnisse von Martin Hempel sind von hoher Relevanz für die Angewandte Physik, die Optoelektronik und die Photonik. IRIS Adlershof gratuliert herzlich.
27.01.2014Scientific Writing Seminar for young IRIS researchers in February
IRIS Adlershof has organized a series of seminars on scientific writing targeting to young researchers working on IRIS relevant research areas.
Three of these two-day-seminars will be conducted in February 2014 (18. & 19., 20. & 21., and 24. & 25. February) by Katherine Tiede, a Canadian linguist, specialized on technical and engineering communication. The seminar focuses on solving problems scientific writers face when they communicate their work in English. A series of linguistic principles for communicating research in the clearest, most coherent, convincing and concise manner will be presented.
A limited number of young researchers can still be accepted as participants. If you wish to apply please contact Ms. Nora Butter: butter@iris-adlershof.de.
30.12.2013Einstein Foundation is funding research project of IRIS-member Prof. Oliver Benson
Oliver Benson, Professor at the Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and member of IRIS Adlershof, and Prof. Kurt Busch (Department of Physics of HU and Max-Born-Institute for non-linear Optics and Short Pulse Spectroscopy) will form a research team for the next three years with Israeli colleagues Prof. Ronen Rapaport and Prof. Uriel Levy from Hebrew University, Jerusalem. As part of Einstein's research framework "Actiplant", the scientists would like to discover how emission and absorption of light can be controlled with the help of findings from quantum mechanics. In this process they are working on a very small scale: They want to examine and manipulate single light quanta.
more...
26.11.2013New Collaborative Research Centre at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
The Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) has approved a new Collaborative Research Centre (CRC) at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. The research group entitled „Molekulare Einblicke in Metalloxid-Wasser-Systeme: Strukturelle Evolution, Grenzflächen und Auflösung“ will apriori be budgeted for three years and nine months. Spokesman of the CRC is Prof. Dr. Christian Limberg (Department of Chemistry). The member of IRIS Adlershof Prof. Dr. Joachim Sauer is participating.
more...
26.11.2013HU-Physicist Janik Wolters wins Berlins Science Slam
At the 28. Science Slam Berlin on November 04, 2013 the physicist Janik Wolters from the group of Prof. Oliver Benson (member of IRIS Adlershof) exicted the audience with his contribution "observation affects movement, the quantum Zeno effect" and took the first place. He asserted in a very strong competition with the fields of law, medicine, physics and biology.
25.11.2013Vom Schülerlabor zum Lehr-Lern-Labor
Das Humboldt-ProMINT-Kolleg widmet sich gemeinsam mit der Freien Universität Berlin und mit den Universitäten in Kiel, Koblenz-Landau, Münster und Oldenburg der Frage, wie Hochschulen ihre Schülerlabore zu Lehr-Lern-Laboren weiterentwickeln und curricular ins Lehramtsstudium einbetten können. Das Ziel: Lehramtsstudierende sollen so frühzeitig Erfahrung im praktischen Unterrichten sammeln. Das Projekt wird von der Deutschen Telekom Stiftung gefördert. Seitens IRIS Adlershof ist Professor Jürg Kramer am ProMINT Kolleg beteiligt.
mehr...
06.11.2013Caroline von Humboldt-Professur 2013 für Frau Prof. Dr. Claudia Draxl
Die diesjährige Caroline von Humboldt-Professur der Humboldt-Universität wird an Frau Prof. Dr. Claudia Draxl (Institut für Physik und IRIS Adlershof) vergeben. Die feierliche Verleihung findet im Dezember statt. Als Auszeichnung für herausragende Leistungen in Forschung und Lehre wird jedes Jahr eine Professorin der HU mit dieser Professur geehrt. Die Namensprofessur ist mit 80.000 Euro dotiert, die insbesondere der Projektförderung und der Unterstützung für die weitere Karriere der Preisträgerin dient. Durch die Auszeichnung soll zudem die öffentliche und internationale Sichtbarkeit der Professorin erhöht werden. Die Caroline von Humboldt-Professur wird abwechselnd in den Geistes- oder Sozialwissenschaften und in den Naturwissenschaften vergeben. IRIS Adlershof gratuliert herzlich.
mehr...
06.11.2013Urania-Medaille an Herrn Prof. Dr. Anton Zeilinger
Herr Prof. Dr. Anton Zeilinger (Institut für Quantenoptik und Quanteninformation Wien und Universität Wien, Präsident der Österreichischen Akademie der Wissenschaften) wurde auf einer Festveranstaltung in der Urania am 21. Oktober 2013 mit der Urania-Medaille 2013 ausgezeichnet. Er erhielt die Medaille für seine beispielhafte Verbindung von international hoch angesehener Leistung in Lehre und Forschung mit der Vermittlung komplexer wissenschaftlicher Fragestellungen an eine breite Öffentlichkeit. Herr Prof. Dr. Zeilinger ist seit 2005 Ehrendoktor der Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultät I der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. IRIS Adlershof gratuliert herzlich.
04.11.2013Call for Applications: 15 doctoral fellowships in Chemistry, Biology, Physics and Natural Sciences Education - Deadline shifted!
SALSA, the Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is announcing 15 doctoral fellowships to begin on April 1st, 2014. The program offers a structured, three-year period of multidisciplinary research combined with an integrated curriculum in Analytical Sciences.
Applications will be accepted upon submission via our online application tool only (www.analytical-sciences.de), which will be accessible from October 10th until November 4th, 2013. November 17th, 2013.Graduate students (master’s degree or equivalent) in chemistry, biology, physics and related disciplines with an interest in Analytical Sciences as well as graduates with a background in natural sciences education are invited to apply. For further information please visit http://www.analytical-sciences.de.
General information for applicants
Online application tool for registration
List of 3rd call projects including abstracts
23.10.2013Strategic partnership between Humboldt-Universität and Princeton University is gaining steam
The strategic partnership, established between Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Princeton University at the beginning of this year is now entering a new level. From October 27 to 28, 2013 researchers from both universities presented recent scientific results on „Novel (Opto)-Electronic Materials“ during a dedicated workshop, organized by IRIS Adlershof. Ways and methods to strengthen the joined scientific cooperation in this innovative, interdisciplinary research field have be discussed.
The Chairmen of the workshop are Professor Antoine Kahn (Department of Electrical Engineering of Princeton University) and Professor Norbert Koch (IRIS Adlershof and Department of Physics of Humboldt-Universität). A Young Researchers Satellite Meeting gave young academics the opportunity to participate in the collaboration. A follow-up workshop is planned in Princeton next spring.
more...
14.10.2013Konstantin Wiegandt receives Humboldt-Award
Mit dem Humboldt-Preis werden ausgezeichnete wissenschaftliche Arbeiten von Studierenden sowie von Nachwuchswissenschaftlerinnen und -wissenschaftlern gewürdigt. Einer der diesjährigen Preisträger ist Dr. Konstantin Wiegandt, ehemaliger Doktorand der Arbeitsgruppe von IRIS-Adlershof Mitglied Prof. Plefka (AG Quantenfeld- und Stringtheorie), der für seine 2012 verteidigte Dissertation "Superconformal Quantum Field Theories in String - Gauge Theory Dualities" ausgezeichnet wurde.
 Im ersten Teil der Dissertation wurde die Berechnung von Wilson-Schleifen in einer Quantenfeldtheorie mit anderen Symmetrien vorgenommen, der N=6 Super Chern-Simons Theorie, die ebenfalls dual zu einer Stringtheorie ist. Dabei stellte sich erstaunlicherweise nicht nur heraus, dass die Wilson-Schleifen mit den Streuamplituden dieser Theorie übereinstimmen, sondern dass diese auch noch äquivalent zu denen der N=4 SYM Theorie sind. Im zweiten Teil der Dissertation wurde die Berechnung von sog. Strukturkonstanten vorgenommen, mit Hilfe derer die Korrelationsfunktionen indirekt konstruiert werden können.
Im ersten Teil der Dissertation wurde die Berechnung von Wilson-Schleifen in einer Quantenfeldtheorie mit anderen Symmetrien vorgenommen, der N=6 Super Chern-Simons Theorie, die ebenfalls dual zu einer Stringtheorie ist. Dabei stellte sich erstaunlicherweise nicht nur heraus, dass die Wilson-Schleifen mit den Streuamplituden dieser Theorie übereinstimmen, sondern dass diese auch noch äquivalent zu denen der N=4 SYM Theorie sind. Im zweiten Teil der Dissertation wurde die Berechnung von sog. Strukturkonstanten vorgenommen, mit Hilfe derer die Korrelationsfunktionen indirekt konstruiert werden können.
mehr...
10.10.2013Call for 15 SALSA doctoral fellowships open in Chemistry, Biology, Physics and Natural Sciences Education
SALSA, the Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is announcing 15 doctoral fellowships to begin on April 1st, 2014. The program offers a structured, three-year period of multidisciplinary research combined with an integrated curriculum in Analytical Sciences.
Applications will be accepted upon submission via our online application tool only (www.analytical-sciences.de), which will be accessible from October 10th until November 4th, 2013. Graduate students (master’s degree or equivalent) in chemistry, biology, physics and related disciplines with an interest in Analytical Sciences as well as graduates with a background in natural sciences education are invited to apply. For further information please visit http://www.analytical-sciences.de.
07.10.2013Humboldt-Universität listed among World University Ranking’s top 100
In the current Times Higher Education World University Ranking 2013/2014 Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is listed on position 94. That means an upgrade of five positions compared to last year's ranking. In the field of global university performance comparison Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is one of the six German Universities listed among the top 100.
more...
01.09.2013Ulrich Panne neuer Präsident der Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung
Professor Ulrich Panne übernimmt ab dem 1. September 2013 die Leitung der Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM). Der Chemiker löst Professor Manfred Hennecke ab, der 11 Jahre die BAM als Präsident leitete und nun in den Ruhestand geht.
Bei seiner Ernennung zum BAM-Präsidenten betonte Ulrich Panne, dass er die Verbindung von Ingenieurwissenschaften und Naturwissenschaften der BAM weiter ausbauen ausmöchte. Nur so können die herausfordernden Themen der Chemie beziehungsweise der Materialwissenschaft und Werkstofftechnik multidisziplinär bearbeitet werden.
Der 49-jährige analytische Chemiker ist seit 2004 an der BAM tätig und leitete die Abteilung 1 Analytische Chemie, Referenzmaterialien. Darüber hinaus ist er Professor für Instrumentelle Analytische Chemie an der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Professor Panne ist Mitinitiator und seit 2012 einer der Sprecher der Graduiertenschule für Analytical Sciences Adlershof (SALSA) innerhalb der Exzellenzinitiative des Bundes und der Länder.
IRIS Adlershof Adlershof gratuliert herzlich!
30.08.2013Grundsteinlegung für das Studentendorf in Adlershof
Nach mehr als sechsjähriger Planung ist auf dem Campus Adlershof der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) am 30. August 2013 der Grundstein für ein weiteres Berliner Studentendorf gelegt worden. In direkter Nähe zu den naturwissenschaftlichen Instituten der HU entsteht ein Gebäudekomplex mit rund 380 Wohnplätzen. Davon sind 120 für HU-Studierende reserviert.
Die ersten Bewohnerinnen und Bewohner werden voraussichtlich im Herbst 2014 einziehen. Alle Zimmer werden über ein eigenes Bad verfügen und um Gemeinschaftsräume wie Wohnzimmer und Küche zu einer Wohnlandschaft gruppiert. Das Studentendorf erstreckt sich auf zehn Gebäude und liegt an der Abram-Joffe-Straße / Ecke Karl-Ziegler-Straße.
Bauherr des neuen Wohncampus ist die Studentendorf Adlershof GmbH, ein Joint Venture der Studentendorf Schlachtensee eG und der Schweizerischen CoOpera Sammelstiftung PUK.
30.08.2013HU Physicists measure the quantum Zeno effect for the first time at a single quantum system
A team of researchers led by Prof. Oliver Benson, a member of IRIS Adlershof, has demonstrated the quantum Zeno effect of a single electron in a solid state system. This promises a deeper understanding of quantum dynamics and thus further insights into the complex interaction of individual quantum systems with their environment.
more...
18.08.2013Carl-Ramsauer-Preis der Physikalischen Gesellschaft zu Berlin an Dr. Tim Schröder
Die Physikalischen Gesellschaft zu Berlin hat Herrn Dr. Tim Schröder, derzeit MIT Cambridge, USA, für seine Dissertationsschrift "Integrated photonic systems for single photon generation and quantum applications: Assembly of fluorescent diamond nanocrystals by novel nano-manipulation techniques", die er in der Arbeitsgruppe von Prof. Oliver Benson, Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof, angefertigt hat, den Carl-Ramsauer-Preis 2013 verliehen.
more...
05.08.2013Ferdinand-Braun-Institut in Adlershof mit "Advanced UV for Life" erfolgreich im Wettbewerb Zwanzig20 des BMBF
"Advanced UV for Life" – so der Name des vom Ferdinand-Braun-Institut in Adlershof koordinierten Konsortiums, das künftig innovative Anwendungen von UV-Licht in Medizin, Wasserbehandlung, Produktionstechnik und Sensorik erschließen wird. Der Zusammenschluss von Forschungseinrichtungen und Industrieunternehmen unterschiedlicher Fachdisziplinen hat sich im Wettbewerb Zwanzig20 im Rahmen der Hightech-Strategie des Bundesministeriums für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) durchgesetzt. IRIS Adlershof gratuliert herzlich.
mehr...
01.08.2013Cluster of Excellence-project
Norbert Koch and Jürgen P. Rabe from IRIS Adlershof, Charlotte Klonk, professor for art history, and further scientists of the project "Designing Laboratories" of the Cluster of Excellence "Image Knowledge Gestaltung. An Interdisciplinary Laboratory" have visited Departments of Chiba University in Japan as well as the Faculty of Science of the National University of Singapore (NUS), and the Graphene Research Centre, the Centre for Quantum Technologies, and the Mechanobiology Institute in order to explore the design of laboratories for interdisciplinary research in the sciences. This is the last of a series of visits, which led the scientists afore to the Nano TecCenter Weiz in Austria, to departments of Princeton University, MIT, Harvard University, and Columbia University in the USA. The derived knowledge shall be used to design the IRIS research building as a prototype of an interdisciplinary laboratory in the sciences (see press release of HU, April 28, 2013).
Vice President Takeshi Tokuhisa of Chiba University
welcomes the delegation of Humboldt-Universität
31.07.2013Cooperation between Tel Aviv University and Humboldt-Universität on Biological and Soft Matter Physics
IRIS Adlershof and the IRI for the Life Sciences wish to intensify their cooperation with the Tel Aviv University (TAU) in the field of biological and soft matter physics. Therefore, they call for proposals to be funded in a bilateral funding scheme. Funding is available for bilateral collaborative research projects comprising researchers or research teams from the two participating universities. The main goal of the program is to support the ongoing and stimulate new collaborations between the research groups of the two Universities. Joint project proposals by scientists from TAU and HU may be submitted until January 31st, 2014.
more...25.07.2013Norbert Koch – Visiting Professor at Chiba University, Japan
Norbert Koch, member of IRIS Adlershof, has been appointed as Visiting Professor at Chiba University, Japan. IRIS Adlershof is cooperating in particular with the group of Professor Nobuo Ueno and with the Graduate School of Advanced Integration Science of Chiba University. Together with Chiba University and the National University of Singapore IRIS Adlershof organized in 2011 the first KOSMOS Summer University on “Frontiers of Organic / Inorganic Hybrid Materials for Electronics and Optoelectronics” .
03.07.2013Ten years Adlershof Campus of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin hase celebrated the ten years birthday of the Campus for sciences in Berlin-Adlershof
more...
29.06.2013GWK beschließt Förderung des Forschungsbau Hybridsysteme für IRIS Adlershof
Einer Empfehlung des Wissenschaftsrats folgend, hat die Gemeinsame Wissenschaftskonferenz (GWK) am 28.06.2013 beschlossen, 37,4 Mio. Euro für die Errichtung eines hochmodernen Forschungsbaus für IRIS Adlershof bereitzustellen. Mit der Förderung werden entsprechend der Förderkriterien des Verfahrens nach Art. 91b GG die herausragende wissenschaftliche Qualität und die nationale Bedeutung des Vorhabens "Organisch-anorganische Hybridsysteme für die Optik, Elektronik und Photonik" gewürdigt. Der Forschungsbau mit einer Gesamtnutzfläche von gut 4.700 Quadratmetern für etwa 140 Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler soll bis zum Jahr 2018 nordöstlich des Instituts für Physik entstehen und IRIS Adlershof zu einem international noch sichtbareren Zentrum dieses innovativen Forschungsfelds ausbauen (s.a. Pressemitteilung der HU vom 28.04.2013).
mehr...
08.06.2013IRIS Adlershof in der Langen Nacht der Wissenschaften 2013
Auch in diesem Jahr stellen die Mitglieder von IRIS Adlershof im Rahmen der Langen Nacht der Wissenschaften einige ihrer Projekte einer breiten Öffentlichkeit vor.
-
Aus einer Kooperation zwischen den Berliner Verkehrsbetrieben und dem Technologiestandort Adlershof resultiert ein besonderes Highlight: zwischen Adlershof, Schöneweide und Karlshorst werden zwei „Rollende Hörsäle“ unterwegs sein, in denen Wissenschaftler, Unternehmer und Standortmanager die Fahrgäste mit Beiträgen zu spannenden Themen der Wissenschaft unterhalten. In einem dieser „Rollenden Hörsäle“ wird IRIS-Sprecher Jürgen P. Rabe die Tram als rollenden Einstein-Zug verwenden. Abfahrt ist um 17:00 an der Haltestelle Adlershof-Magnusstraße.
-
IRIS-Mitglied Alexander Reinefeld bietet am Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Vorträge und Führungen u. a. zum Ursprung des Computers, zu autostereoskopischen Displays und zu computergestützter Molekülentwicklung an.
-
Im Programm „Daten Striptease“ der Arbeitsgruppe Datenbanken und Informationssysteme (DBIS) von IRIS-Mitglied Johann-Christoph Freytag erfahren die Besucher anhand von alltäglichen Szenarios, wie ihre Daten aufgespürt und zu Informationen kombiniert werden, die ihnen beruflich, sozial oder finanziell schaden können.
-
Im Max-Born-Institut für Nichtlineare Optik und Kurzzeitspektroskopie, welches von IRIS-Mitglied Thomas Elsässer geleitet wird, können sich Besucher in Laborbsichtigungen, Ausstellungen und anhand von Experimenten zu extrem kurzen Lichtimpulsen und Lasern informieren.
-
Mitarbeiter der IRIS-Arbeitsgruppe "Physik der Makromoleküle" geben Interessierten einen Einblick in die Welt der Moleküle. Einzelne DNA-Stränge auf Glimmer werden mithilfe der Kraftmikroskopie gerastert und anschaulich gemacht, Oberflächen mit Höhenunterschieden, nicht größer als ein einige Atome, werden genau bestimmt. In einem zweiten Experiment werden einzelne Moleküle gedehnt und zerrissen. Beide Messprinzipien werden am Modell an großen Objekten, z. B. einem menschlichen Haar, gelochter Pappkarton oder Draht, erklärt.
-
Unter dem Titel „Was ein Lehrer wissen muss“ gibt das Humboldt-ProMINT-Kolleg einen Einblick in die Wissenschaft vom Lehren und Lernen in den mathematisch naturwissenschaftlichen Fächern.
25.05.2013CRC 658 takes third funding period
The Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft has decided to pronlongate the funding of the Collaborative Research Centre CRC 658 "Elementary processes in molecular switches at surfaces" for four more years, until the end of June 2017. The CRC investigates molecular switching processes driven by external excitations in well defined molecular systems at solid surfaces. Spokesman is Professor Felix von Oppen (FU Berlin). The members of IRIS Adlershof Professor Claudia Draxl and Prof Stefan Hecht are significantly involved in the CRC 658 as principal investigators.
22.05.2013Graduiertenkollegs „Masse, Spektrum, Symmetrie: Teilchenphysik in der Ära des Large Hadron Colliders“ und „Self-Assembled Soft Matter Nano-Structures at Interfaces” gehen in die zweite Förderperiode
Die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) hat die Förderung zweier Graduiertenkollegs, an denen IRIS Adlershof beteiligt ist, für weitere viereinhalb Jahre beschlossen und stellt hierfür insgesamt über sieben Millionen Euro zur Verfügung.
Im Graduiertenkolleg 1504 „Masse, Spektrum, Symmetrie: Teilchenphysik in der Ära des Large Hadron Colliders“ kooperieren Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, der Technischen Universität Dresden und des DESY Zeuthen zu theoretischen und experimentellen Fragen der Teilchen- und Astroteilchenphysik. Verbindendes Glied aller Standorte ist die Mitarbeit im ATLAS-Experiment am Large Hadron Collider (LHC) des CERN in Genf. Im Sommer des vergangenen Jahres gelang dort der Nachweis der Existenz von Higgs-Bosonen. Sprecher des Kollegs ist Prof. Heiko Lacker vom Institut für Physik der HU Berlin. Seitens IRIS Adlershof sind Prof. Jan Plefka und Prof. Matthias Staudacher beteiligt.
mehr...
Im Internationalen Graduiertenkolleg 1524 „Self-Assembled Soft Matter Nano-Structures at Interfaces” erforschen Nachwuchswissenschaftlerinnen und Nachwuchswissenschaftler die Eigenschaften selbstorganisierter Nanostrukturen aus weicher organischer und biomolekularer Materie an Grenzflächen. Dabei werden sie von Forscherinnen und Forschern der Technischen Universität Berlin, der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin sowie des Max-Planck-Institut für Kolloid- und Grenzflächenforschung in Potsdam betreut. Von US-Seite sind die North Carolina State University, die University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, die University of Pennsylvania sowie neu die Duke University beteiligt. Sprecher des Kollegs ist Prof. Martin Schoen von der TU Berlin. Seitens IRIS Adlershof sind Prof. Matthias Ballauff sowie als stellvertretende Sprecher des Kollegs Prof. Regine von Klitzing und Prof. Jürgen P. Rabe beteiligt.
15.05.2013Moderner Forschungsbau für Hybridsysteme in Optoelektronik und Nanoanalytik
Wissenschaftsrat empfiehlt Baufinanzierung für das IRIS Adlershof der Humboldt-Universität

Die Mitglieder des Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences - IRIS Adlershof der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin haben Grund zur Freude: Der Wissenschaftsrat hat auf seiner Frühjahrssitzung Bund und Ländern empfohlen, 37,4 Mio Euro für einen modernen Forschungsbau bereitzustellen.
Mit einer Gesamtnutzfläche von gut 4.700 Quadratmetern wird so auf dem Campus Adlershof der HU, in unmittelbarer Nähe der Institute für Physik und Chemie, ein neuer, hochmoderner Forschungsbau für ca. 140 Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler entstehen.
„Die Empfehlung des Wissenschaftsrates für den IRIS-Forschungsbau ist eine besondere Auszeichnung, die einmal mehr die hohe Leistungsfähigkeit unseres Konzepts Integrativer Forschungsinstitute sowie die der beteiligten Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler bestätigt“, sagt HU-Präsident Prof. Dr. Jan-Hendrik Olbertz.
„Wir freuen uns sehr, dass es uns gelungen ist, den Wissenschaftsrat von der Qualität und der Relevanz unseres Forschungsprogramms zu überzeugen“, unterstreicht IRIS-Sprecher Prof. Dr. Jürgen P. Rabe. „Das gibt uns die Chance, IRIS Adlershof zu einem international noch sichtbareren Zentrum der Erforschung von organisch-anorganischen Hybridsystemen für die Optik, Elektronik und Photonik auszubauen.“
Der stete und rasante Fortschritt in der Mikroelektronik und in den optischen Technologien ist Taktgeber für zahlreiche Innovationen. Die etablierte und über Jahrzehnte äußerst erfolgreiche Halbleitertechnologie stößt dabei jedoch zunehmend an Grenzen, vor allem wo es um Multifunktionalität sowie Ressourcen schonende Herstellung und energieeffizienten Betrieb einschlägiger Bauelemente geht. Der Übergang zu strukturierten Verbundsystemen aus unterschiedlichen organischen und anorganischen Materialien auf Nanoebene, die am IRIS Adlershof erforscht werden, erschließt dagegen neue Eigenschaften und damit neue Anwendungsperspektiven. Diese sind sehr breit: So können hocheffiziente Hybrid-Solarzellen dazu beitragen, die Energiewende zu beschleunigen. Die Integration von multifunktionalen Hybridelementen auf kleinsten Längenskalen bei gleichzeitig minimiertem Energieverbrauch eröffnet aber auch neue Möglichkeiten für differenziertere Diagnostik sowie für die elektronische und optische Verarbeitung von Informationen.
Das Forschungsprogramm des IRIS Adlershof bündelt die Expertise von insgesamt 15 Arbeitsgruppen der HU, die auf diesem Gebiet eng mit dem Helmholtz-Zentrum für Materialien und Energie Berlin (HZB), dem Max-Born-Institut für Nichtlineare Optik und Kurzzeitspektroskopie (MBI) sowie der Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM) zusammen arbeiten.
Dazu wird eine Core Facility mit dem Joint Lab for Structural Research (JLSR) und Open Access Laboratories (OPAL) for Advanced Materials und Analytical Sciences entstehen, die auch innovativen Unternehmen und Gründungsinitiativen sowie Kooperationspartnern aus der Freien Universität Berlin, der Technischen Universität Berlin und dem Fraunhofer Institut für angewandte Polymerforschung in Golm offen stehen. Internationale Kooperationen gibt es insbesondere mit der Princeton University, der National University of Singapore, der Chiba University in Tokyo sowie der Tel Aviv University.
Die an der HU bereits jetzt sehr gut aufgestellte Nachwuchsförderung wird von den neuen, exzellenten Arbeitsmöglichkeiten im IRIS-Forschungsbau ebenfalls stark profitieren. Dazu ist die Einrichtung von vier neuen Nachwuchsgruppen geplant. Darüber hinaus werden Doktorandinnen und Doktoranden von Verbundprojekten wie dem Sonderforschungsbereich 951 „Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics“ (HIOS) und der „Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof“ (SALSA) in das Forschungsprogramm einbezogen. Auch den Studierenden des Internationalen Master Studienganges „Polymer Science“ werden die neuen Labor- und Begegnungsflächen offen stehen.
Wissenschaftrat, 26. April 2013
15.04.2013Call for 15 SALSA doctoral fellowships open
SALSA, the Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, is announcing 15 doctoral fellowships to begin on October 1st, 2013. The program offers a structured, three-year period of multidisciplinary research combined with an integrated curriculum in Analytical Sciences. Application deadline is extended toMay 13th, 2013.
more…
11.04.2013Hochtechnologiestandort Berlin Adlershof auf klarem Wachstumskurs
 Professor Peter Frensch, Vizepräsident für Forschung der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU), blickt auf der Jahrespressekonferenz der Adlershofer Standortpartner auf ein ausgesprochen erfolgreiches Jahr zurück. In der zweiten Runde des Exzellenzwettbewerbs war die HU im Juni 2012 zur Exzellenzuniversität gekürt worden. Sie erreichte neben der erfolgreichen Fortsetzung von Projekten der ersten Förderperiode gemeinsam mit der Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung eine Förderzusage für die Graduiertenschule SALSA (Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof). Dank der Mittel des im Rahmen der Exzellenzinitiative geförderten Zukunftskonzepts der HU wird auch IRIS Adlershof an Fahrt gewinnen. So soll ein ehemaliger Kasernenkomplex auf dem Campus zum hochmodernen Forschungsbau für IRIS umgestaltet werden.
Professor Peter Frensch, Vizepräsident für Forschung der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU), blickt auf der Jahrespressekonferenz der Adlershofer Standortpartner auf ein ausgesprochen erfolgreiches Jahr zurück. In der zweiten Runde des Exzellenzwettbewerbs war die HU im Juni 2012 zur Exzellenzuniversität gekürt worden. Sie erreichte neben der erfolgreichen Fortsetzung von Projekten der ersten Förderperiode gemeinsam mit der Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung eine Förderzusage für die Graduiertenschule SALSA (Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof). Dank der Mittel des im Rahmen der Exzellenzinitiative geförderten Zukunftskonzepts der HU wird auch IRIS Adlershof an Fahrt gewinnen. So soll ein ehemaliger Kasernenkomplex auf dem Campus zum hochmodernen Forschungsbau für IRIS umgestaltet werden.
Bericht über Adlershof (2012) [PDF 2,8 MB]
WISTA Management GmbH, April 2013
mehr...
09.04.2013Quantum Light from Diamond and Plastic
A group of researchers led by IRIS Adlershof member Oliver Benson has developed a simple method to fabricate stable sources of single light quanta. The ansatz is based on a novel hybrid approach combining two completely different material systems: Nano-diamonds and photo resist. In this way it was possible to write nearly arbitrary three-dimensional structures, which contain single diamond fragments with single colour centres.
more...
28.03.2013Katharina Schultens mit dem Leonce-und-Lena-Preis ausgezeichnet
Katharina Schultens, Geschäftsführerin der Graduate School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof (SALSA) ist mit dem Leonce-und-Lena-Preis der Stadt Darmstadt ausgezeichnet worden. Dieser Preis gilt als der bedeutendste Literaturpreis für junge Autorinnen und Autoren auf dem Gebiet der Lyrik im deutschsprachigen Raum. IRIS Adlershof gratuliert Frau Schultens ganz herzlich.
mehr...
05.03.2013Humboldt-Universität mit international drittbestem Ruf aller deutschen Universitäten
Die Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (HU) hat international den drittbesten Ruf aller deutschen Universitäten. Im aktuellen Reputations-Ranking des britischen Magazins "Times Higher Education" belegt die HU Platz 72.
mehr...
28.02.2013New EU Initial Training Network (ITN) for doctoral candidates in the area mathematical physics
The Marie Curie Initial Training Network GATIS (Gauge Theory as to Integrable System) has started its work. The Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin participates with a team of scientists around Prof. Dr. Matthias Staudacher, member of IRIS Adlershof.
more...
18.02.2013How to make contact between carbon compounds and metals
Organic electronics has already hit the market in smart-phone displays and holds great promise for future applications like flexible electroluminescent foils (a potential replacement for conventional light bulbs) or solar cells that convert sunlight to electricity. A reoccurring problem in this technology is to establish good electrical contact between the active organic layer and metal electrodes. Organic molecules are frequently used also for this purpose. Until now, however, it was practically impossible to accurately predict which molecules performed well on the job. They basically had to be identified by trial-and-error. Now, an international team of scientists around Dr. Georg Heimel and Prof. Norbert Koch (member of IRIS Adlershof) has unraveled the mystery of what these molecules have in common. Their discovery enables more focused improvements to contact layers between metal electrodes and active materials in organic electronic devices.
more...
29.01.2013Brückenschlag von der Grundlagenforschung zur Anwendung
Immer mehr Forschungsergebnisse von Mitgliedern von IRIS Adlershof stoßen auf wachsendes Interesse von Wirtschaftsunternehmen und fließen in die Entwicklung innovativer Produkte ein. So haben zum Beispiel die IRIS-Mitglieder Prof. Norbert Koch und Prof. Stefan Hecht im Rahmen eines inzwischen abgeschlossenen BMBF-Verbundvorhabens grundlegende Erkenntnisse zu organischen Materialien und deren Optimierung für organische Leuchtdioden (OLEDs) gewonnen. Wie diese Resultate effektiv zur Herstellung neuartiger Bauteile für die Fahrzeugbeleuchtung und -Instrumentierung verwendet werden können, wurde kürzlich auf einem von Prof. Koch moderierten Workshop im Rahmen der 13th International Conference Intelligent Automotive Lighting 2013 mit Vertretern der Wirtschaft diskutiert.
mehr...
20.01.2013Princeton University HU’s first profile partner
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Princeton University have concluded a contract on profile partnership. Members of IRIS Adlershof are substantially involved in this cooperation. An exchange of faculties and PhD-candidates is planed within the scope of the cooperation-program. Moreover, joint scientific events as symposia and summer schools will be organized.
more…
18.12.2012

The Trudelturm (a vertical wind tunnel for spinning tests) in Adlershof in winter
Video of a spinning experiment in a reconstruction at NASA LaRC
17.12.2012Humboldt-Forschungspreis für Vladimir A. Smirnov
Dr. Vladimir A. Smirnov von der Staatlichen Universität Moskau hat einen Humboldt-Forschungspreis erhalten. Im Rahmen des damit verbundenen Forschungsaufenthalts verbringt er in diesem und den kommenden Jahren insgesamt acht Monate an der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin in der Gruppe "Mathematische Physik von Raum, Zeit und Materie" von Prof. Dr. Matthias Staudacher, Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof, sowie vier Monate am Karlsruher Institut für Technologie (KIT) bei Prof. Dr. Matthias Steinhauser. Mit dem Preis zeichnet die Alexander von Humboldt-Stiftung Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler aus, deren grundlegende Entdeckungen, Erkenntnisse oder neue Theorien das eigene Fachgebiet nachhaltig geprägt haben und von denen auch in der Zukunft weitere Spitzenleistungen erwartet werden können. Er ist mit 60.000 Euro dotiert. Dr. Smirnov ist einer der herausragendsten Forscher auf dem Gebiet der perturbativen Quantenfeldtheorie, insbesondere der Evaluierung von Mehrschleifen-Feynman-Diagrammen. Er hat mehrere Schlüsseltechniken entwickelt, die hochkomplizierte für die phänomenologische Teilchenphysik und die Mathematische Physik relevante Berechnungen ermöglichen. Während seines Aufenthalts in Deutschland möchte Dr. Smirnov neue Klassen von Feynman-Integralen untersuchen, die mehrere direkte Anwendungen sowohl in der Quantenchromodynamik als auch in supersymmetrischen Yang-Mills-Theorien haben.
15.12.2012Detlef Günther, ETH Zürich, Visiting Fellow at Humboldt-Universität
Detlef Günther, professor for Trace Element and Micro Analysis at ETH Zürich and member of the School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof (SALSA) at the Humboldt-Universität, is one of the world’s leading experts in the field of inorganic Mass Spectrometry. The Einstein Visiting Fellow’s funding enables him, on the one hand, to intensify current existing research projects with the colleagues at SALSA, and, on the other hand, especially to promote talented young scientists, while he will revert to his expertise in the field of the analysis of nanoparticles. IRIS Adlerhof congratulates and is looking forward to their cooperation.
more...
14.12.2012Jochen Brüning elected member of the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton 2012-2013
IRIS Adlershof member Prof. Jochen Brüning has been elected as member of the School of Mathematics at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton 2012-2013.
more...
13.12.2012Tiburtius-Award 2012 for Asbjörn Burow
Dr. Asbjörn Burow was honored with this year’s Tiburtius Award of the Land Berlin. He was granted the first prize for best dissertation, which is endowed with € 4,000, for his thesis "Methods for chemical structures of arbitrary dimensionality based on the density functional theory under periodic boundary conditions". Dr. Burow was supervised by IRIS Adlershof member Prof. Joachim Sauer, Department of Chemistry.
more...
08.12.2012Einstein Foundation is funding research projects of Claudia Draxl and Matthias Staudacher
The Einstein Foundation Berlin is funding six new research projects of Berlin’s top scientists according to the foundation’s funding policy “Einstein-Forschungsvorhaben”. This includes the joint-project “ETERNAL - Exploring Thermoelectric Properties of Novel Materials" of IRIS Adlershof member and Einstein-Professor Claudia Draxl, Department of Physics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, together with Prof. Klaus Müller, TU Berlin, and Prof. Matthias Scheffler, Fritz-Haber-Institut, as well as the project "Gravitation and High Energy Physics" of IRIS Adlershof member Matthias Staudacher, professor at the Departments of Mathematics and Physics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
more...
06.12.2012Leibniz Prize 2013 for Peter Hegemann
Peter Hegemann, professor for experimental biophysics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and member of UniCat, has been granted the DFG Leibniz Prize 2013. Prof. Hegemann is one of the founders of the research field of optogenetics – a new and innovative method, with which a wide variety of cell types can be "switched" using light once they are equipped with a specific light receptor protein. IRIS Adlershof congratulates the laureate and is sharing his delight about this outstanding award.
more...
22.11.2012CRC 647 "Space - Time - Matter" takes third funding period
The Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft has decided to pronlongate the funding of the Collaborative Research Centre CRC 647 "Space - Time - Matter" for four more years, until the end of 2016. Since the CRC 647 was established at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin in 2005, theoretical physicists and mathematicians of the Humboldt-Universität, the Freie Universität Berlin, the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics Potsdam, as well as of the Universität Potsdam have been jointly doing basic research on topics related to gravitational and quantum field theory. With this approach, the CRC has been gradually generating a central platform for mathematical physics in the region Berlin/Potsdam. Four members of IRIS Adlershof, Prof Brüning, Prof Kreimer, Prof Plefka, and Prof Staudacher are significantly involved in the CRC as principal investigators.
more...
22.11.2012Horst Bredekamp has been granted the Berliner Wissenschaftspreis 2012
This year’s "Berliner Wissenschaftspreis des Regierenden Bürgermeisters von Berlin" (Science award of Berlins governing mayoe) has been granted to Prof Horst Bredekamp. The prize is endowed with €40,000 and dignifies the art historian – working at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin - for his outstanding scientific achievements. Among other activities, Prof Bredekamp is one of the spokesmen of the Cluster of Excellence "Image Knowledge Gestaltung. An Interdisciplinary Laboratory", in which IRIS Adlershof also is involved.
more...
15.11.2012Call for 15 SALSA doctoral fellowships open
The School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof, SALSA, is a new Graduate School at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, established in the framework of the German Excellence Inititative. SALSA started its work on November 1st , 2012 und has now launched a call for applications for altogether 15 doctoral fellowships.
more…
14.11.2012Carl-Ramsauer-Award 2012 for Sylvia Schikora
For her dissertation "All-optical noninvasive delayed feedback control of semiconductor lasers", Dr Sylvia Schikora has been granted the Carl-Ramsauer-Award 2012 by the Physikalische Gesellschaft zu Berlin. Dr Sylvia Schikora is research associate in Prof Fritz Henneberger’s (member of IRIS Adlershof) research group.
15.10.2012IRIS Adlershof bezieht das IRIS-Haus Zum Großen Windkanal 6
Seit seiner Gründung im Jahr 2009 war IRIS Adlershof Gast in den Räumlichkeiten des Instituts für Physik im Lise Meitner-Haus. Nun hat die Humboldt-Universität Büro-, Besprechungs- und Seminarräume im neu hergerichteten IRIS-Haus Zum Großen Windkanal 6 in unmittelbarer Nachbarschaft des Lise Meitner-Haus eingerichtet. Der erste Bauabschnitt wurde zwischenzeitlich an IRIS übergeben. Dort sind zunächst die Geschäftsstellen von IRIS Adlershof, des SFB 951 „Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics“ (HIOS) und der Graduiertenschule für Analytical Sciences Adlershof (SALSA), sowie die theoretisch arbeitenden IRIS-Mitglieder Prof. Claudia Draxl (Theoretische Festkörperphysik) und Prof. Matthias Staudacher (Mathematische Physik von Raum, Zeit und Materie) mit ihren Arbeitsgruppen untergebracht. Außderdem werden IRIS-Mitglied Prof. Matthias Ballauff (Weiche Materie und funktionale Materialien) sowie Prof. Joachim Dzubiella (Theorie weicher Materie) einziehen. Darüber hinaus gibt es vor allem Büros für Mitglieder von verschiedenen nationalen und internationalen Graduiertenprogrammen sowie für Gäste.
In einem zweiten Bauabschnitt soll bis Ende 2013 Platz für weitere, vorwiegend theoretisch arbeitende IRIS-Mitglieder und deren Arbeitsgruppen im IRIS-Haus geschaffen werden. Für das IRIS-Forschungsfeld "Hybridsysteme für Optik und Elektronik" ist ein eigener dedizierter Forschungsbau mit einer Core Facility und einschlägigen Speziallaboren in der Planung.
04.10.2012Humboldt-Universität listed among World University Ranking’s top 100
In the current Times Higher Education World University Ranking 2012/2013 Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is listed on position 99. That means an upgrade of ten positions compared to last year's ranking. In the field of global university performance comparison Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is one of the four German Universities listed among the top 100.
more...
27.09.2012Polydays 2012: Polymers and Light – International Symposium of the Berlin-Brandenburg Association of Polymer Science at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin in Adlershof
Polymers and light are at the heart of modern science and technologies. The advantageous properties of both biological and synthetic polymers can be custom-designed and -tuned by controlling their chemical structure and -- often hierarchical -- supramolecular organization, in order to obtain functional systems capable of performing complex tasks. Light, on the other hand, provides additional means to fabricate and analyze polymeric systems, but also to control their function. For example, nature taught us how sunlight can be harvested and converted into electrical energy using organic photovoltaic systems. On the other hand electrical energy can be efficiently converted back into light in polymer-based light-emitting diodes.
“Polydays 2012: Polymers and Light” aims to highlight the exciting science currently going on at the interface of polymers and light. The Polydays series is organized biannually by the Berlin-Brandenburg Association of Polymer Science (BVP) and dedicated to modern topics of polymer research. This year‘s conference will take place from September 30 to October2, 2012 at the Campus Adlershof of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin. Among the speakers are outstanding international researchers including T. Aida (Tokyo), C.J. Barrett (Montreal), P. Fratzl (Potsdam), J.M.J. Frechét (Thuwal, Saudi Arabia), M. Havenith (Bochum), G.D. Scholes (Toronto), and C.G. Willson (Austin).
more...
21.09.2012Humboldt-Universität and Bundesdruckerei (Federal Printing Office) jointly open research lab
On September 18, 2012, Professor Peter Frensch, Vice President for Research of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, and Ulrich Hamann, Chairman of the Management Bord of Bundesdruckerei GmbH, jointly opened the “BeID-Lab” (Berlin electronic IDentity Laboratory). The new lab is located at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and was launched as a result of the previous existing and well-established research cooperation between the Department of Computer Science of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Bundesdruckerei GmbH. The "BeID-Lab" partners plan push ahead with joint research activities and implement specific measures to promote talented young scientists working in the field of "Secure Identity” and advanced security technologies.
more...
30.08.2012IRIS-Mitglied Prof. Stefan Hecht mit einem ERC Starting Grant ausgezeichnet
Prof. Stefan Hecht (Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof) und Prof. Hans Börner (beide Institut für Chemie der Humboldt-Universität) wurden vom Europäischen Forschungsrat (European Research Council, ERC) mit je einem der renommierten ERC Starting Grants ausgezeichnet. Damit konnten sie sich in einem zweistufigen hochkompetitiven Verfahren erfolgreich in der europäischen Nachwuchselite behaupten und erhalten nun für eine Dauer von fünf Jahren jeweils eine Fördersumme von 1,5 Mio. Euro, um ihre Forschung auf dem vom ERC attestierten Spitzenniveau zu konsolidieren.
Im Projekt “Light4Function“ wird Prof. Hecht mit seiner Gruppe verschiedene Strategien verfolgen, um mit Hilfe von Licht diverse Funktionen von Reaktivität und Katalyse bis hin zu Ladungstransport und Bewegung zu steuern. „Unsere bisherigen Anstrengungen, die Vorteile von Licht zur Kontrolle von molekularen Prozessen zu nutzen, sind dadurch nicht nur gewürdigt worden, sondern wir werden diese in Zukunft nun entscheidend intensivieren können,“ freut sich Hecht über die üppigen Fördermittel aus Brüssel. Stefan Hecht hat seit 2006 den Lehrstuhl für Organische Chemie und Funktionale Materialien am Institut für Chemie der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin inne. Prof. Börner und sein Team werden in ihrem Vorhaben “Sip – Specifically Interacting Polymers“ spezifisch wechselwirkende Polymere entwickeln. Seit 2009 leitet er das Labor für Organische Synthese funktionaler Systeme am Institut für Chemie der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
mehr…
03.07.2012Julius Springer Prize awarded to IRIS-member Thomas Elsässer
Thomas Elsässer, director at the Max-Born-Institute and member of IRIS Adlershof, and Horst Weller (Universität Hamburg) are awarded the Julius Springer Prize for Applied Physics 2012. The scientists are honored for their pioneering achievements and detailed understanding of elementary processes on the sub-nanoscale.
more...
26.06.2012Organic Thin-Film Transistors Adressable by Light
Organic semiconductors are key components for the development of printable, flexible, and large-area electronics. To realize complex device functions the materials should exhibit several (meta-stable) states, between which can be switched selectively with different stimuli ("addressing"). Amongst possible stimuli, light is very attractive as it provides unprecedented spatio-temporal control and can be easily interfaced with advanced optics. However, in order to introduce light-responsiveness in organic devices photoswitchable molecular building blocks have to be incorporated into the material, ideally in a convenient and practical process.
An international research team including Stefan Hecht and Norbert Koch – both members of IRIS Adlershof – has now realized such “smart“ transistors that can be addressed by light. As described in their article in Nature Chemistry the authors demonstrated a new concept by introducing photoswitchable electron-hole traps into the active layer of the device. These specifically designed small molecules are able to interfere with the charge flow through the transistor’s semiconducting polymer in one particular state, which is generated by illumination with UV-light. Illumination with visible light disables the traps and re-establishes the initial state, in which charge flow is not affected. The new method of simple blending of trap molecules with the semiconductor matrix is highly effective yet simple, and hence applicable to large-scale device fabrication processes. The light-programmable transistors could serve as multifunctional elements in logic circuits.
25.06.2012IRIS-member Jürg Kramer new Head of the Deutsche Mathematiker-Vereinigung
From January 1st, 2013, Jürg Kramer, professor of mathematics and it didactics at Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and member of IRIS Adlershof, is going to be the new president of the Deutsche Mathematiker-Vereinigung (DMV). The decision has been announced this week by the DMV executive committee. Jürg Kramer is currently holding the position of the DMV treasurer. He will hold the presidential chair for two years and in honorary post.
15.06.2012IRIS Adlershof participating in all three funding lines of the Excellence Initiative
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is one of Germany’s 11 “Universities of Excellence”. It was successful in all three funding lines in the second round of the Excellence Initiative of the German federal and state governments.
In the context of its Institutional Strategy “education through learning and research” Humbodlt-Universität foresees the establishment of a Strategic Innovation Fund, which will focus mainly on the successful HU research format of Integrative Research Institutes (IRIs). This plan envisages the further development of IRIS Adlershof, the establishment of the IRI for the Life Sciences, and promotion of the IRI THESys (The Great Transformation of Human-Environmental Systems) for research on the topics of sustainability, land use and globalisation.
Members of IRIS Adlershof participate in the “School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof – SALSA” (Matthias Ballauff, Oliver Benson, Stefan Hecht and Jürgen P. Rabe) as well as in the Clusters of Excellence Image Knowlegde Gestaltung. An Interdisciplinary Laboratory (Jochen Brüning, Norbert Koch und Jürgen P. Rabe) and Unifying concepts in Catalysis – UniCat (Joachim Sauer).
more...
08.06.2012IRIS Adlershof in der Langen Nacht der Wissenschaften 2013
Auch in diesem Jahr stellen die Mitglieder von IRIS Adlershof im Rahmen der Langen Nacht der Wissenschaften einige ihrer Projekte einer breiten Öffentlichkeit vor:
-
Aus einer Kooperation zwischen den Berliner Verkehrsbetrieben und dem Technologiestandort Adlershof resultiert ein besonderes Highlight: zwischen Adlershof, Schöneweide und Karlshorst werden zwei „Rollende Hörsäle“ unterwegs sein, in denen Wissenschaftler, Unternehmer und Standortmanager die Fahrgäste mit Beiträgen zu spannenden Themen der Wissenschaft unterhalten. In einem dieser „Rollenden Hörsäle“ wird IRIS-Sprecher Jürgen P. Rabedie Tram als rollenden Einstein-Zug verwenden.
-
IRIS-Mitglied Alexander Reinefeld bietet am Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Vorträge und Führungen u. a. zum Ursprung des Computers, zu autostereoskopischen Displays und zu computergestützter Molekülentwicklung an.
-
Im Programm „Datenstriptease“ der Arbeitsgruppe Datenbanken und Informationssysteme (DBIS) von IRIS-Mitglied Johann-Christoph Freytag erfahren die Besucher anhand von alltäglichen Szenarios, wie ihre Daten aufgespürt und zu Informationen kombiniert werden, die ihnen beruflich, sozial oder finanziell schaden können.
-
Im Max-Born-Institut für Nichtlineare Optik und Kurzzeitspektroskopie, welches von IRIS-Mitglied Thomas Elsässer geleitet wird, können sich Besucher in Laborbsichtigungen, Ausstellungen und anhand von Experimenten zu extrem kurzen Lichtimpulsen und Lasern informieren.
-
Mitarbeiter der IRIS-Arbeitsgruppe "Physik der Makromoleküle" geben Interessierten einen Einblick in die Welt der Moleküle. Einzelne DNA-Stränge auf Glimmer werden mithilfe der Kraftmikroskopie gerastert und anschaulich gemacht, Oberflächen mit Höhenunterschieden, nicht größer als ein einige Atome, werden genau bestimmt. In einem zweiten Experiment werden einzelne Moleküle gedehnt und zerrissen. Beide Messprinzipien werden am Modell an großen Objekten, z. B. einem menschlichen Haar, gelochter Pappkarton oder Draht, erklärt.
-
Unter dem Titel „Was ein Lehrer wissen muss“ gibt das Humboldt-ProMINT-Kolleg einen Einblick in die Wissenschaft vom Lehren und Lernen in den mathematisch naturwissenschaftlichen Fächern.
02.06.2012Get in touch with members of IRIS Adlershof at the smartest night of the year
On June 2nd it will be time again: leading research organisations in Berlin and Potsdam will open their doors from 5.00 pm to 1.00 am for a scientific happening of very special kind. IRIS members will introduce the visitor into their field of research at the campus Adlershof. So is e.g. Professor Plefka giving an overview on “Die Welt als Hologramm: Neues aus der Stringtheorie”. About „Wissenschaft vom Lehren und Lernen in den mathematisch-naturwissenschaftlichen Fächern“ informs the ProMINT Kolleg. The research group around Professor Rabe will depict how single molecules can be torn apart. Meanwhile Professor Freytag’s group is inviting to a “Daten Striptease”. Professor Elsässer and his team are presenting experiments on light and laser, where the visitor is even invited to participate in, at the MBI Berlin.
more...
30.05.2012HU-Beteiligung an einem Projekt der Einstein-Stiftung zur Materialforschung an Pflanzen
Silica (Siliziumoxid) kann einen positiven Effekt auf Pflanzen haben. Es erhöht die Ernteausbeute und mildert den Einfluss pflanzlicher Stressfaktoren. Der bisher nur wenig verstandene Wirkmechanismus soll in einem neuen, von der Einstein Stiftung Berlin geförderten Projekt untersucht werden. Hier arbeiten Forscherinnen und Forscher der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, der Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung und der Hebrew University Jerusalem zusammen.
mehr...
15.05.2012Polydays 2012: Polymers and Light
Polymers and light are at the heart of modern science and technologies. The advantageous properties of both biological and synthetic polymers can be custom-designed and -tuned by controlling their chemical structure and -- often hierarchical -- supramolecular organization, in order to obtain functional systems capable of performing complex tasks. Light, on the other hand, provides additional means to fabricate and analyze polymeric systems, but also to control their function. Polydays 2012 aims to highlight the exciting science currently going on at the interface of polymers and light. Find out more at www.polydays.de or contact us directly: polydays2012polydays.de.
more...
14.05.2012Einstein Stiftung bewilligt neues Einstein-Zentrum in der Mathematik
Die Einstein Stiftung Berlin fördert zukünftig das neue Einstein-Zentrum für Mathematik Berlin, das die Aktivitäten dreier erfolgreicher Einrichtungen der Berliner Mathematik, dem DFG-Forschungszentrum Matheon, der Berlin Mathematical School (BMS) und des Deutschen Zentrums für Lehrerbildung Mathematik (DZLM) bündeln soll.
An dem von den drei großen Berliner Universitäten, dem Weierstraß-Institut für Angewandte Analysis und Stochastik sowie dem Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik betriebenen neuen Einstein-Zentrum ist das Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof, Prof. Jürg Kramer, als Koordinator des DZLM maßgeblich beteiligt.
more...
12.05.2012Neues internationales Graduiertenkolleg an der Humboldt-Universität eingerichtet
Die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) hat ein neues Internationales Graduiertenkolleg mit dem Titel „Moduli und automorphe Formen: arithmetische und geometrische Aspekte“ an der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin eingerichtet. Sprecher ist das Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof, Professor Jürg Kramer. Kooperationspartner sind die niederländischen Universitäten in Leiden und Amsterdam.
mehr...
02.05.2012Mathematik, Physik und Chemie der HU Berlin überzeugen mit Spitzenpositionen im CHE Ranking
Im aktuellen CHE Hochschulranking, das am 2. Mai 2012 im neuen ZEIT Studienführer 2012/13 veröffentlicht wurde, erzielten in IRIS Adlershof vertretene Fächer sehr gute Bewertungen. So rangiert die Mathematik bei der Forschungsreputation sowie bei den Veröffentlichungen und den Forschungsgeldern pro Wissenschaftler bundesweit auf Spitzenplätzen. Die Studierenden sind insbesondere mit der IT-Infrastruktur sehr zufrieden. Die Physik konnte vor allem in den Kategorien Veröffentlichungen und Erfindungen pro Wissenschaftler sowie Promotionen pro Professor mit Spitzenplätzen punkten. Im Votum der Studierenden wird neben der sehr guten räumlichen und IT-Infrastruktur vor allem eine sehr gute Einbeziehung in die Lehrevaluation positiv gewürdigt. In der Chemie werden die Räume und die Ausstattung der Praktikumslabore mit Spitzennoten bewertet.
more…
27.03.2012Prof. J.C. Freytag, Ph.D. betreut drei Firmenausgründungen
06.03.2012“Outstanding referee award” der American Physical Society an Prof. Dr. Lutz Schimansky-Geier und Prof. Dr. Oliver Benson
Prof. Dr. Lutz Schimansky-Geier (Institut für Physik der HU) und Prof. Dr. Oliver Benson (Institut für Physik und IRIS Adlershof der HU) wurden mit einem “Outstanding referee award” für das Jahr 2012 der Zeitschriften der American Physical Society ausgezeichnet. Der Preis würdigt jedes Jahr etwa 150 von den ca. 60.000 aktiven Reviewern. Die Auswahl basiert auf der Qualität, Anzahl und Verlässlichkeit der Begutachtungen.
more...
27.02.2012Neue Materialien für die Photovoltaik Helmholtz-Energie-Allianz am Campus Adlershof
Das Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin und das Forschungszentrum Jülich bilden zusammen mit der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, der Universität Potsdam und der Freien Universität Berlin eine der drei neuen Energie-Allianzen, die von der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft ins Leben gerufen wurden. Ziel dieser Energie-Allianz mit dem Namen „Anorganisch/organische Hybrid-Solarzellen und -Techniken für die Photovoltaik“ ist es, den drängenden Forschungsbedarf zum raschen Umbau der Energieversorgung gezielt zu decken. Sprecher der Energie-Allianz ist Prof. Norbert Koch, Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof. Das Vorhaben wird durch den Impuls- und Vernetzungsfonds der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft für drei Jahre gefördert, wobei die universitären Partner zusätzlich eigene Mittel einbringen. Eine Fortsetzung der Forschung auch über die drei Jahre hinaus, ist geplant.
more...
02.02.2012How Plastics become conducting through impurity molecules – mechanisms of doping organic semiconductors revealed
Over the past years, organic electronics is being developed as emerging technology. In collaboration with the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin (HZB), scientists in the research group around IRIS-Member Prof. Norbert Koch could now reveal the mechanism that governs the doping of organic semiconductors. Their results indicate that there is no direct electron transfer to or from dopant molecules. In contrast to previous suggestions, inter-molecular complexes are formed first. Only the excitation of such complexes leads to mobile charge carriers, which increase the conductivity.
more...
28.01.2012First place for the Team around Katja Wundermann, ProMINT-Kolleg, in the European-League of SPHERE Competition 2011 arranged by MIT, NASA and ESA
Katja Wundermann, delegated teacher at the ProMINT-Kolleg, takes with pupils of the Käthe-Kollwitz-Oberschule and in alliance with the Berliner Heinrich-Hertz-Gymnasium and a team of Turin (both secondary schools) first place in the European-League. The SPHERES-satellites are part of the ZERO-Robotics/SPHERES competition arranged by MIT, NASA and the European Space Agency ESA. The final round of the US-teams and the EU-teams, both have been carried out on board at the international space station ISS. Via live video conference to ISS the members of the European alliances at ESAs headquarter in Noordwijk (NL) could check the capability of their codes in direct competition.
more...
16.01.2012Moving closer towards complex nanostructures: Chemists at Humboldt-Universität succeeded in establishing a directed linkage of tiny programmable molecular components
„Controlling on-surface polymerization by hierarchical and substrate-directed growth“
Published in “Nature Chemistry” (March 2012 issue, online 15 January 2012)
Organizing matter on the smallest scale, i. e. in the region of just few nanometers (1 nm = one billionth of a meter), and making it utilizable are the key challenges of nanotechnology. In doing so, strong interest lies in controlled establishing of stable and well-defined nanostructures on the basis of single molecular components. A few years ago such bottom-up nano-architecture could be realized for its first time, however according to the one-step method with a limited level of complexity.
The same research team, consisting of chemists of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin around Professor Stefan Hecht (member of IRIS Adlershof), succeeded in cooperation with physics of the Fritz-Haber-Institut and of the Laboratorio TASC in Trieste to considerably improve the method they once developed.
more...
07.12.2011Joint Laboratory for Structural Research (JLSR) opened at IRIS Adlershof
The JLSR ist an entity of IRIS Adlershof, in which Humboldt-Universität cooperates with the Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie GmbH and Technischen Universität Berlin. It covers a field ranging from crystalline semiconductors and isolators to organic molecular and supramolecular systems up to biomaterials.
more...
02.11.2011Claudia Draxl first Einstein-Professor of Humboldt-Universität
With the support of the Einstein Foundation Berlin, the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin has been successful in winning the well-respected physicist Claudia Draxl. Ms Draxl is an international respected excellent scientist on the field of Theoretical Solid State Physics. One key aspect of her scientific research lies in the field of interactions and suggestions in nanostructures and hybrid material, which is thematically connected to the field of research of IRIS Adlershof.
more...
28.10.2011The Caroline-von-Humboldt-Preis 2011 goes to Ms Costanza Toninelli, scientist on the field of nanostructures
With The Caroline-von-Humboldt-Preis award, endowed with €15,000.00, is annually granted to excellent young female scientists occupied at the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin for outstanding research. It is the highest endowed research award of its kind in Germany, granted for the second time and is explicitly announced for young female scientists. This year’s awardee is the physicist Ms Dr. Costanza Toninelli.
The award will be granted to Ms Dr. Costanza Toninelli at the Humboldt-Unversität zu Berlin’s Senatssaal on the second of November.
Prof. Peter Frensch, Vice President for Research and Chairman of the Jury, explains: „Ms Toninelli’s fantastic project is extremely impressive. It deals with photonics in nanostructures and is in particular about stable molecules, which are embedded in semiconductor nanostructures”. At the moment Ms Toninelli is busy with her postdoctoral research at the ETH Zurich and will be due to the award working as “Scientist in Residence” within the research group of Prof. Oliver Benson, meber of IRIS Adlershof, at the Institute of Physics, above all at the Collaborative Research Centre HIOS (SFB 951). This Collaborative Research Center is doing research on artificial hybrid materials consisting of semiconductors, conjugated organic materials, and metal nanostructures. The scientists aim to bring these diverse materials in harmony in order to gain new physical and chemical qualities for optoelectronic elements.
For registration please contact: cvh-prizehu-berlin.de
more...
14.10.2011IRIS member Professor Jürg Kramer elected to Academia Europaea
Mr. Jürg Kramer, Professor for Mathematics and Math Education at the Institute of Mathematics of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and member of IRIS Adlershof, has been elected member of Academia Europaea.
more...
07.10.2011New European research project launched at IRIS Adlershof
Norbert Koch, Professor for Supramolecular Systems at Humboldt-Universität’s Department of Physics and member of IRIS Adlershof, coordinates the project “Hybrid organic/inorganic memory elements for integration of electronic and photonic circuitry” (HYMEC), which is funded by the FP7-NMP Work Programme of the European Commission. Partners in this project include universities and research institutions in Belgium, Germany, Italy, Austria, France, and Poland, as well as a high-tech enterprise.
The main objectives of HYMEC are to unravel all relevant properties of hybrid materials comprising metal nanoparticles and conjugated organic semiconductors, and to demonstrate their function in non-volatile memory elements. These elements will be addressable electrically and optically, which potentially enables direct interfacing of future electronic and photonic circuitry.
The project started on 1. October 2011 and is embedded in the research field "Molecular Systems", one of the core competences of IRIS Adlershof.
more...
Contact:
Prof. Dr. Norbert Koch
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
IRIS Adlershof and Department of Physics
Newtonstraße 15
12489 Berlin
eMail: norbert.kochphysik.hu-berlin.de
07.10.2011Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin on position 109 of World University Ranking
In the current Times Higher Education World University Ranking Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin is showing position 109. That means in the field of international university performance comparisons an upgrade of 69 positions compared to last year’s ranking.
more...
01.09.2011Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin submits long-term requests to Excellence Competition
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin applies for funding for world-class research with 15 long-term requests in the second round of the Excellence Competition hold by the German Federal Government and the Länder in all three funding lines - with its future concept “Education through learning and research: individuality - openness - guidance” and applications for four Clusters of Excellence and ten Graduate Schools.
The future concept contains comprehensive programs for the formation of three Integrative Research Institutes (IRI). Along with the enlargement of IRIS Adlershof, which has been working successfully since it was founded in 2009, further IRI’s are on the way to be established. It is planned to open up an IRI for the Life-Sciences and one dealing with sustainability, land use and globalisation.
more...
08.07.2011Chemiker entwickeln Drähte für Prototypen molekularer Computer
Eine Gruppe organischer Synthetiker um IRIS-Mitglied Professor Stefan Hecht entwickelt im Rahmen des Projekts „Atomic Scale and Single Molecule Logic Gate Technologies (AtMol)“ molekulare Bausteine zur Herstellung einzelner molekularer Drähte mit dem Ziel, einen ersten Prototypen Molekül-basierter Computerchips zu realisieren. Die von der Arbeitsgruppe Hecht modellierten Nanodrähte werden anschließend in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Fritz-Haber-Institut hinsichtlich ihrer elektrischen Leitfähigkeit untersucht. Nach erfolgreicher Herstellung und Testung sollen diese Molekülschaltkreise dann von anderen Wissenschaftlern mit winzigen Nano-Elektroden kontaktiert werden und letztlich in einem kompletten molekularen Chip verpackt werden.
Das Projekt, in welchem ein internationales Konsortium aus Wissenschaftlern und Ingenieuren über einen Zeitraum von vier Jahren zusammenarbeitet, wird von der Europäischen Union mit 10 Millionen Euro gefördert.
mehr…
25.06.2011Nationales Zentrum für Lehrerbildung im Fach Mathematik an der Humboldt-Universität
Ein Konsortium aus sechs Hochschulen unter Führung der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin hat die von der Deutsche Telekom Stiftung initiierte Ausschreibung für ein Nationales Zentrum für Lehrerbildung im Fach Mathematik (NZLM) gewonnen. Ziel des NZLM ist es, die Lehrerbildung in Deutschland spürbar und nachhaltig zu verbessern. Dafür stellt die Deutsche Telekom Stiftung 5 Millionen Euro, verteilt auf 5 Jahre, zur Verfügung und investiert damit in ihr bisher größtes Einzelvorhaben.
Am NZLM, das von IRIS-Mitglied Professor Jürg Kramer geleitet wird, sind neben der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin auch die Freie Universität Berlin, die Deutsche Universität für Weiterbildung in Berlin, die Ruhr-Universität Bochum, die Universität Duisburg-Essen und die Universität Paderborn beteiligt.
mehr...
14.06.2011IRIS Adlershof organizes the first KOSMOS Summer University on the topic „Frontiers of Organic / Inorganic Hybrid Materials for Electronics and Optoelectronics”
The first KOSMOS Summer University of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, KOSMOS 2011, will take place September 17 through 25, 2011 on the topic „Frontiers of Organic/ Inorganic Hybrid Materials for Electronics and Optoelectronics”. It will be organized by the Integrative Research Institute for the Sciences IRIS Adlershof in collaboration with Chiba University Japan and the National University of Singapore. We cordially invite Master students in the final phase of their studies, doctoral candidates and postdocs to work here, together with internationally acknowledged experts in the field of physics and chemistry of hybrid materials, on this highly promising class of new materials.
Programme more...
25.05.2011New Collaborative Research Centre on Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS) at Humboldt Universität zu Berlin
The Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) has decided to support the new Collaborative Research Centre CRC 951 “Hybrid Inorganic/Organic Systems for Opto-Electronics (HIOS)”. The Collaborative Research Centre is focusing on innovative hybrid systems, uniting inorganic semiconductors, metal nanostructures and conjugated organic materials. The fundamental chemical, electronic and photonic interactions, arising from the different nature of the components, will be elucidated.
In the long term the CRC aims for solid-state functional elements for Opto-Electronics scalable to meso- and nanoscopic dimensions, exhibiting superior performance not achievable with any of the individual material classes alone. On the part of the Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, which holds primary responsibility, the IRIS-members Matthias Ballauff, Oliver Benson, Thomas Elsässer, Stefan Hecht, Fritz Henneberger (designated spokesman), Norbert Koch and Jürgen P. Rabe as well as further scientists of the Institute of Physics and the Institute of Chemistry are involved. Moreover, members of the Technische Universität Berlin, Universität Potsdam, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie, Max Born Institut für Nichtlineare Optik und Kurzzeitspektroskopie, Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Gesellschaft and Paul Drude Institut für Festkörperelektronik participate in the research as well.
In the first quadrennial funding period the DFG will provide more than 8 million euros for eighteen scientific and three central projects. This amount is, among others, meant for approximately thirty additional positions for Ph.D. students, Postdocs and technical staff.
more...
24.05.2011The Humboldt-University succeeds in "Qualitätspakt Lehre"
Sponsorship over 13million Euro to support the apprenticeship until 2016
The Humboldt-University succeeds in "Qualitätspakt Lehre". The Application with the title "Übergänge", which focusses on the transitions between the periods of school and dissertation or between the periods of university and the profession, will be supported with over 13 million Euro until 2016. The "ProMINT - Kolleg" from IRIS Adlershof achieves an important contribution to that project.
more...
23.05.2011The first German-Brazilian doctorate program at the HU
The exploration of networks with a complex topology is in focus of the first German-Brazilian doctorate program called „Dynamical Phenomena in complexe Networks“. Next to the leading Humboldt-University IRIS Adlershof and the Institute for Physics and Mathematics participate.
more...
05.05.2011Particpiation in new DFG Research Unit
The research group led by Professor Oliver Benson, member of IRIS Adlershof, will participate in the newly established DFG Research Unit „Diamond Materials and Quantum Application“. Within the subproject "Integrated quantum optics and nanophotonics with defect centers in nano-diamonds" the specific expertise concerning integrated quantum optics will be provided.
The Research Unit with its spokesperson Professor Jörg Wachtrup, Universität Stuttgart, is devoted to diamonds, a very promising quantum material, and is using technological fundamentals to produce more controlled and increasingly complex diamond structures. To accomplish this, the
Research Unit is bringing together experts on material growth, structure and defect creation as well as quantum optics and spintronics. Focus is primarily on the use of "quantum diamonds" in the areas of quantum photonics and spintronics. The results produced by the Research Unit could lead to applications in, among other areas, medicine.
11.03.2011Humboldt-Universität unter den 100 renommiertesten Universitäten weltweit
Das britische Magazin Times Higher Education hat am 10. März 2011 sein neues Reputations-Ranking veröffentlicht. Die Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin erlangte im internationalen Hochschulvergleich den 72. Rang.
Als ein Aspekt des jährlich erscheinenden World University Ranking basiert die Erhebung zur Reputation auf einer Befragung von rund 13.400 erfahrenen Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftlern aus 131 Ländern. Erstmalig wurden die Daten zum Ruf einer universitären Einrichtung gesondert veröffentlicht. Die Befragten wurden beispielsweise um ihre Meinung gebeten, welche Universität sie international in ihrem Fachbereich am renommiertesten halten. HU-Präsident Jan-Hendrik Olbertz zum Ranking: „Im nationalen Maßstab ein durchaus beachtliches Ergebnis.“Insgesamt haben es vier deutsche Hochschulen unter die 100 renommiertesten Universitäten weltweit geschafft – neben der HU konnten sich die Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, die Technische Universität München sowie die Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg unter den Top 100 platzieren.
mehr...
02.03.2011Humboldt-Universität im Exzellenzwettbewerb in allen drei Förderlinien eine Runde weiter
Die Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin bleibt im Wettbewerb um die Förderung der Spitzenforschung in der Exzellenzinitiative von Bund und Ländern weiter im Rennen. Die Humboldt-Universität wurde heute DFG und vom Wissenschaftsrat (WR) dazu aufgefordert, bis zum 1. September 2011 in allen drei Förderlinien - Graduiertenschulen, Exzellenzcluster und Zukunftskonzept – Langanträge zu erarbeiten. Der Campus Adlershof der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin geht mit Anträgen für zwei Graduiertenschulen in die nächste Phase des Wettbewerbs:
Graduiertenschule für Analytical Sciences Adlershof (SALSA)
Designierte Sprecher: Prof. Dr. Janina Kneipp/Chemie, Prof. Dr. Ulrich Panne/Chemie
Analytische Wissenschaft ist entscheidend für viele wissenschaftliche und technische Problemlösungen und Innovationen. Die Graduiertenschule SALSA soll durch ihren interdisziplinären Ansatz in Ausbildung und Forschung, durch ein neues Curriculum und die Zusammenarbeit von Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftlern der Analytischen und Physikalischen Chemie, Biologie, Physik, Statistik, Modellierung und Didaktik nachhaltig zur Erneuerung der Analytical Sciences mit einem Fokus der „Analytic City Adlershof“ beitragen.
FutureLand Graduate School - Wege zu einer nachhaltigen Landnutzung
Designierter Sprecher: Prof. Dr. Patrick Hostert/Geografie
In der FutureLand Graduate School sollen aus systemanalytischer, prozessorientierter und sozio-kultureller Sicht Ansätze zu nachhaltigen Landnutzungsstrategien entwickelt werden. Dazu bedarf es einer neuen Generation von Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftlern, um die komplexen Fragestellungen mittels interdisziplinärer Ansätze zu beantworten. Die konzeptionelle und modellhafte Verknüpfung von Methoden unterschiedlicher Fachkulturen stellt in diesem Zusammenhang eine besondere Herausforderung dar. Themen umfassen beispielsweise Anpassungsstrategien der Landwirtschaft an den Klimawandel, Wege zum Erhalt von Ökosystemleistungen oder Untersuchungen zum Ein-fluss unserer Lebensgewohnheiten auf die globale Landnutzung und den Kohlenstoffhaushalt.
mehr...
27.01.2011Dissertation-Prize Adlershof 2010 goes to Dr. Michael Barth
The research is a cooperation of the Physics Department and the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin and is also embedded within the Integrative Research Institute for the Science IRIS Adlershof.
11.12.2010Die kleinste Lichtquelle der Welt
Physikern der Humboldt-Universität ist es gelungen, die kleinste fasergekoppelte Lichtquelle der Welt zu konstruieren. Diese Lichtquelle besteht aus nur zwei Komponenten – aus einem speziellen, winzig kleinen Diamanten und aus einer handelsüblichen Glasfaser. Auf Grund des Durchmessers der Glasfaser von nur 90 Mikrometern (1 Mikrometer = 1 Millionstel Meter) hat das gesamte System lediglich die Ausmaße eines menschlichen Haares. Die Ergebnisse der Arbeit wurden jetzt in der Online-Ausgabe von Nano Letters veröffentlicht.
mehr...
28.11.2010Alexander von Humboldt-Forschungspreis für Prof. Jelena Vučković
Frau Prof. Jelena Vučković (Stanford University), die ab 2011 am IRIS Adlershof sowie am Institut für Physik der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin Forschungsarbeiten zum Thema „Hybride Quantensysteme für die fundamentale Optik und Photonik“ betreiben wird, ist nun mit dem renommierten Alexander von Humboldt-Forschungspreis ausgezeichnet worden.
mehr...
03.11.2010CHE ExcellenceRanking 2010: Spitzenplatzierungen für die Humboldt-Universität
Erneut konnte die Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin im aktuellen ExcellenceRanking des Centrums für Hochschulentwicklung (CHE) für drei mathematisch-naturwissenschaftliche Fächer Spitzenplatzierungen erreichen. Damit zählen die Biologie, die Mathematik und die Physik an der HU im europäischen Vergleich zu den besonders forschungsstarken und international orientierten Fachbereichen.
mehr...
18.10.2010Stefan Hecht mit Klung-Wilhelmy-Weberbank-Preis ausgezeicnet
Stefan Hecht, Professor für Organische Chemie und funktionale Materialien an der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin und Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof hat für seine bahnbrechenden Arbeiten auf dem Gebiet funktionaler organischer Nanostrukturen den mit 100.000 € dotierten Klung-Wilhelmy-Weberbank-Preis zuerkannt bekommen. Der Preis wurde am 5. November 2010 feierlich im Henry-Ford-Bau der Freien Universität Berlin verliehen.
Der Klung-Wilhelmy-Weberbank-Preis zählt zu den angesehensten wissenschaftlichen Auszeichnungen für Nachwuchswissenschaftler in Deutschland – nicht zuletzt deshalb, weil fünf der bisherigen Preisträger später den Nobelpreis und weitere Preisträger andere bedeutende nationale und internationale Auszeichnungen erhalten haben.
mehr...
17.09.2010Joachim Sauer mit Liebig-Denkmünze ausgezeichnet
Joachim Sauer, Professor für Quantenchemie an der Humboldt- Universität und Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof, erhält die Liebig- Denkmünze 2010, mit der die Gesellschaft Deutscher Chemiker seit 1903 hervorragende Leistungen auf dem gesamten Gebiet der Chemie auszeichnet.
Der Preis wird am 20. September 2010 auf einer Festsitzung anlässlich der diesjährigen Tagung der Gesellschaft Deutscher Naturforscher und Ärzte in Dresden verliehen.
19.08.2010DFG flexibilisiert Förderbedingungen
Die von der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) geförderten Wissenschaftlerinnen und Wissenschaftler sollen ihre Fördermittel künftig noch freier und ganz an den konkreten Bedürfnissen des geförderten Projekts ausgerichtet verwenden können. Um dies zu erreichen, hat die DFG ihre Förderbedingungen in einem zentralen Punkt neu geregelt und weiter flexibilisiert.
Aufgrund dieser Neuregelung kann die Entscheidung darüber, ob die Fördermittel für Personal, Sachmittel oder Geräte verwendet werden, in Zukunft grundsätzlich von den Universitäten und Forschungseinrichtungen selbst getroffen werden. Die bislang praktizierte Form der sogenannten Stellenbewilligung wird damit durch ein System der freien Umdisposition von Mitteln ersetzt. Als Konsequenz wird die DFG künftig statt Stellen pauschalierte Geldbeträge bewilligen.
02.08.2010Grenzüberschreitender Ansatz: Bericht der Berliner Zeitung über IRIS Adlershof
Neues Interdisziplinäres Institut in Adlershof verzahnt Forschung aus Physik, Mathematik, Chemie und Informatik. Ein Artikel von Jan Steeger in der Berliner Zeitung vom 28.07.2010
mehr...
08.07.2010Thomas Elsässer zum Mitglied der Berlin-Brandenburgischen Akademie der Wissenschaften gewählt
Der Physiker Thomas Elsässer, Mitglied von IRIS Adlershof, S-Professor am Institut für Physik der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin und Direktor am Max-Born-Institut, wurde zum ordentlichen Mitglied der Berlin-Brandenburgischen Akademie der Wissenschaften gewählt. Er gehört der Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Klasse der BBAW an.
mehr...
22.06.2010ERC Starting Grant für Janina Kneipp
Der Europäische Forschungsrat (European Research Council, ERC) hat Janina Kneipp mit einem ERC Starting Grant ausgezeichnet. Diese Preise werden seit 2007 an international herausragende Nachwuchswissenschaftler vergeben und wurden 2009 zum dritten Mal ausgeschrieben. Für die Auswahl der durch den ERC geförderten Projekte bilden die Exzellenz von Antragsteller und Projekt sowie das Umfeld des Antragstellers die Auswahlkriterien. Janina Kneipp ist seit 2008 Junior(S)-Professorin für Analytische Chemie am Institut für Chemie der Humboldt-Universität und der Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und –prüfung (BAM). Im Rahmen des durch den ERC geförderten Projektes wird sie in den nächsten 5 Jahren mit ihrer Gruppe neue mikrospektroskopische Methoden für analytische Anwendungen weiterentwickeln.
22.06.2010Alexander von Humboldt-Professur für Dirk Kreimer
Der Physiker Dirk Kreimer, international führender Forscher auf dem Gebiet der
Mathematischen Physik, ist jetzt mit einer Alexander von Humboldt-Professur
ausgezeichnet worden. An den Preis geknüpft ist der Antritt der Professur an der
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin.
mehr...
04.06.20101st International IRIS-Symposium on Hybrid Systems for Optics and Electronics - IRIS 1
The 1st International IRIS-Symposium on Hybrid Systems for Optics and Electronics - IRIS 1 will take place on July 13th, 2010 and July 14th, 2010 in Berlin Adlershof.
more...
31.03.2010Ruf an Frau Dr. Saskia Fischer
Frau Dr. Saskia Fischer (Ruhr-Universität Bochum) hat einen Ruf auf die W3-Professur "Neue Materialien" am Institut für Physik der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin erhalten.
mehr...
25.03.2010Rufannahme durch Dr. Matthias Staudacher
Herr Dr. Matthias Staudacher hat seinen Ruf auf die Professur "Mathematische Physik von Raum, Zeit und Materie" mit Wirkung zum 1. April 2010 angenommen. Die W3-Professur ist von den Instituten für Physik und Mathematik der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin als gemeinsame Brückenprofessur eingerichtet worden.
14.03.2010Leibniz-Preis an Prof. Peter Fratzl
Professor Fratzl, Direktor am Max-Planck-Institut für Kolloid- und Grenzflächenforschung Potsdam/Golm und seit 2004 Honorarprofessor am Institut für Physik der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin hat den von der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) jährlich für Spitzenleistungen in der Forschung verliehenen Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz-Preis 2010 erhalten.
mehr...
14.03.2010Bunsen-Kirchhoff-Preis an Prof. Janina Kneipp
Frau Kneipp, seit April 2008 S-Juniorprofessorin für Analytische Chemie an der Humboldt Universität zu Berlin und der BAM (Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung), hat den von der Deutschen Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Angewandte Spektroskopie (DASp) vergebenen "Bunsen-Kirchhoff-Preis für analytische Spektroskopie" erhalten, der für herausragende Leistungen vor allem jüngerer Wissenschaftler aus Universitäten, Forschungsinstituten oder der Industrie in der analytischen Spektroskopie vergeben wird.
mehr...
14.03.2010ERC Grant für Prof. Dr. Thomas Elsässer
Professor Thomas Elsässer, Direktor am Max-Born-Institut für Nichtlineare Optik und Kurzzeitspektroskopie im Forschungsverbund Berlin e. V. und S-Professor am Institut für Physik der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, erhält vom Europäischen Forschungsrat (ERC) einen "Advanced Grant" in Höhe von 2,49 Millionen Euro.
mehr...
14.03.2010CHE-Forschungsranking im Fach Physik aktualisiert
Das Institut für Physik der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin rangiert unter den ersten sechs deutschen Physikfachbereichen beim Parameter "Publikationen pro Jahr", der sich aus der über die Jahre 2005-07 gemittelten Zahl der Publikationen und der Zitationsrate ergab.
mehr...


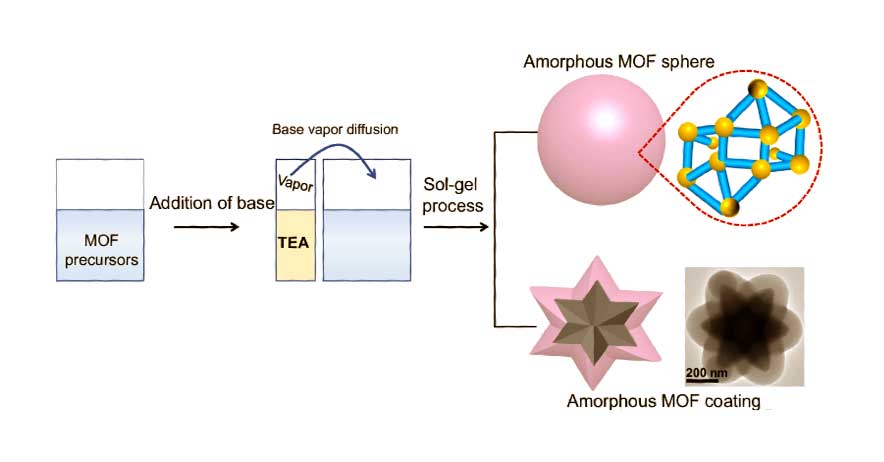

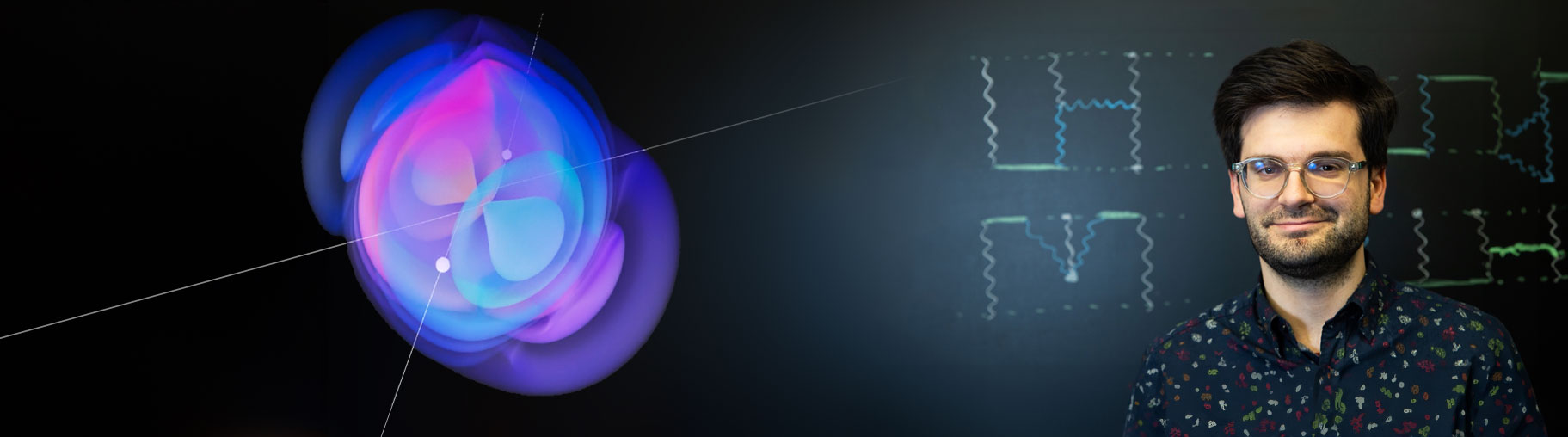 Dr. Mogull & Visualization of the scattering of two black holes including a wave profile
Dr. Mogull & Visualization of the scattering of two black holes including a wave profile